Physical Examination
The principal signs of cerebellar dysfunction are the following: Ataxia: unsteadiness or incoordination of limbs, posture, and gait. A disorder of the control of force and timing of movements leading to abnormalities of speed, range, rhythm, starting, and stopping.
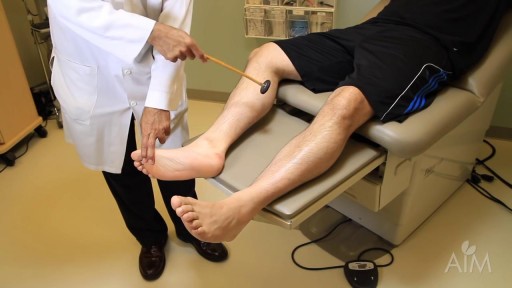
In a normal person, when a muscle tendon is tapped briskly, the muscle immediately contracts due to a two-neuron reflex arc involving the spinal or brainstem segment that innervates the muscle. The afferent neuron whose cell body lies in a dorsal root ganglion innervates the muscle or Golgi tendon organ associated with the muscles; the efferent neuron is an alpha motoneuron in the anterior horn of the cord. The cerebral cortex and a number of brainstem nuclei exert influence over the sensory input of the muscle spindles by means of the gamma motoneurons that are located in the anterior horn; these neurons supply a set of muscle fibers that control the length of the muscle spindle itself.

Start in RLQ (so you don’t miss a giant spleen). Get your fingers set then ask patient to take a deep breath. Don’t dip your fingers or do anything but wait. When patient expires, take up new position. Note lowest point of spleen below costal margin, texture of splenic contour, and tenderness If spleen is not felt, repeat with pt lying on right side. Gravity may bring spleen within reach. “LET THE SPLEEN PALPATE YOUR FINGERS AND NOT THE OTHER WAY AROUND. THERE IS NO GOLD, SO DON’T DIG!”

About Us Contact Disclaimer Get Published! Follow Us Epomedicine Medical Students Clinical Discussion Cases Emergencies Blog Medical Mnemonics Clinical Skills Search Subjects Clinical examination Gastrointestinal system Internal medicine Updated on January 31, 2017 Percussion of Spleen Traube’s semilunar space Borders: Superiorly: Left 6th rib superiorly Laterally: Left midaxillary line or Left anterior axillary line Inferiorly: Left costal margin Method: Patient’s position: supine with left arm slightly abducted. Percuss: from medial to lateral Interpretation: Resonance (Normal) and Dullness (Splenomegaly) Also: Pleural effusion or mass in stomach may cause dullness in Traube’s space.
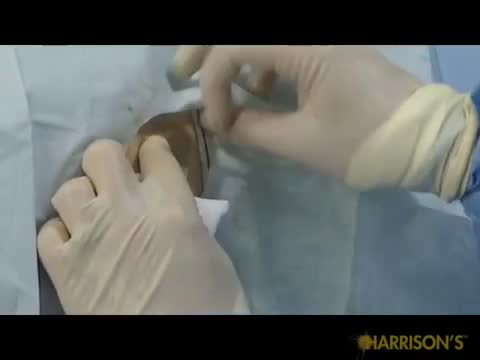
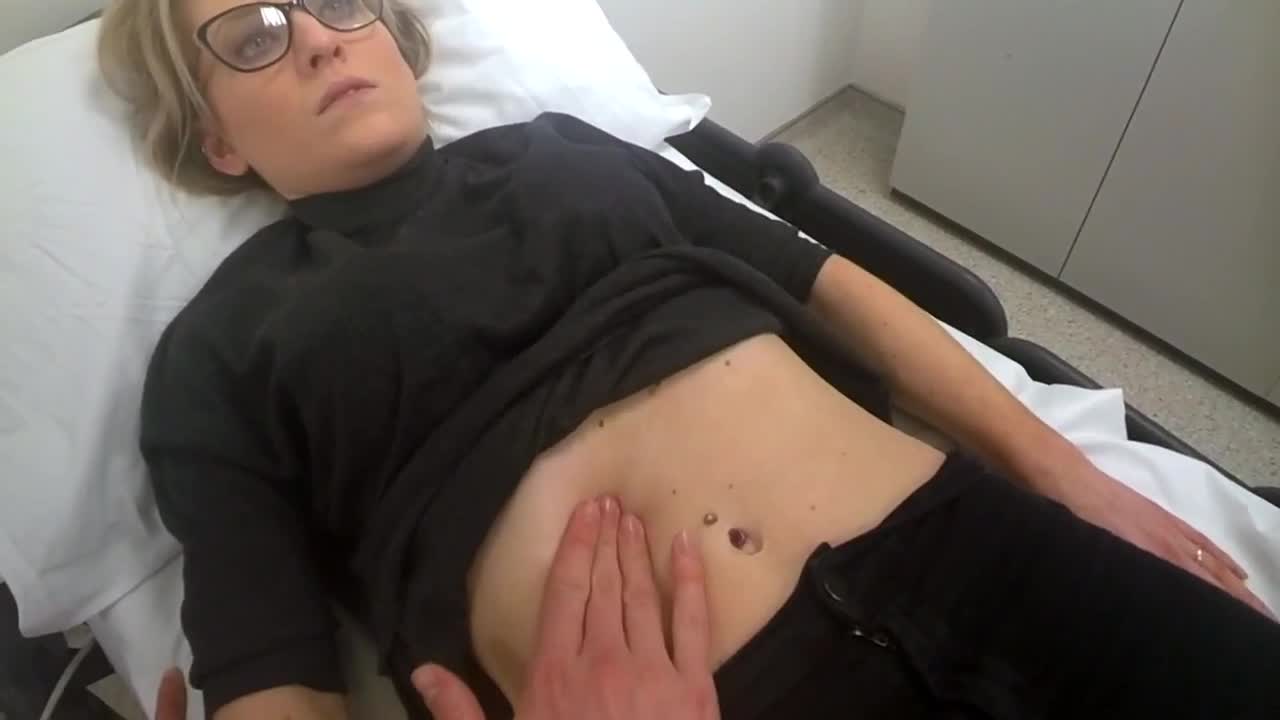
Paracentesis is a procedure to take out fluid that has collected in the belly (peritoneal fluid). This fluid buildup is called ascites . Ascites may be caused by infection, inflammation, an injury, or other conditions, such as cirrhosis or cancer. The fluid is taken out using a long, thin needle put through the belly.
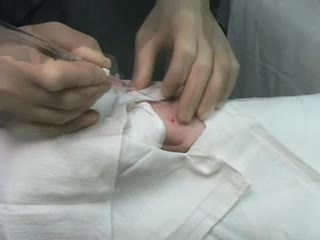
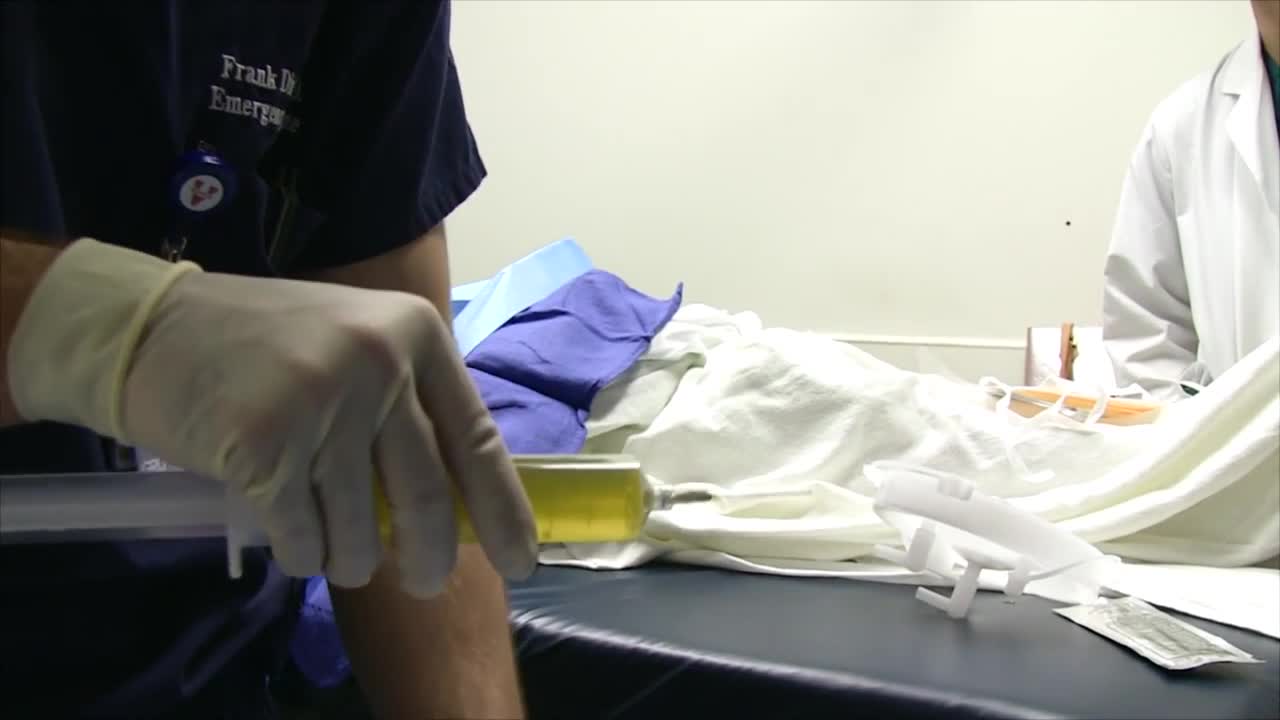
Arterial line placement is a common procedure in various critical care settings. Intra-arterial blood pressure (BP) measurement is more accurate than measurement of BP by noninvasive means, especially in the critically ill. [1] Intra-arterial BP management permits the rapid recognition of BP changes that is vital for patients on continuous infusions of vasoactive drugs. Arterial cannulation also allows repeated arterial blood gas samples to be drawn without injury to the patient.

A bone marrow biopsy removes a small amount of bone and a small amount of fluid and cells from inside the bone (bone marrow). A bone marrow aspiration removes only the marrow. These tests are often done to find the reason for many blood disorders and may be used to find out if cancer or infection has spread to the bone marrow. Bone marrow aspiration removes a small amount of bone marrow fluid and cells through a needle put into a bone. The bone marrow fluid and cells are checked for problems with any of the blood cells made in the bone marrow. Cells can be checked for chromosome problems. Cultures can also be done to look for infection. A bone marrow biopsy removes bone with the marrow inside to look at under a microscope. The aspiration (taking fluid) is usually done first, and then the biopsy.

The maneuver is commonly used during some activities: Straining to have a bowel movement Blowing a stuffy nose Certain medical tests or exams As a pressure equalization technique by scuba divers, sky divers and airplane passengers The effect of the Valsalva Maneuver is a drastic increase in the pressure within the thoracic cavity.

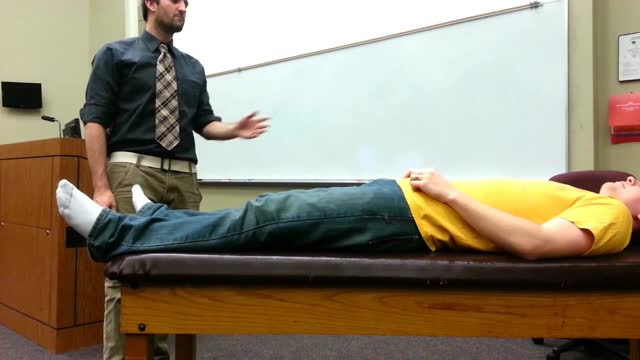
The "Get up and go" test is most commonly used to assess postural stability. In this test, the physician instructs the patient to stand up from a chair without assistance, walk a short distance, turn around, return, and sit down again. If the patient is unsteady or has difficulties during the test, further evaluation is necessary.

This type of gait is most often seen in peripheral nerve disease where the distal lower extremity is most affected. Because the foot dorsiflexors are weak, the patient has a high stepping gait in an attempt to avoid dragging the toe on the ground.
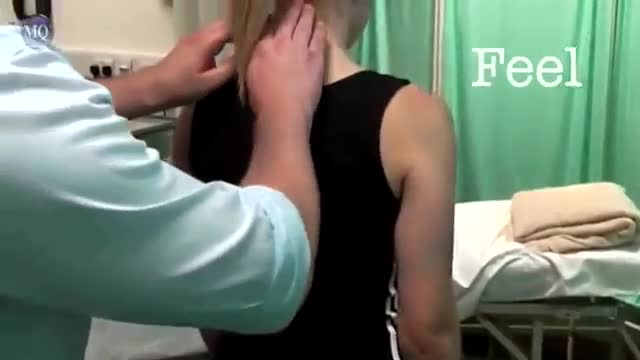
The examination consists of three portions: Inspection, Palpation, and Synthesis of data from these techniques In addition to palpating for size, also note the gland texture, mobility, tenderness and the presence of nodules. Inspection Inspection: Anterior Approach The patient should be seated or standing in a comfortable position with the neck in a neutral or slightly extended position. Cross-lighting increases shadows, improving the detection of masses. To enhance visualization of the thyroid, you can: Extending the neck, which stretches overlying tissues Have the patient swallow a sip of water, watching for the upward movement of the thyroid gland. quicktime video 251KB video demo from Return to the Bedside Inspection: Lateral Approach After completing anterior inspection of the thyroid, observe the neck from the side. Estimate the smooth, straight contour from the cricoid cartilage to the suprasternal notch. Measure any prominence beyond this imagined contour, using a ruler placed in the area of prominence. Palpation Note: There is no data comparing palpation using the anterior approach to the posterior approach so examiners should use the approach that they find most comfortable. Palpation: Anterior Approach placement of hands for palpatation of thyroid in anterior approach The patient is examined in the seated or standing position. Attempt to locate the thyroid isthmus by palpating between the cricoid cartilage and the suprasternal notch. Use one hand to slightly retract the sternocleidomastoid muscle while using the other to palpate the thyroid. Have the patient swallow a sip of water as you palpate, feeling for the upward movement of the thyroid gland. quicktime video 454KB video demo from Return to the Bedside. Palpation: Posterior Approach placement of hands for palpatation of thyroid in posterior approach The patient is examined in the seated or standing position. Standing behind the patient, attempt to locate the thyroid isthmus by palpating between the cricoid cartilage and the suprasternal notch. Move your hands laterally to try to feel under the sternocleidomstoids for the fullness of the thyroid. Have the patient swallow a sip of water as you palpate, feeling for the upward movement of the thyroid gland.