جدیدترین ویدیوها
Norepinephrine is synthesized from dopamine by dopamine β-hydroxylase.[7] It is released from the adrenal medulla into the blood as a hormone, and is also a neurotransmitter in the central nervous system and sympathetic nervous system where it is released from noradrenergic neurons.
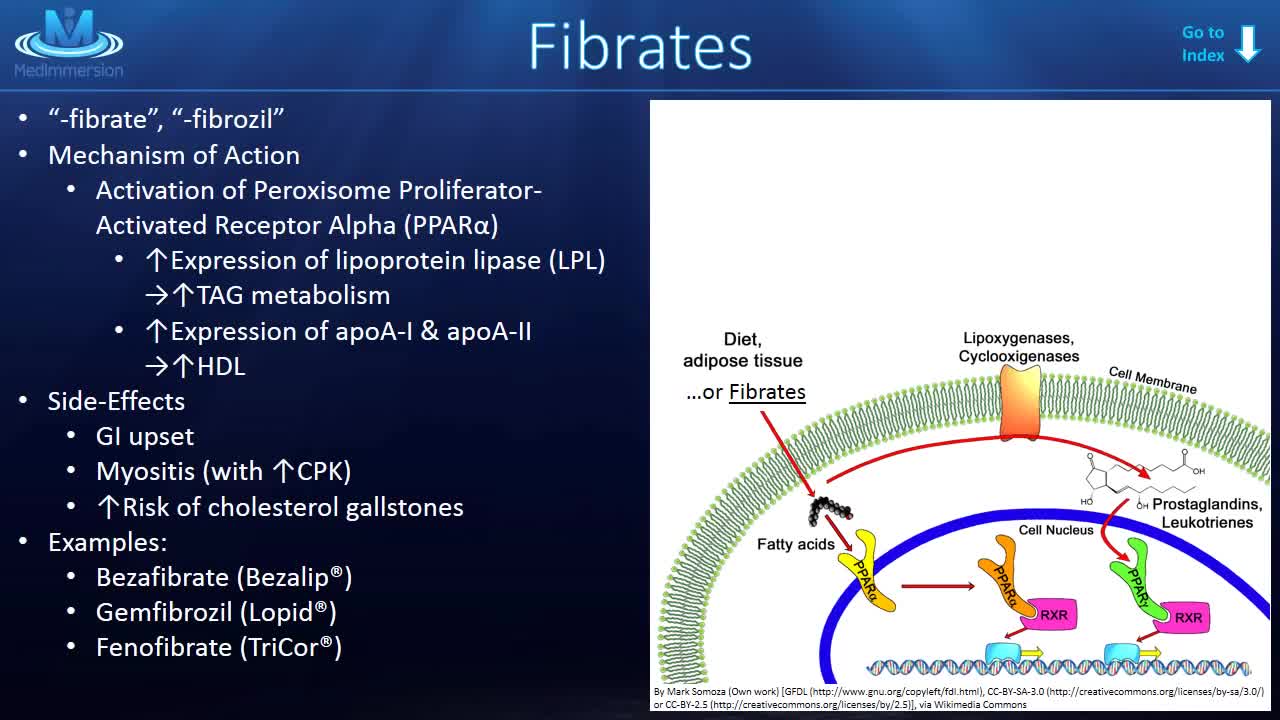
Lipid-Lowering Agents HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors (statins) These agents inhibit the rate-limiting step in cholesterol biosynthesis by competitively inhibiting HMG-CoA reductase. Note the following: Low-density lipoprotein (LDL) reduction of 25%-60% Examples include Atorvastatin, fluvastatin, lovastatin, pitavastatin, pravastatin, rosuvastatin, simvastatin Contraindications include hypersensitivity, active liver disease, pregnancy, lactation, coadministration with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors (selected statins) Vitamin B3 Vitamin B3 inhibits very-low-density lipoprotein (VLDL) synthesis. Note the following: LDL reduction of 10% High-density lipoprotein (HDL) increase of 20% Example includes Niacin (nicotinic acid) Contraindications include hypersensitivity, liver disease, active peptic ulcer, severe hypotension, arterial bleeding Fibrates Fibrates enhance lipoprotein lipase, resulting in increased VLDL catabolism, fatty acid oxidation, and triglycerides elimination. They decrease hepatic extraction of free fatty acids. Note the following: LDL reduction of 15% Triglyceride reduction of 35% Examples include Gemfibrozil, fenofibrate, fenofibrate (micronized), fenofibric acid Contraindications include active liver disease, renal disease, primary biliary cirrhosis, gallbladder disease 2-Azetidiones These agents inhibit sterol transporter at brush border and, consequently, intestinal absorption of cholesterol. LDL reduction of 15% Example includes Ezetimibe Contraindications include hypersensitivity, coadministration with statins (if active liver disease) Bile acid sequestrants These agents lower cholesterol and LDL via bile duct sequestration. Note the following: LDL reduction of 15% Examples include Cholestyramine, colesevelam, colestipol Contraindications include biliary/bowel obstruction, serum triglycerides >300-500 mg/dL, history of hypertriglyceridemia-induced pancreatitis

This medication is used in emergencies to treat very serious allergic reactions to insect stings/bites, foods, drugs, or other substances. Epinephrine acts quickly to improve breathing, stimulate the heart, raise a dropping blood pressure, reverse hives, and reduce swelling of the face, lips, and throat.

Dopamine is the one neurotransmitter that everyone seems to know about. Vaughn Bell once called it the Kim Kardashian of molecules, but I don’t think that’s fair to dopamine. Suffice it to say, dopamine’s big. And every week or so, you’ll see a new article come out all about dopamine.

Angina, stroke and other vascular conditions are often caused by atherosclerosis ('arteriosclerosis') and treated by stenting, where doctors open up a blocked artery in the heart by inserting a sliver of metal into the artery to keep it open. However, there are allegations that far too many stents are being put in when medications and lifestyle changes could do the job just as well if not better.

Coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) is a type of surgery that improves blood flow to the heart. Surgeons use CABG to treat people who have severe coronary heart disease (CHD). CHD is a disease in which a waxy substance called plaque (plak) builds up inside the coronary arteries.
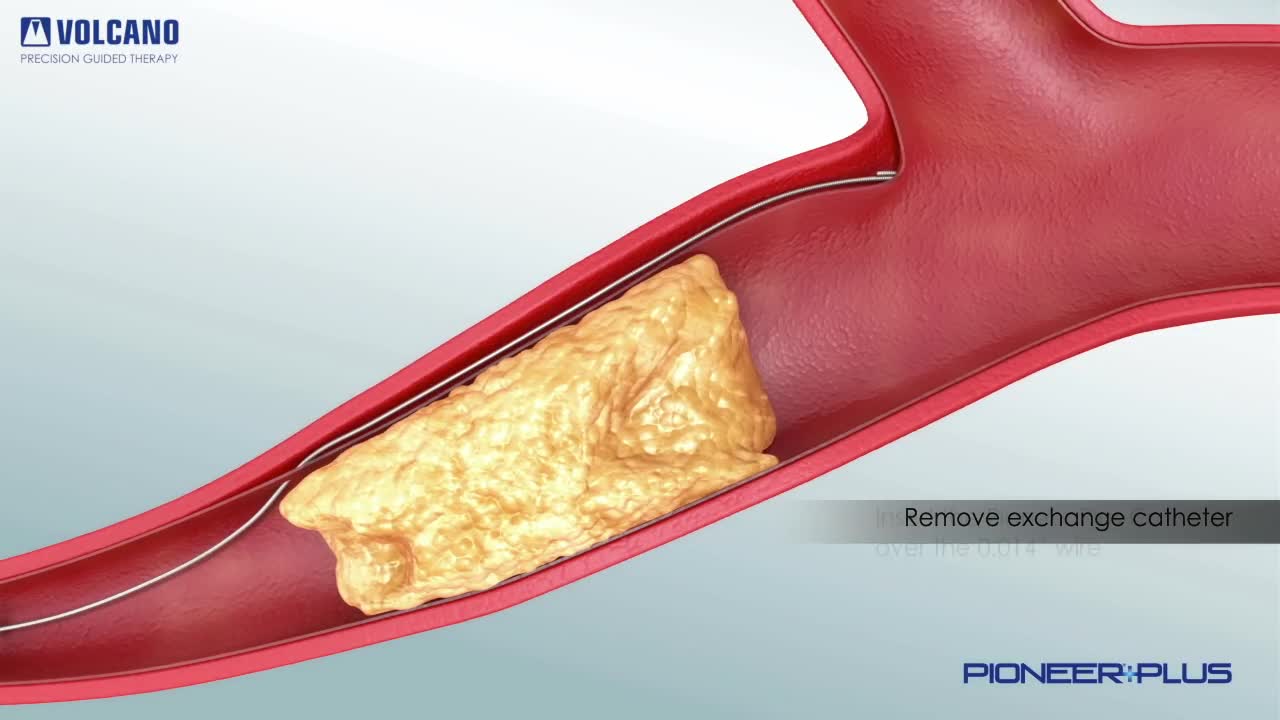
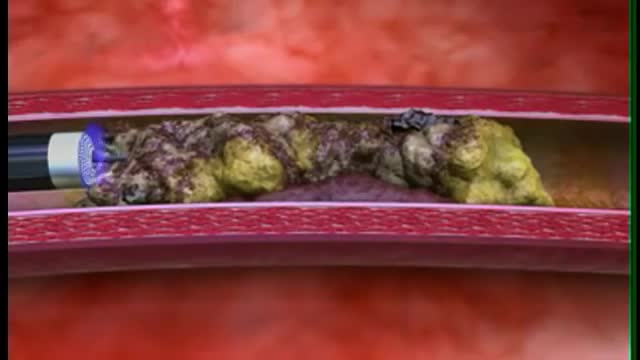
Preventing heart attacks and stroke can involve extensive surgery to remove plaque from your arteries, but as FOX17's Nick Paranjape shows us, there's a new procedure in Middle Tennessee that is less invasive and substantially cuts down on your recovery time. At 76, Jimmy Wilkie of Hendersonville exercises on his treadmill 3-4 times a week. Recently, he started having pain in his left leg. It was so bad, he couldn't even walk. Turned out, Mr. Wilkie had a blocked artery in his leg. In years past, this would've required major bypass surgery. Not anymore!"The Turbohawk Catheter has really opened a new door for us," says Dr. Dan Wunder.Dr. Wunder, an Interventional Radiologist at Premier Radiology in Madison, is talking about the Turbohawk. It's a device which is inserted into the blocked artery, and inside the Turbohawk are 4 tiny blades."It can cut the plaque and with that shape of the disc it cuts with it pushes it forward into the catheter," says Dr. Wunder.The one-hour procedure doesn't just push the plaque to the sides where it can re-grow, but instead grabs it and removes it!"We pull it back out and it fills up," says Dr. Wunder. "Empty it out, go back down and we can cut some more out."Before and after images really say it all."They used a roto rooter as he called it," says Wilkie.A roto rooter, Turbohawk, call it what you want, but Wilkie says all he knows is the procedure worked right away!"There wasn't any pain at all in my leg," says Wilkie.It's rare, but the outpatient procedure can have complications like plaque getting pushed down in the leg. Dr. Wunder says the main symptoms of a blockage in your legs is having severe pain or cramping when you're walking or exercising.
CRT provides a cost-effective measure for industry to reduce workplace injuries before they occur. CRT uses the latest Isokinetic Testing technology and equipment to match the physical capability of the worker with the physical demands of the job.