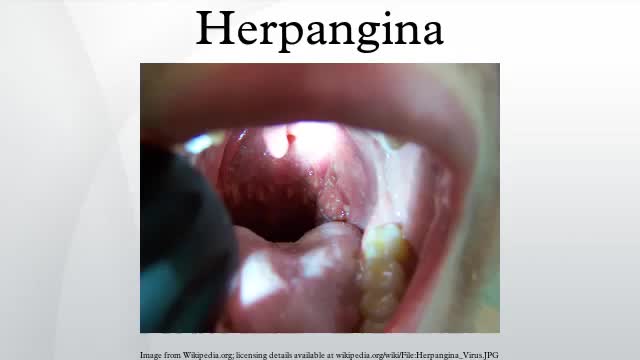
General Medical Videos
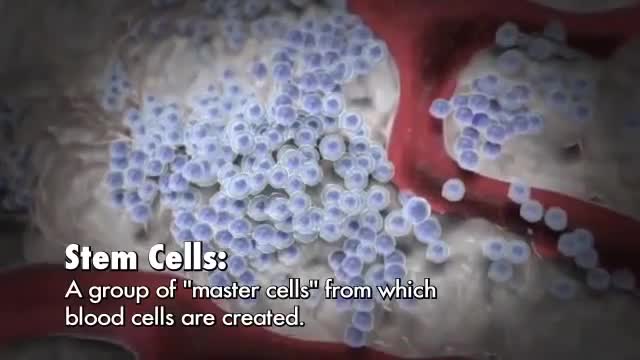
Red blood cells, most white blood cells, and platelets are produced in the bone marrow, the soft fatty tissue inside bone cavities. Two types of white blood cells, T and B cells (lymphocytes), are also produced in the lymph nodes and spleen, and T cells are produced and mature in the thymus gland.
Chagas disease is common in South America, Central America and Mexico, the primary home of the triatomine bug. Rare cases of Chagas disease have been found in the southern United States, as well. Also called American trypanosomiasis, Chagas disease can infect anyone, but is diagnosed most often in children.

This patient has infectious mononucleosis (IM), a disease caused by the Epstein-Barr virus. IM is a systemic viral infection that is usually seen in children and adolescents. The common presentation is fever with pharyngitis or tonsillitis, cervical adenopathy, splenomegaly, and mild hepatitis.

Acute intermittent porphyria (AIP) is a rare autosomal dominant metabolic disorder affecting the production of heme, the oxygen-binding prosthetic group of hemoglobin. It is characterized by a deficiency of the enzyme porphobilinogen deaminase.

Eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis (EGPA; also known as Churg-Strauss syndrome [CSS] or allergic granulomatosis) is a rare autoimmune condition that causes inflammation of small and medium-sized blood vessels (vasculitis) in persons with a history of airway allergic hypersensitivity (atopy).
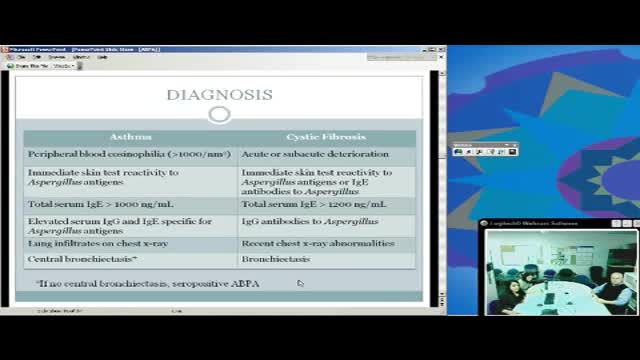
Allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis (ABPA) is a condition characterised by an exaggerated response of the immune system (a hypersensitivity response) to the fungus Aspergillus (most commonly Aspergillus fumigatus). It occurs most often in patients with asthma or cystic fibrosis.

Aspergillosis is the name given to a wide variety of diseases caused by infection by fungi of the genus Aspergillus. The majority of cases occur in people with underlying illnesses such as tuberculosis or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), but with otherwise healthy immune systems.

Toxoplasmosis (tok-so-plaz-MOE-sis) is a disease that results from infection with the Toxoplasma gondii parasite, one of the world's most common parasites. Toxoplasmosis may cause flu-like symptoms in some people, but most people affected never develop signs and symptoms. For infants born to infected mothers and for people with weakened immune systems, toxoplasmosis can cause extremely serious complications. If you're generally healthy, you probably won't need any treatment for toxoplasmosis. If you are pregnant or have lowered immunity, certain medications can help reduce the infection's severity. The best approach, though, is prevention.

Candida Albicans is more than just yeast- for most people, it's already mutated into a more aggressive fungal form that eats holes through the intestinal tract causing many of todays health problems like food allergies, autoimmune disorders, Crohn's disease, IBS, low energy and many more aggressive diseases. People need to know what it is and what to do about it.

systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS). This is most likely secondary to sepsis from an infection of the patient's Hickman catheter given the associated skin findings, although culture results are needed to confirm this diagnosis. The patient's low blood pressure is likely secondary to developing septic shock, and he has already appropriately been treated with intravenous fluids. Catheter removal is indicated given his hemodynamic instability. Catheter removal is also indicated in patients with severe sepsis with organ hypoperfusion, endocarditis, suppurative thrombophlebitis, or persistent bacteremia after 72 hours of appropriate antibiotic therapy. Long term catheters should also be removed if culture results are positive for S. aureus, P. aeruginosa, fungi, or mycobacteria.
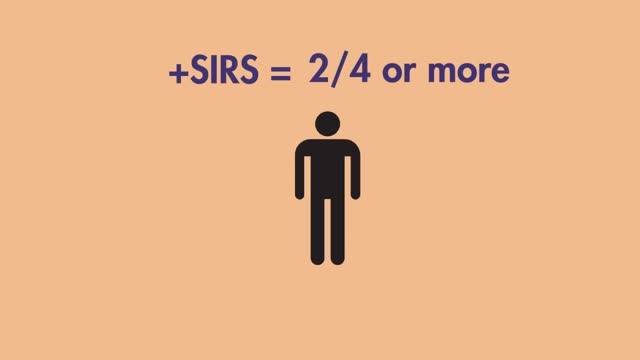
Learn the SIRS Criteria and how to calculate it. Greater than or equal to 2 or more of the following: Temperature Fever of greater than 38°C (100.4°F) or Less than 36°C (96.8°F) Heart Rate Greater than 90 beats per minute Respiratory Rate Greater than 20 breaths per minute or PaCO2 of less than 32mm Hg White Blood Cell Count Greater than 12,000cells/mm³ or Less than 4,000cells/mm³ or Greater than 10% Bands