Top videos
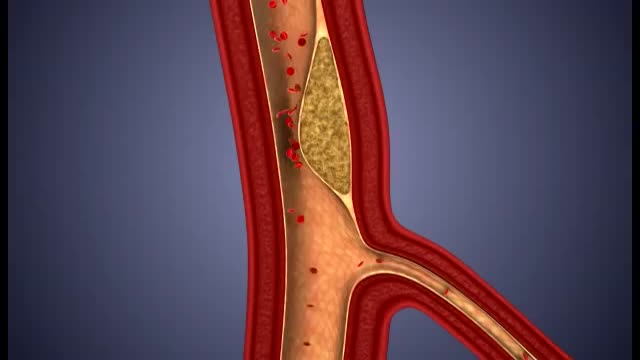
What damage does atherosclerosis cause? Plaque may partially or totally block the blood's flow through an artery in the heart, brain, pelvis, legs, arms or kidneys. Some of the diseases that may develop as a result of atherosclerosis include coronary heart disease, angina (chest pain), carotid artery disease, peripheral artery disease (PAD) and chronic kidney disease.
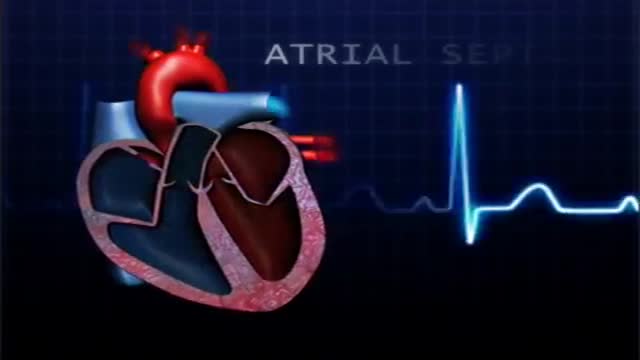
atrial septal defect (ASD) is a hole in the wall between the two upper chambers of your heart (atria). The condition is present from birth (congenital). Small atrial septal defects may close on their own during infancy or early childhood. Large and long-standing atrial septal defects can damage your heart and lungs. Small defects may never cause a problem and may be found incidentally. An adult who has had an undetected atrial septal defect for decades may have a shortened life span from heart failure or high blood pressure that affects the arteries in the lungs (pulmonary hypertension). Surgery may be necessary to repair atrial septal defects to prevent complications
A ventricular septal defect (VSD) is an opening or hole in the wall that separates the two lower chambers of the heart. This wall is called the ventricular septum. The hole causes oxygen-rich blood to leak from the left side of the heart to the right side. This causes extra work for the right side of the heart, since more blood than necessary is flowing through the right ventricle to the lungs.
The urinary bladder is a hollow muscular organ that collects urine from the kidneys before disposal by urination. A hollow muscular, and distensible (or elastic) organ, the bladder sits on the pelvic floor. Urine enters the bladder via the ureters and exits via the urethra.
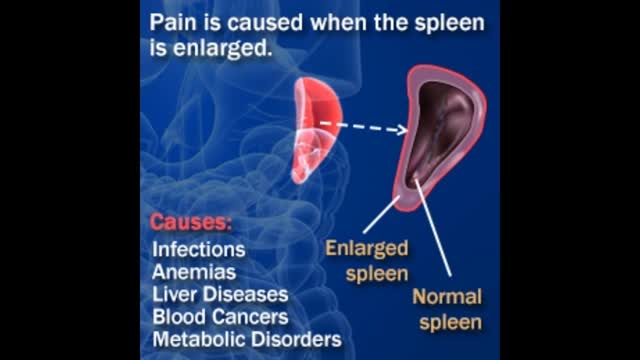
The spleen, a spongy, soft organ about as big as a person’s fist, is located in the upper left part of the abdomen, just under the rib cage. The splenic artery brings blood to the spleen from the heart. Blood leaves the spleen through the splenic vein, which drains into a larger vein (the portal vein) that carries the blood to the liver. The spleen has a covering of fibrous tissue (the splenic capsule) that supports its blood vessels and lymphatic vessels. The spleen is made up of two basic types of tissue, each with different functions: White pulp Red pulp The white pulp is part of the infection-fighting (immune) system. It produces white blood cells called lymphocytes, which in turn produce antibodies (specialized proteins that protect against invasion by foreign substances). The red pulp filters the blood, removing unwanted material. The red pulp contains other white blood cells called phagocytes that ingest microorganisms, such as bacteria, fungi, and viruses. It also monitors red blood cells, destroying those that are abnormal or too old or damaged to function properly. In addition, the red pulp serves as a reservoir for different elements of the blood, especially white blood cells and platelets (cell-like particles involved in clotting). However, releasing these elements is a minor function of the red pulp.
An enlarged spleen can be caused by infections, cirrhosis and other liver diseases, blood diseases characterized by abnormal blood cells, problems with the lymph system, or other conditions. Other causes of an enlarged spleen include: Inflammatory diseases such as sarcoidosis, lupus, and rheumatoid arthritis.
Dehydration can also be a cause of kidney stones. A common symptom is having a lower left abdominal pain, fever, nausea, groin pain and vomiting. Lower left abdominal pain can also be caused by an infection of the kidneys. It usually begins with the bladder and then reaches out to the kidneys.
The pain of ovulation can range from a mild twinge to severe discomfort and usually lasts from minutes to hours. It is generally felt on one side of the abdomen and may vary each month, depending on which ovary is releasing the egg during that cycle.
It's a symptom of heart disease but typically does not cause permanent damage to the heart. It is, though, a sign that you are a candidate for a heart attack at some point in the future. The chest pain may spread to your arm, shoulder, jaw, or back. It may feel like a pressure or squeezing sensation.
Top 10 Foods that Can Kill You
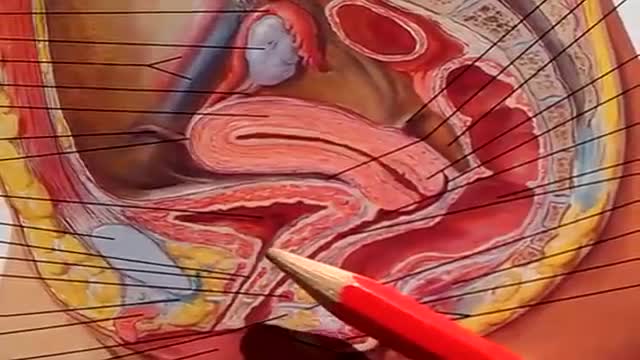
The most common position of the uterus is anteverted (cervix angles forward) and anteflexed (body is flexed forward). The position of the uterus in the adult is liable to considerable variation, depending chiefly on the condition of the bladder and rectum. Adnexa: In gynecology, the appendages of the uterus, namely the ovaries, the Fallopian tubes, and the ligaments that hold the uterus in place.
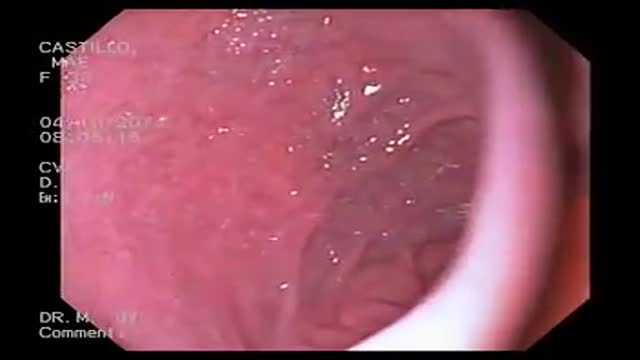
A gastroscopy is a procedure where a thin, flexible tube called an endoscope is used to look inside the oesophagus (gullet), stomach and first part of the small intestine (duodenum). It's also sometimes referred to as an upper gastrointestinal endoscopy. The endoscope has a light and a camera at one end.
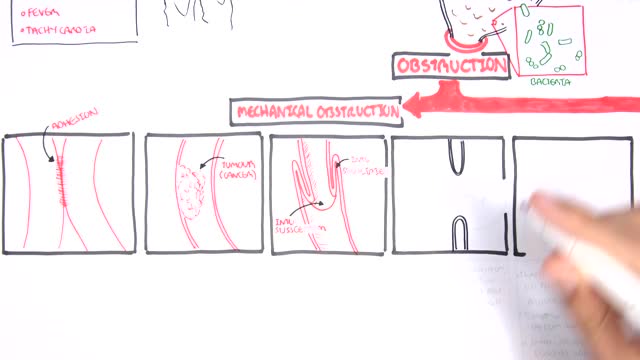
A bowel obstruction happens when either your small or large intestine is partly or completely blocked. The blockage prevents food, fluids, and gas from moving through the intestines in the normal way. The blockage may cause severe pain that comes and goes. This topic covers a blockage caused by tumors, scar tissue, or twisting or narrowing of the intestines. It does not cover ileus, which most commonly happens after surgery on the belly (abdominal surgery). What causes a bowel obstruction? Tumors, scar tissue (adhesions), or twisting or narrowing of the intestines can cause a bowel obstruction. These are called mechanical obstructions . In the small intestine, scar tissue is most often the cause. Other causes include hernias and Crohn's disease, which can twist or narrow the intestine, and tumors, which can block the intestine. A blockage also can happen if one part of the intestine folds like a telescope into another part, which is called intussusception.
Sepsis is a potentially life-threatening complication of an infection. Sepsis occurs when chemicals released into the bloodstream to fight the infection trigger inflammatory responses throughout the body. This inflammation can trigger a cascade of changes that can damage multiple organ systems, causing them to fail. If sepsis progresses to septic shock, blood pressure drops dramatically, which may lead to death. Anyone can develop sepsis, but it's most common and most dangerous in older adults or those with weakened immune systems. Early treatment of sepsis, usually with antibiotics and large amounts of intravenous fluids, improves chances for survival. Symptoms & causes Symptoms Many doctors view sepsis as a three-stage syndrome, starting with sepsis and progressing through severe sepsis to septic shock. The goal is to treat sepsis during its early stage, before it becomes more dangerous. Sepsis To be diagnosed with sepsis, you must exhibit at least two of the following symptoms, plus a probable or confirmed infection: Body temperature above 101 F (38.3 C) or below 96.8 F (36 C) Heart rate higher than 90 beats a minute Respiratory rate higher than 20 breaths a minute Severe sepsis Your diagnosis will be upgraded to severe sepsis if you also exhibit at least one of the following signs and symptoms, which indicate an organ may be failing: Significantly decreased urine output Abrupt change in mental status Decrease in platelet count Difficulty breathing Abnormal heart pumping function Abdominal pain Septic shock To be diagnosed with septic shock, you must have the signs and symptoms of severe sepsis — plus extremely low blood pressure that doesn't adequately respond to simple fluid replacement. When to see a doctor Most often sepsis occurs in people who are hospitalized. People in the intensive care unit are especially vulnerable to developing infections, which can then lead to sepsis. If you get an infection or if you develop signs and symptoms of sepsis after surgery, hospitalization or an infection, seek medical care immediately. Causes While any type of infection — bacterial, viral or fungal — can lead to sepsis, the most likely varieties include: Pneumonia Abdominal infection Kidney infection Bloodstream infection (bacteremia) The incidence of sepsis appears to be increasing in the United States. The causes of this increase may include: Aging population. Americans are living longer, which is swelling the ranks of the highest risk age group — people older than 65. Drug-resistant bacteria. Many types of bacteria can resist the effects of antibiotics that once killed them. These antibiotic-resistant bacteria are often the root cause of the infections that trigger sepsis. Weakened immune systems. More Americans are living with weakened immune systems, caused by HIV, cancer treatments or transplant drugs. Risk factors Sepsis is more common and more dangerous if you: Are very young or very old Have a compromised immune system Are already very sick, often in a hospital's intensive care unit Have wounds or injuries, such as burns Have invasive devices, such as intravenous catheters or breathing tubes Complications Sepsis ranges from less to more severe. As sepsis worsens, blood flow to vital organs, such as your brain, heart and kidneys, becomes impaired. Sepsis can also cause blood clots to form in your organs and in your arms, legs, fingers and toes — leading to varying degrees of organ failure and tissue death (gangrene). Most people recover from mild sepsis, but the mortality rate for septic shock is nearly 50 percent. Also, an episode of severe sepsis may place you at higher risk of future infections.
The arm and leg muscles are affected later. Myasthenia gravis (MG) is an autoimmune disease — a disease that occurs when the immune system attacks the body's own tissues. In MG, that attack interrupts the connection between nerve and muscle — the neuromuscular junction.
Hodgkin's lymphoma — formerly known as Hodgkin's disease — is a cancer of the lymphatic system, which is part of your immune system. In Hodgkin's lymphoma, cells in the lymphatic system grow abnormally and may spread beyond the lymphatic system. As Hodgkin's lymphoma progresses, it compromises your body's ability to fight infection. Hodgkin's lymphoma is one of two common types of cancers of the lymphatic system. The other type, non-Hodgkin's lymphoma, is far more common. Advances in diagnosis and treatment of Hodgkin's lymphoma have helped give people with this diagnosis the chance for a full recovery. The prognosis continues to improve for people with Hodgkin's lymphoma.
The long-standing answer has been that sneezing is a reflex. When irritants — such as germs, dust, pollen, animal dander, or pollutants, just to name just a few — infiltrate the nose lining, the brain sends out a signal to get rid of it. That triggers a deep breath, which gets held in the lungs.
Pancreatic cysts are saclike pockets of fluid on or in your pancreas, a large organ behind the stomach that produces hormones and enzymes that help digest food. Most pancreatic cysts aren't cancerous, and many don't cause symptoms. They're typically found during imaging testing for another problem. Some are actually noncancerous (benign) pockets of fluids lined with scar or inflammatory tissue, not the type of cells found in true cysts (pseudocysts). But some pancreatic cysts can be or can become cancerous. Your doctor might take a sample of the pancreatic cyst fluid to determine if cancer cells are present. Or your doctor might recommend monitoring a cyst over time for changes that indicate cancer.
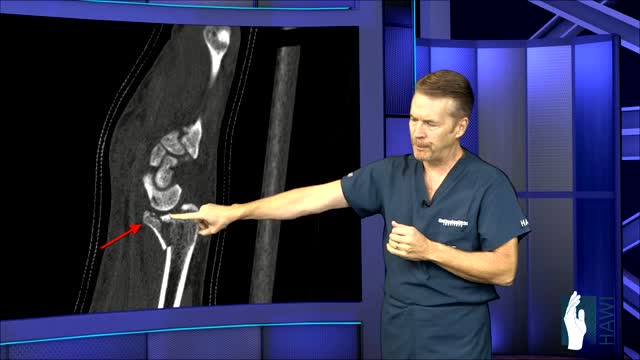
A distal radius fracture almost always occurs about 1 inch from the end of the bone. The break can occur in many different ways, however. One of the most common distal radius fractures is a Colles fracture, in which the broken fragment of the radius tilts upward. This fracture was first described in 1814 by an Irish surgeon and anatomist, Abraham Colles -- hence the name "Colles" fracture.
There are a number of different causes of vertigo. Vertigo can be defined based upon whether the cause is peripheral or central. Central causes of vertigo arise in the brain or spinal cord while peripheral vertigo is due to a problem within the inner ear. The inner ear can become inflamed because of illness, or small crystals or stones found normally within the inner ear can become displaced and cause irritation to the small hair cells within the semicircular canals, leading to vertigo. This is known as benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV).