Mga nangungunang video
Acute kidney failure — also called acute renal failure or acute kidney injury — develops rapidly over a few hours or a few days. Acute kidney failure is most common in people who are already hospitalized, particularly in critically ill people who need intensive care. Acute kidney failure can be fatal and requires intensive treatment. However, acute kidney failure may be reversible. If you're otherwise in good health, you may recover normal or nearly normal kidney function
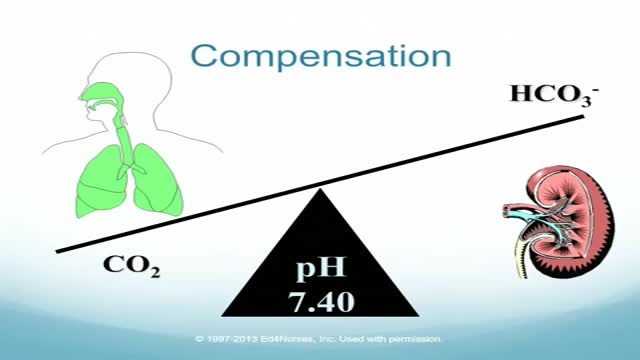
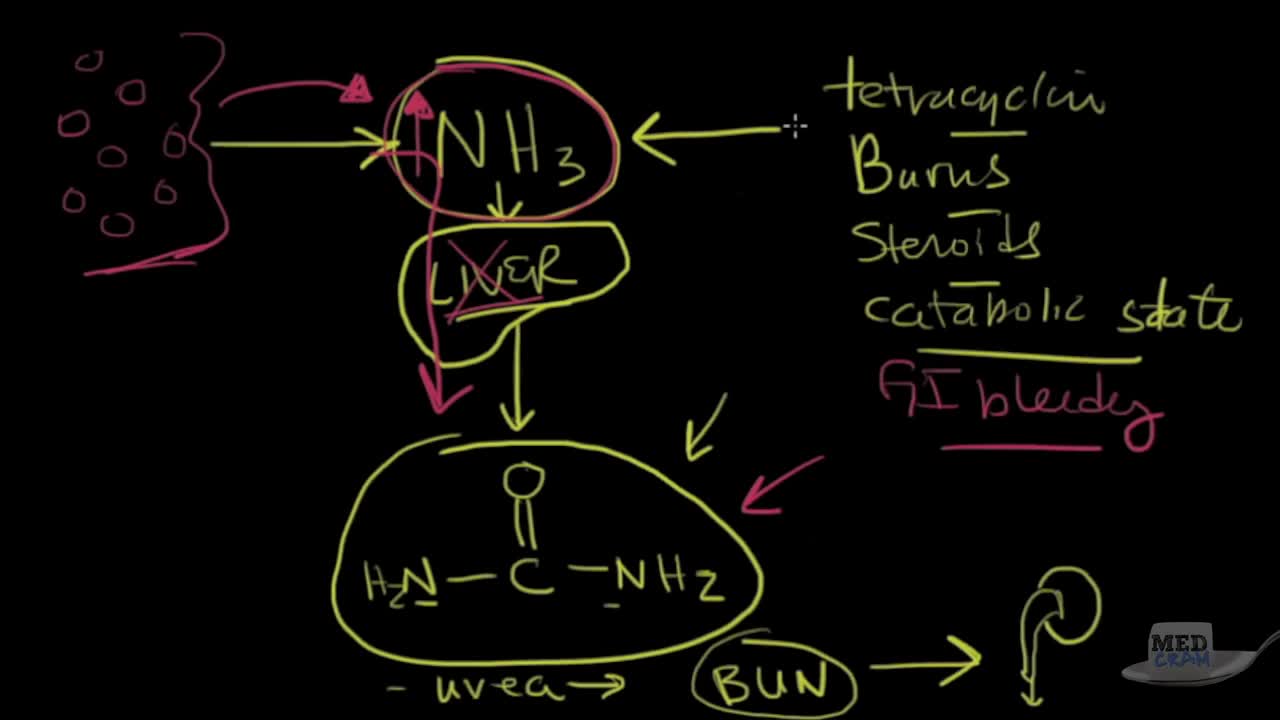
Four-Step Guide to ABG Analysis Is the pH normal, acidotic or alkalotic? Are the pCO2 or HCO3 abnormal? Which one appears to influence the pH? If both the pCO2 and HCO3 are abnormal, the one which deviates most from the norm is most likely causing an abnormal pH. Check the pO2. Is the patient hypoxic?

Kidney failure and transplant options One of the most serious complications of polycystic kidney disease is kidney failure. This is when the kidneys are no longer able to filter waste products, maintain fluid balance, and maintain blood pressure on their own. When this occurs, your doctor will discuss options with you that may include a kidney transplant or dialysis treatments to act as artificial kidneys. If your doctor does place you on a kidney transplant list, there are several factors that determine your placement. These include your overall health, expected survival, and time you have been on dialysis. It’s also possible that a friend or relative could donate a kidney to you. Because people can live with only one kidney with relatively few complications, this can be an option for families who have a willing donor. The decision to undergo a kidney transplant or donate a kidney to a person with kidney disease can be a difficult one. Speaking to your nephrologist can help you weigh your options. You can also ask what medications and treatments can help you live as well as possible in the meantime. According to the University of Iowa, the average kidney transplant will allow kidney function from 10 to 12 years.
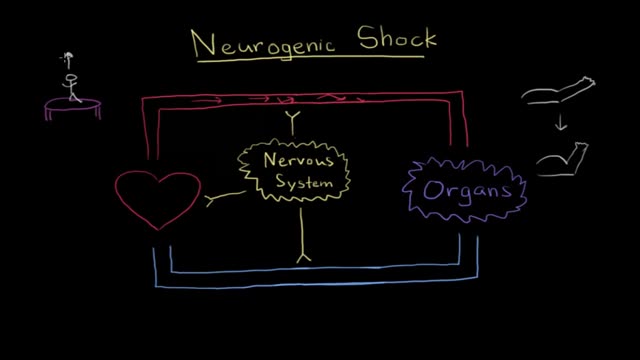
Neurogenic shock is a distributive type of shock resulting in low blood pressure, occasionally with a slowed heart rate, that is attributed to the disruption of the autonomic pathways within the spinal cord. It can occur after damage to the central nervous system such as spinal cord injury.
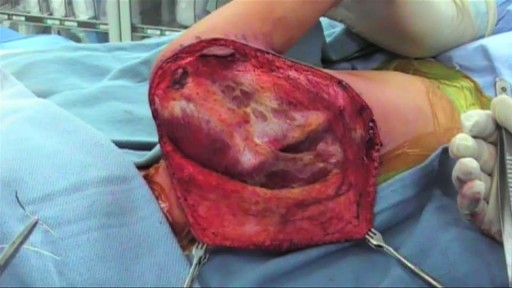
Ewing's sarcoma typically occurs in children and young adults. It often begins in the legs, bones of the pelvis, and arms. Bone pain, localized swelling, and tenderness are symptoms. In rare cases bone fractures may also be found. Treatments include chemotherapy, surgery, and radiation.

Carbon monoxide poisoning occurs after too much inhalation of carbon monoxide (CO). Carbon monoxide is a toxic gas, but, being colorless, odorless, tasteless, and initially non-irritating, it is very difficult for people to detect.

Dehydration is a condition that occurs when the loss of body fluids, mostly water, exceeds the amount that is taken in. With dehydration, more water is moving out of our cells and bodies than what we take in through drinking. We lose water every day in the form of water vapor in the breath we exhale and in our excreted sweat, urine, and stool. Along with the water, small amounts of salts are also lost.

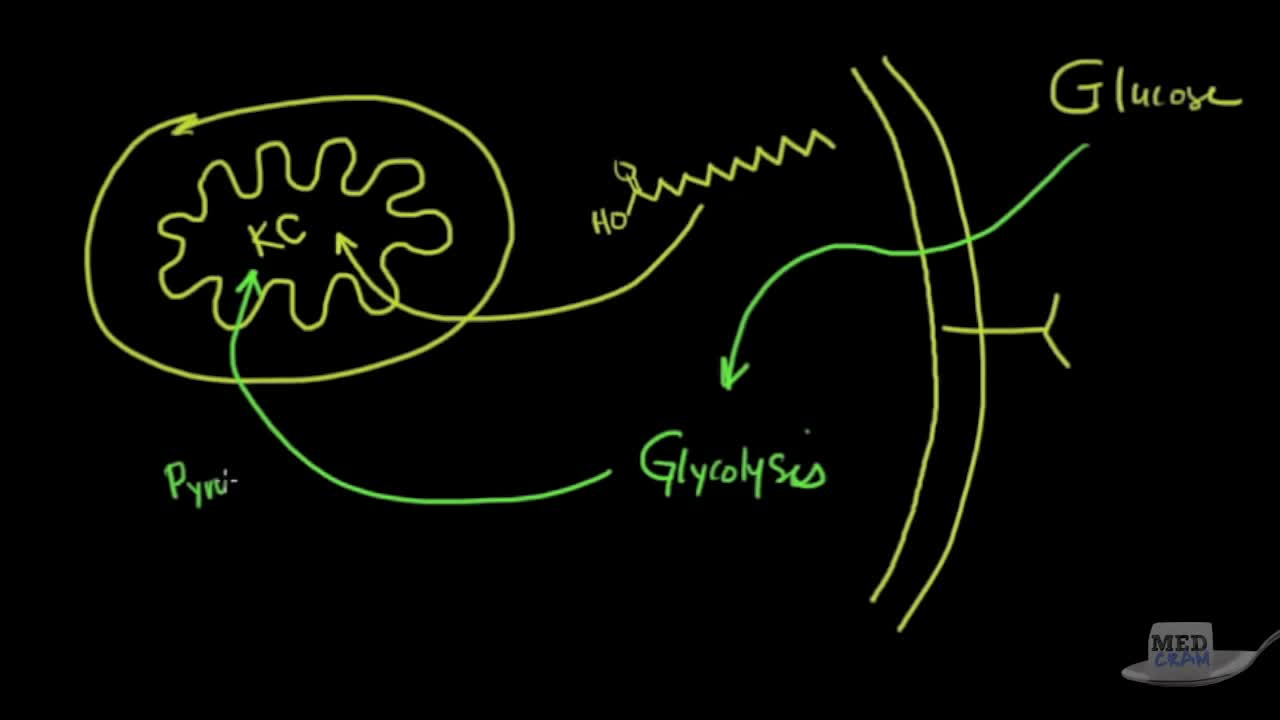
What is polycystic kidney disease? Polycystic kidney disease (also called PKD) causes numerous cysts to grow in the kidneys. These cysts are filled with fluid. If too many cysts grow or if they get too big, the kidneys can become damaged. PKD cysts can slowly replace much of the kidneys, reducing kidney function and leading to kidney failure. How common is PKD? In the United States about 600,000 people have PKD. It is the fourth leading cause of kidney failure. It is found in all races and occurs equally in men and women. It causes about 5% of all kidney failure. What other organs besides the kidney are affected by PKD? PKD can affect other organs besides the kidney. People with PKD may have cysts in their liver, pancreas, spleen, ovaries, and large bowel. Cysts in these organs usually do not cause serious problems, but can in some people. PKD can also affect the brain or heart. If PKD affects the brain, it can cause an aneurysm. An aneurysm is a bulging blood vessel that can burst, resulting in a stroke or even death. If PKD affects the heart, the valves can become floppy, resulting in a heart murmur in some patients. What are the clues that someone has PKD? Most people do not develop symptoms until they are 30 to 40 years old. The first noticeable signs and symptoms may include: Back or side pain An increase in the size of the abdomen Blood in the urine Frequent bladder or kidney infections High blood pressure High blood pressure is the most common sign of PKD. Occasionally, patients may develop headaches related to high blood pressure or their doctors may detect high blood pressure during a routine physical exam. Because high blood pressure can cause kidney damage, it is very important to treat it. In fact, treatment of high blood pressure can help slow or even prevent kidney failure. Fluttering or pounding in the chest About 25% of PKD patients have a so-called floppy valve in the heart, and may experience a fluttering or pounding in the chest as well as chest pain. These symptoms almost always disappear on their own but may be the first hint that someone has PKD. How is PKD diagnosed? Ultrasound is the most reliable, inexpensive and non-invasive way to diagnose PKD. If someone at risk for PKD is older than 40 years and has a normal ultrasound of the kidneys, he or she probably does not have PKD. Occasionally, a CT scan (computed tomography scan) and MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) may detect smaller cysts that cannot be found by an ultrasound. MRI is used to measure and monitor volume and growth of kidneys and cysts. In some situations, genetic testing might also be done. This involves a blood test that checks for abnormal genes that cause the disease. Genetic testing is not recommended for everyone. The test is costly, and it also fails to detect PKD in about 15% of people who have it. However, genetic testing can be useful when a person: has an uncertain diagnosis based on imaging tests has a family history of PKD and wants to donate a kidney is younger than 30-years old with a family history of PKD and a negative ultrasound, and is planning to start a family
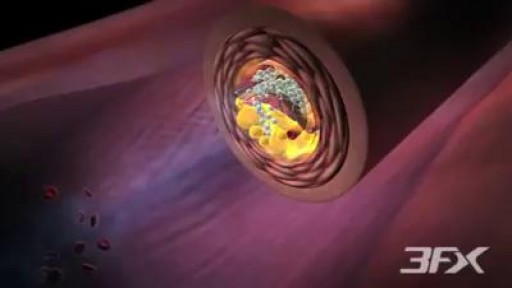
Experts once believed that atherosclerosis, or hardening of the arteries, developed when too much cholesterol clogged arteries with fatty deposits called plaques. ... Researchers have discovered how diabetes, by driving inflammation and slowing blood flow, dramatically accelerates atherosclerosis.Mar 17, 2008 Past studies had shown diabetes to worsen atherosclerosis, but its exact link to related inflammation had remained unclear. The current results provides the first mechanistic description of how diabetes takes away the ability of fast blood flow force to protect blood vessels, arguing that it does so by interfering with ERK5 and its signaling partners.

The easy experimental answer to this question is 264 hours (about 11 days). In 1965, Randy Gardner, a 17-year-old high school student, set this apparent world-record for a science fair. Several other normal research subjects have remained awake for eight to 10 days in carefully monitored experiments. None of these individuals experienced serious medical, neurological, physiological or psychiatric problems. On the other hand, all of them showed progressive and significant deficits in concentration, motivation, perception and other higher mental processes as the duration of sleep deprivation increased. Nevertheless, all experimental subjects recovered to relative normality within one or two nights of recovery sleep. Other anecdotal reports describe soldiers staying awake for four days in battle, or unmedicated patients with mania going without sleep for three to four days.

Symptoms of liver failure include vomiting, diarrhea and fatigue as well as the symptoms from stage 3. While the progression from cirrhosis to failure can take years, the damage is irreversible and leads to eventual death. The key to treating liver disease is to diagnose the condition as early as possible.