Latest videos
Syringomyelia (sih-ring-go-my-E-lee-uh) is the development of a fluid-filled cyst (syrinx) within your spinal cord. Over time, the cyst may enlarge, damaging your spinal cord and causing pain, weakness and stiffness, among other symptoms. Syringomyelia has several possible causes, though the majority of cases are associated with a condition in which brain tissue protrudes into your spinal canal (Chiari malformation). Other causes of syringomyelia include spinal cord tumors, spinal cord injuries and damage caused by inflammation around your spinal cord. If syringomyelia isn't causing any problems, monitoring the condition may be all that's necessary. But if you're bothered by symptoms, you may need surgery.
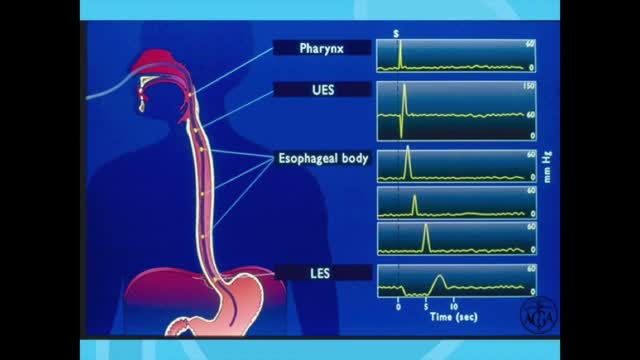
Esophageal manometry is a test used to measure the function of the lower esophageal sphincter (the valve that prevents reflux of gastric acid into the esophagus) and the muscles of the esophagus (see diagram). This test will tell your doctor if your esophagus is able to move food to your stomach normally.
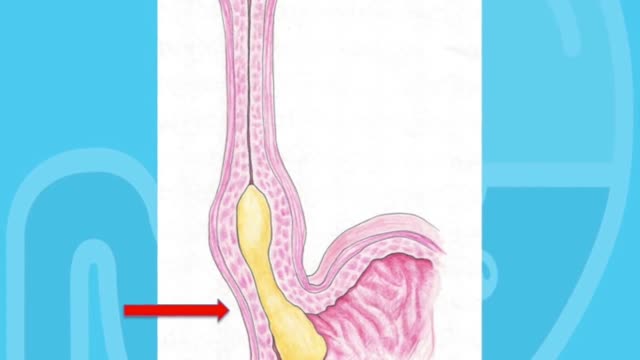
Achalasia is a neurogenic esophageal motility disorder characterized by impaired esophageal peristalsis and a lack of lower esophageal sphincter relaxation during swallowing. Symptoms are slowly progressive dysphagia, usually to both liquids and solids, and regurgitation of undigested food. Evaluation typically includes manometry, barium swallow, and endoscopy. Treatments include dilation, chemical denervation, surgical myotomy, and peroral endoscopic myotomy.

Dumping syndrome is a condition that can develop after surgery to remove all or part of your stomach or after surgery to bypass your stomach to help you lose weight. Also called rapid gastric emptying, dumping syndrome occurs when food, especially sugar, moves from your stomach into your small bowel too quickly. Most people with dumping syndrome develop signs and symptoms, such as abdominal cramps and diarrhea, 10 to 30 minutes after eating. Other people have symptoms one to three hours after eating, and still others have both early and late symptoms. Generally, you can help prevent dumping syndrome by changing your diet after surgery. Changes might include eating smaller meals and limiting high-sugar foods. In more-serious cases o

Dumping syndrome is a condition that can develop after surgery to remove all or part of your stomach or after surgery to bypass your stomach to help you lose weight. Also called rapid gastric emptying, dumping syndrome occurs when food, especially sugar, moves from your stomach into your small bowel too quickly.Diet: Eating too much sugar can cause sugars to pass into the colon, making the bacteria there get all excited and cause diarrhea. Other things like sorbitol, a sweetener in some sugarless candy, can also cause diarrhea through osmosis. Malabsorption: Some people don't digest sugars or fats properly.
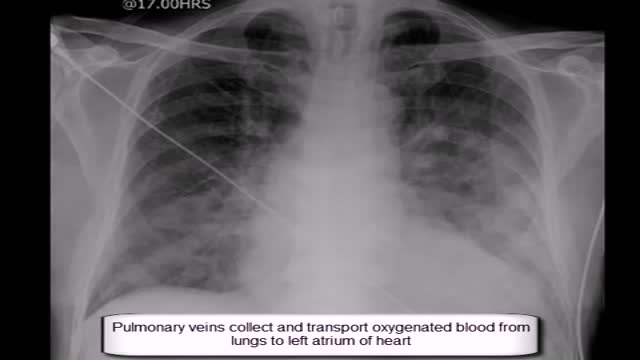
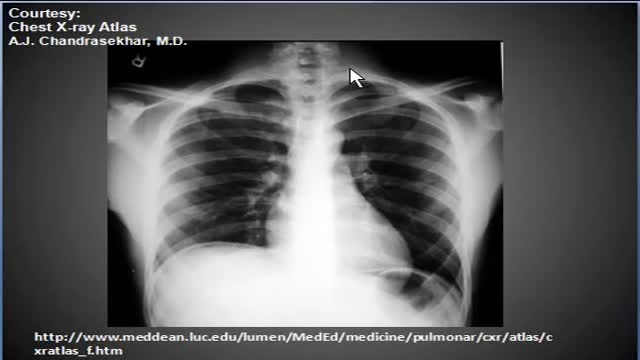
Expand Section. Pulmonary edema is often caused by congestive heart failure. When the heart is not able to pump efficiently, blood can back up into the veins that take blood through the lungs. As the pressure in these blood vessels increases, fluid is pushed into the air spaces (alveoli) in the lungs.
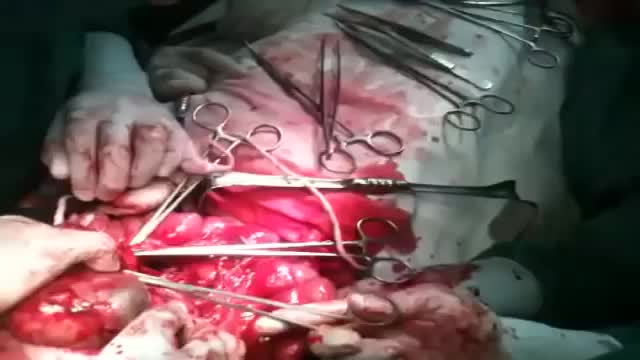
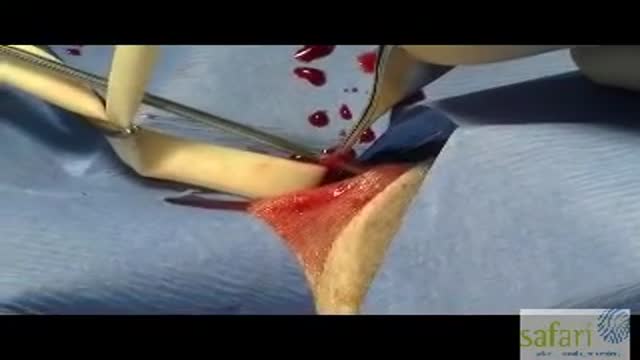
Mesenteric cyst is one of the rarest abdominal tumours, with approximately 820 cases reported since 1507. The incidence varies from 1 per 100,000 to 250,000 admissions. The lack of characteristic clinical features and radiological signs may present great diagnostic difficulties.
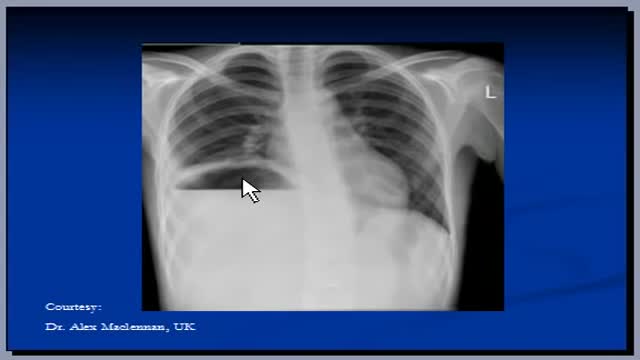
Suspect that a patient has a subphrenic abscess if he deteriorates, or recovers and then deteriorates, between the 14th and the 21st day after a laparotomy, with a low, slowly increasing, swinging fever, sweating, and a tachycardia. This, and a leucocytosis, show that he has ''pus somewhere', which is making him anorexic, wasted, and ultimately cachectic. If he has no sign of a wound infection, a rectal examination is negative, and his abdomen is soft and relaxed, the pus is probably under his diaphragm. The pus might be between his diaphragm and his liver, in (1) his right or (2) his left subphrenic space, or under his liver in (3) his right or (4) his left subhepatic space in his lesser sac. He may have pus in more than one of these spaces. Explore him on the suspicion that he might have a subphrenic abscess. Exploration is not a major operation; the difficulty is knowing where to explore, so refer him if you can. If you cannot refer him, explore him yourself. If you fail to find pus, you have done him no harm; missing a subphrenic abscess is far worse. If it is anterior, you can drain it by going under his costal margin anteriorly. If it is posterior, you can go through the bed of his 12th rib posteriorly.

Of the many factors that affect your compatibility with a man, one of the biggest (or smallest) is in his pants. As with humour, interests or habits, the wrong fit can leave you cold. Or traumatised. In a study of 1,661 penises, Dr Debby Herbenick, author of Sex Made Easy, found an almost nine-inch difference in erection size: from 1.6 inches to 10.2. And since absolutely nothing outside the package tells you what to expect with the package, you have to test compatibility the hard way. Sometimes you hit your jackpot, sometimes it's just fine, and sometimes he's the guy on either end of that erection spectrum. These writers have been there, so here's what they learned - and how you can deal (without the gasp reflex).

Erectile dysfunction (ED) is the inability to get or keep an erection firm enough for sexual function. It’s a common sexual problem, affecting as many as 30 million men in the United States. Most cases of ED have a physical cause, such as heart disease, diabetes, and obesity. Lifestyle choices like smoking and drinking excessive amounts of alcohol can also lead to ED. But for some men, psychological issues are the root of the problem.

Phencyclidine (PCP) was developed in the 1950s as an intravenous anesthetic but, due to the side effects of confusion and delirium, its development for human medical use was discontinued. In its pure form, it is a white crystalline powder that readily dissolves in water or alcohol and has a distinctive bitter chemical taste. On the illicit drug market, Phencyclidine contains a number of contaminants as a result of makeshift manufacturing, causing the color to range from tan to brown, and the consistency to range from powder to a gummy mass. It is available in a variety of tablets, capsules, and colored powders, which are either taken orally or snorted. The liquid form of phencyclidine is actually phencyclidine base dissolved most often in ether, a highly flammable solvent. For smoking, phencyclidine is typically sprayed onto leafy material such as mint, parsley, oregano, or marijuana.
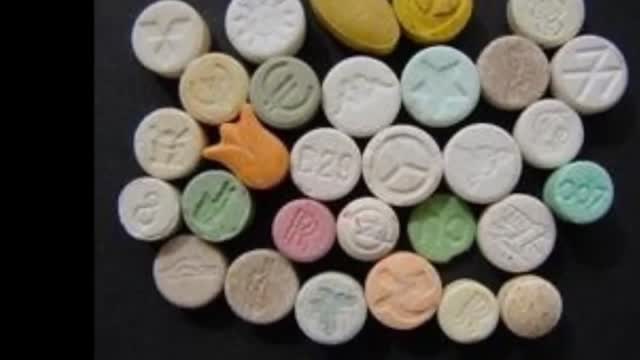
LSD is one of the most potent, mood-changing chemicals. It is manufactured from lysergic acid, which is found in the ergot fungus that grows on rye and other grains. It is produced in crystal form in illegal laboratories, mainly in the United States. These crystals are converted to a liquid for distribution. It is odorless, colorless, and has a slightly bitter taste.

Smallpox disease is a serious, highly contagious, and often life-threatening infection marked by a rash of round pox (blisters) on the face, arms, and legs. It is caused by the Variola virus. The last case of smallpox in the United States was in 1949.

Wetness. Even the most absorbent diaper leaves some moisture on your child's skin. And when your child's urine mixes with bacteria from his stool, it breaks down into ammonia, which can be very harsh on the skin. That's why children with frequent bowel movements or diarrhea are more prone to diaper rash.