Latest videos

Pharyngitis is caused by swelling in the back of the throat (pharynx) between the tonsils and the voice box (larynx). Most sore throats are caused by colds, the flu, coxsackie virus or mono (mononucleosis). Bacteria that can cause pharyngitis in some cases: Strep throat is caused by group A streptococcus.

15th August Special Offer - Get 50% discount on Chemical Peel & Medical Facial ! offer valid till 31st August 2018 ! Call now 09958221983 to book appointment! Send your Query: info@drkashyap.com #MedicalFacial #ChemicalPeels #Facial #SkinCare #NonSurgical #Treatments #Clinic #Delhi #India #15thAugust #IndependenceDay
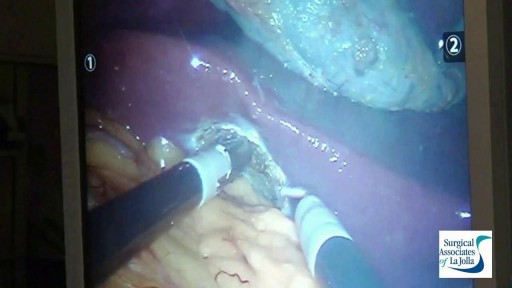
The type of operation performed for removal of pancreatic cancer is based on the location of the tumor. For tumors of the head and neck of the pancreas a Whipple procedure, (also called a pancreaticoduodenectomy) is performed. This is a complex operation perfected at Johns Hopkins. This video will explain the surgery and what patients can expect.
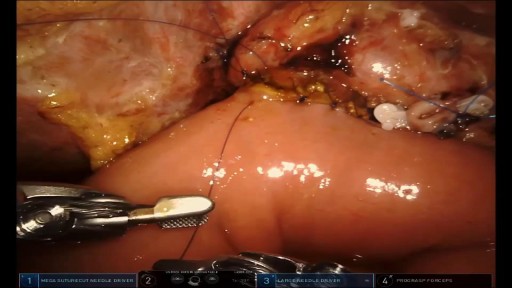
Among common cancers, pancreatic cancer has one of the poorest prognoses. Because pancreatic cancer often grows and spreads long before it causes any symptoms, only about 6% of patients are still alive five years after diagnosis. For some pancreatic patients, however, a complex surgery known as the Whipple procedure may extend life and could be a potential cure. Those who undergo a successful Whipple procedure may have a five-year survival rate of up to 25%.

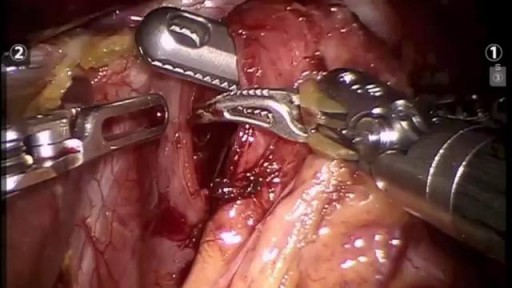
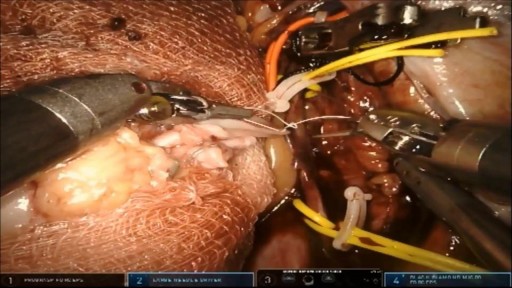
A young patient undergoes state of the art robotic surgery for Ovarian Cancer and Endometrial Cancer in Chicago, IL. The surgery is performed by noted gynecologic oncologist and expert robotic surgeon M. Patrick Lowe MD. Dr Lowe has been performing robotic surgery since 2006 and is one of a few gynecologic oncologist in the United States who utilizes robotics for ovarian cancer.

The G-SHOT® (clinical description: G-Spot Amplification™ or GSA™), is a simple, nonsurgical, physician-administered treatment that can temporarily augment the Grafenburg spot (G-Spot) in sexually active women with normal sexual function.