সর্বশেষ ভিডিও
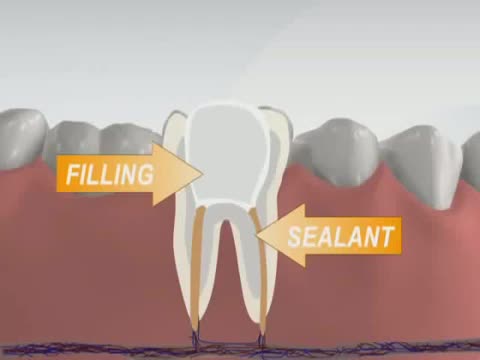
Has your dentist or endodontist told you that you need root canal treatment? If so, you're not alone. Millions of teeth are treated and saved each year with root canal, or endodontic, treatment. Remember, root canal treatment doesn't cause pain, it relieves it. Watch our videos below to learn more! Inside the tooth, under the white enamel and a hard layer called the dentin, is a soft tissue called the pulp. The pulp contains blood vessels, nerves and connective tissue, and helps to grow the root of your tooth during development. In a fully developed tooth, the tooth can survive without the pulp because the tooth continues to be nourished by the tissues surrounding it.
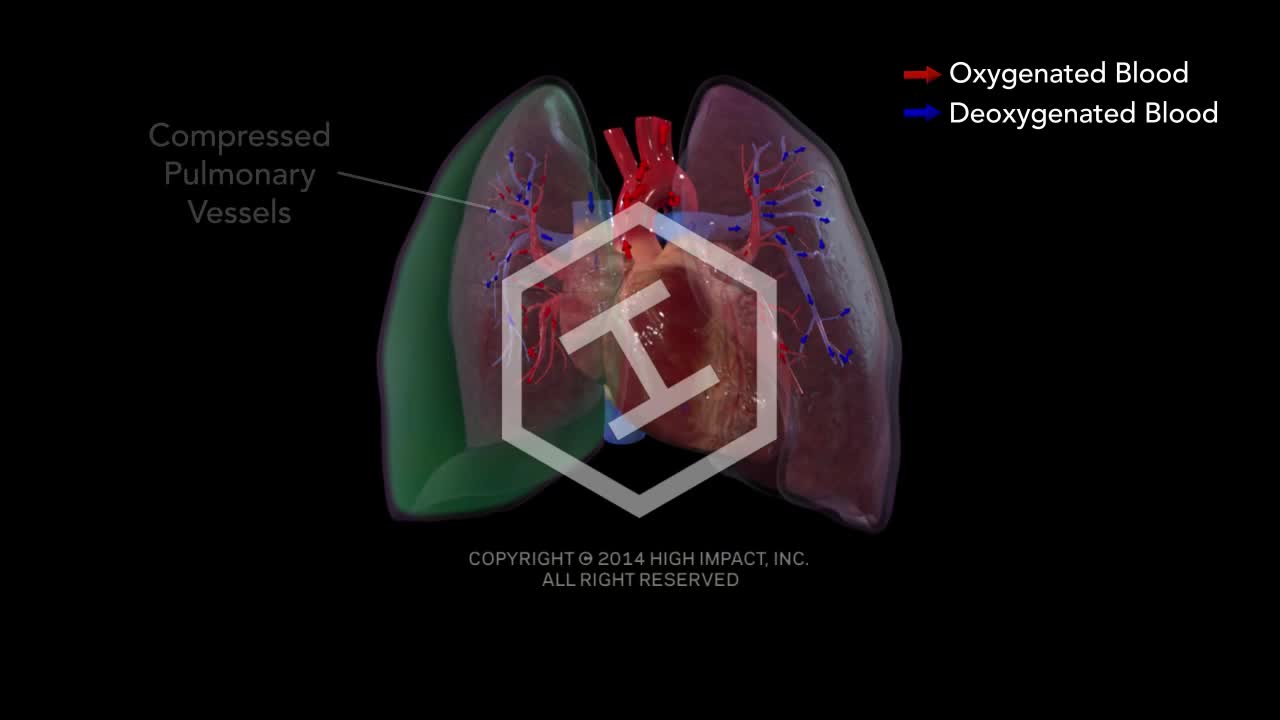
Tension pneumothorax develops when a lung or chest wall injury is such that it allows air into the pleural space but not out of it (a one-way valve). As a result, air accumulates and compresses the lung, eventually shifting the mediastinum, compressing the contralateral lung, and increasing intrathoracic pressure enough to decrease venous return to the heart, causing shock. These effects can develop rapidly, particularly in patients undergoing positive pressure ventilation.

Hemothorax is the presence of blood in the pleural space. The source of blood may be the chest wall, lung parenchyma, heart, or great vessels. Although some authors state that a hematocrit value of at least 50% is necessary to differentiate a hemothorax from a bloody pleural effusion, most do not agree on any specific distinction. Hemothorax is usually a consequence of blunt or penetrating trauma. Much less commonly, it may be a complication of disease, may be iatrogenically induced, [1] or may develop spontaneously. [2] Prompt identification and treatment of traumatic hemothorax is an essential part of the care of the injured patient. The upright chest radiograph is the ideal primary diagnostic study in the evaluation of hemothorax (see Workup). In cases of hemothorax unrelated to trauma, a careful investigation for the underlying source must be performed while treatment is provided.
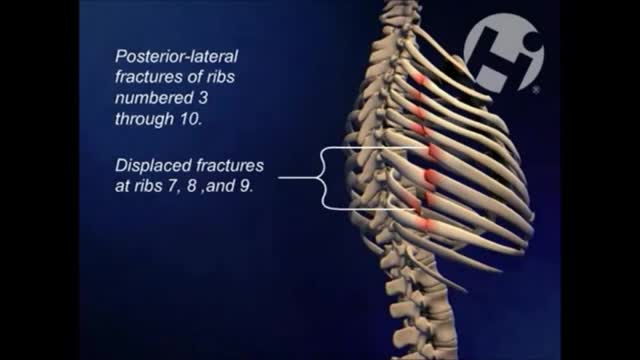
hemothorax is most often defined as rapid accumulation of ≥ 1000 mL of blood. Shock is common. Patients with large hemorrhage volume are often dyspneic and have decreased breath sounds and dullness to percussion (often difficult to appreciate during initial evaluation of patients with multiple injuries).
A pneumothorax can be caused by a blunt or penetrating chest injury, certain medical procedures, or damage from underlying lung disease. Or it may occur for no obvious reason. Symptoms usually include sudden chest pain and shortness of breath. On some occasions, a collapsed lung can be a life-threatening event.
A pneumothorax (noo-moe-THOR-aks) is a collapsed lung. A pneumothorax occurs when air leaks into the space between your lung and chest wall. This air pushes on the outside of your lung and makes it collapse. In most cases, only a portion of the lung collapses.
This 3D medical animation contains the discharge instructions for removal of a Foley catheter from a man. The step-by-step procedures for emptying the Foley bag and removing the Foley catheter are shown. Symptoms requiring a follow-up call to the surgeon are listed.

http://remodela-o-seu-corpo.good-info.co Posturas De Yoga, Alimentos Para Perder Barriga, Yoga Emagrece, Yoga Principiantes, Bhakti Yoga. Melhor Exercício de Yoga para Definir o Abdômen Tenho sempre recebendo perguntas sobre qual exercício fazer para fortalecer o núcleo abdominal e assim deixar a barriga mais plana. Na verdade, a construção de um "abdômen definido" é provavelmente o mais cobiçado objetivo físico para homens e mulheres. Vou te mostrar como fortalecer o seu abdômen com um simples exercício de Yoga, e assim ajudar você a ter aquela barriguinha lisa. Fortalecendo o seu abdômen com algumas rodadas da posição de barco! A prática regular de posição de barco, vai ajudá-la a desenvolver fortes músculos abdominais, bem como melhorar a função do seu sistema digestivo. Além disso, a força central que você irá construir aqui é transferida para qualquer outra atividade que você fizer. Mantenha estas dicas em mente ao praticar a Posição Barco: Comece na posição Shavasana (posição base supino) Respire e contraia o abdômen Simultaneamente levante os ombros e as pernas em uma distância igual afastando do chão (cerca de 15 cm) Seus braços e dedos dos pés devem estar em alinhamento Respire naturalmente por algumas respirações e solte a pose expirando e baixando lentamente o seu corpo para a posição inicial Repita 10-20 vezes Faça algumas respirações abdominais profundas entre cada repetição para relaxar os músculos abdominais Quando realizada na parte da manhã, essa rotina simples vai energizar o seu corpo inteiro, preparando-a para o dia seguinte. E não importa quando você irá executá-lo, mas ele irá fortalecer e esculpir o seu abdômen e deixar a sua barriga lisa e deslumbrante! Tenha Um Corpo Mais Sexy! sem exercícios, sem aeróbica e sem ter que ir a academia! clicando aqui http://como-perder-gordura-abdominal.blogspot.com/
Paracentesis is a procedure to take out fluid that has collected in the belly (peritoneal fluid). This fluid buildup is called ascites . Ascites may be caused by infection, inflammation, an injury, or other conditions, such as cirrhosis or cancer. The fluid is taken out using a long, thin needle put through the belly.
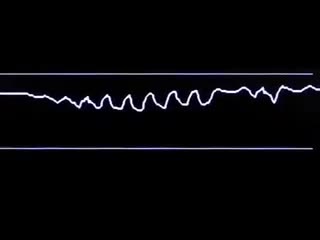
Capnography, the graphic display of the exhaled and inhaled carbon dioxide concentration plotted against time, is used to monitor ventilation. This video reviews the principles of capnography and explains how to interpret the information it provides.
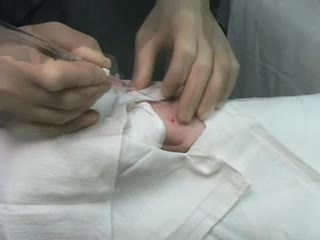
Arterial line placement is a common procedure in various critical care settings. Intra-arterial blood pressure (BP) measurement is more accurate than measurement of BP by noninvasive means, especially in the critically ill. [1] Intra-arterial BP management permits the rapid recognition of BP changes that is vital for patients on continuous infusions of vasoactive drugs. Arterial cannulation also allows repeated arterial blood gas samples to be drawn without injury to the patient.
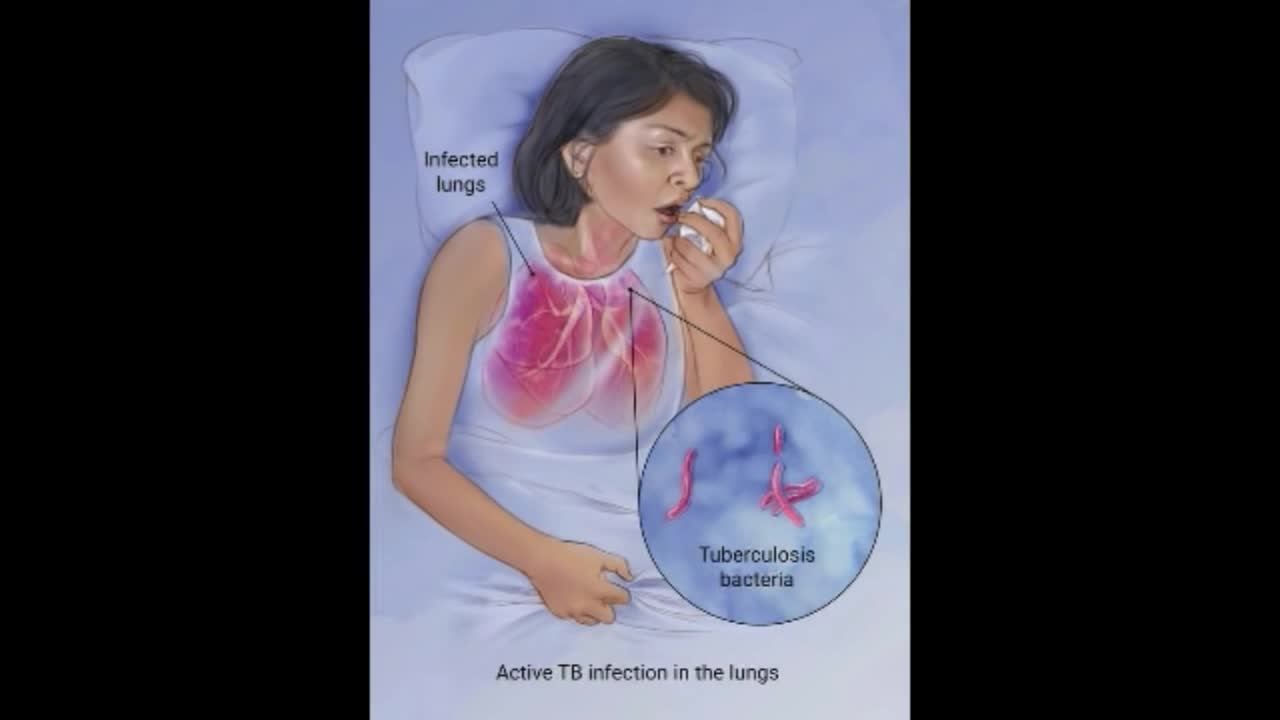
Although your body may harbor the bacteria that cause tuberculosis, your immune system usually can prevent you from becoming sick. For this reason, doctors make a distinction between: Latent TB. In this condition, you have a TB infection, but the bacteria remain in your body in an inactive state and cause no symptoms. Latent TB, also called inactive TB or TB infection, isn't contagious. It can turn into active TB, so treatment is important for the person with latent TB and to help control the spread of TB. An estimated 2 billion people have latent TB. Active TB. This condition makes you sick and can spread to others. It can occur in the first few weeks after infection with the TB bacteria, or it might occur years later. Signs and symptoms of active TB include: Coughing that lasts three or more weeks Coughing up blood Chest pain, or pain with breathing or coughing Unintentional weight loss Fatigue Fever Night sweats
Tuberculosis (TB) is a potentially serious infectious disease that mainly affects your lungs. The bacteria that cause tuberculosis are spread from one person to another through tiny droplets released into the air via coughs and sneezes.

Pneumonia is an infection that inflames the air sacs in one or both lungs. The air sacs may fill with fluid or pus (purulent material), causing cough with phlegm or pus, fever, chills, and difficulty breathing. A variety of organisms, including bacteria, viruses and fungi, can cause pneumonia.

Thoracentesis is a minimally invasive procedure used to diagnose and treat pleural effusions, a condition in which there is excess fluid in the pleural space, also called the pleural cavity. This space exists between the outside of the lungs and the inside of the chest wall.