Latest videos

Eczema, or atopic dermatitis, is a rash that primarily occurs in people with asthma or allergies. The rash is often reddish and itchy with a scaly texture. Psoriasis is a common skin condition that can cause a scaly, itchy, red rash to form along the scalp, elbows, and joints.Apr 13, 2016
Classical PKU is an autosomal recessive disorder, caused by mutations in both alleles of the gene for phenylalanine hydroxylase (PAH), found on chromosome 12. In the body, phenylalanine hydroxylase converts the amino acid phenylalanine to tyrosine, another amino acid.

PKU is inherited in families in an autosomal recessive pattern. Autosomal recessive inheritance means that a person has two copies of the gene that is altered. Usually, each parent of an individual who has PKU carries one copy of the altered gene. ... Gene alterations (mutations) in the PAH gene cause PKU.

If you have gestational diabetes, your baby may be at increased risk of: Excessive birth weight. Extra glucose in your bloodstream crosses the placenta, which triggers your baby's pancreas to make extra insulin. This can cause your baby to grow too large (macrosomia).
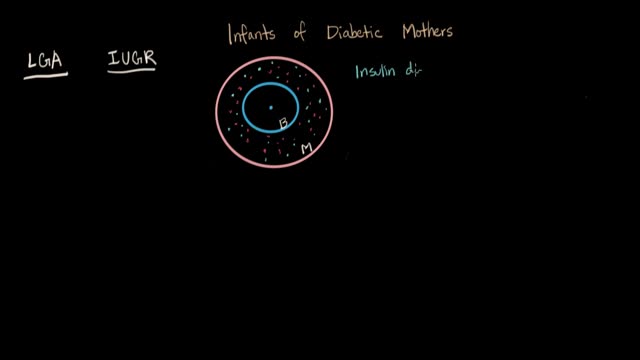
Because the continuous supply of glucose is stopped after birth, the neonate develops hypoglycemia because of insufficient substrate. Stimulation of fetal insulin release by maternal hyperglycemia during labor significantly increases the risk of early hypoglycemia in these infants.

Women who have untreated chlamydia might develop pelvic inflammatory disease, which can cause ectopic pregnancies, chronic pelvic pain and infertility. ... The antibiotics used to treat chlamydia are safe in pregnancy and are used in pregnant women for many other types of infections.
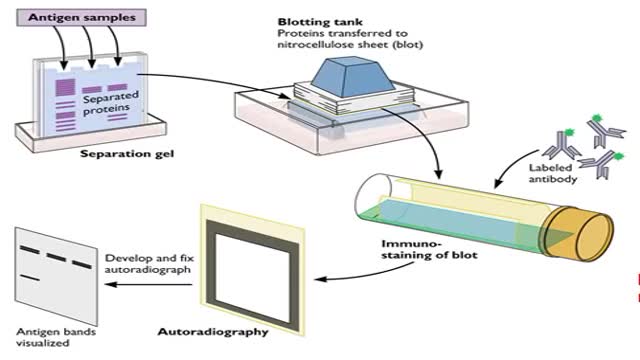
The window period is the time from infection until a test can detect any change. The average window period with HIV-1 antibody tests is 25 days for subtype B. Antigen testing cuts the window period to approximately 16 days and nucleic acid testing (NAT) further reduces this period to 12 days.[2] Performance of medical tests is often described in terms of: sensitivity: The percentage of the results that will be positive when HIV is present specificity: The percentage of the results that will be negative when HIV is not present. All diagnostic tests have limitations, and sometimes their use may produce erroneous or questionable results. False positive: The test incorrectly indicates that HIV is present in a non-infected person. False negative: The test incorrectly indicates that HIV is absent in an infected person.

Mother-to-child transmission of HIV is the spread of HIV from an HIV-infected woman to her child during pregnancy, childbirth (also called labor and delivery), or breastfeeding (through breast milk). Mother-to-child transmission of HIV is also called perinatal transmission of HIV.
Diagnosis of HIV infection in infants is aided by HIV culture or DNA/RNA polymerase chain reaction (PCR); positive results are confirmed by repeating the test. In suspected cases, HIV testing should occur in the newborn period (ie, before the infant is 48 h old), at age 1-2 months, and again at age 3-6 months.

Beckwith-Wiedemann Syndrome (BWS) is a congenital overgrowth syndrome, which can affect all systems of the body. It was first recognised in 1963-64 by Dr J. Bruce Beckwith, a paediatric pathologist in America and, independently, by Dr H.E. Wiedemann, a German geneticist.
Testicular sperm aspiration (TESA) is a procedure performed for men who are having sperm retrieved for in vitro fertilization/intracytoplasmic sperm injection (IVF/ICSI). It is done with local anesthesia in the operating room or office and is coordinated with their female partner's egg retrieval.

Dilation and curettage (D&C) is a procedure to remove tissue from inside your uterus. Doctors perform dilation and curettage to diagnose and treat certain uterine conditions — such as heavy bleeding — or to clear the uterine lining after a miscarriage or abortion. In a dilation and curettage — sometimes spelled "dilatation" and curettage — your doctor uses small instruments or a medication to open (dilate) your cervix — the lower, narrow part of your uterus. Your doctor then uses a surgical instrument called a curette to remove uterine tissue. Curettes used in a D&C can be sharp or use suction
Dilation and curettage (D&C) is a procedure to remove tissue from inside your uterus. Doctors perform dilation and curettage to diagnose and treat certain uterine conditions — such as heavy bleeding — or to clear the uterine lining after a miscarriage or abortion.

Hysteroscopy is a procedure that allows your doctor to look inside your uterus in order to diagnose and treat causes of abnormal bleeding. Hysteroscopy is done using a hysteroscope, a thin, lighted tube that is inserted into the vagina to examine the cervix and inside of the uterus.
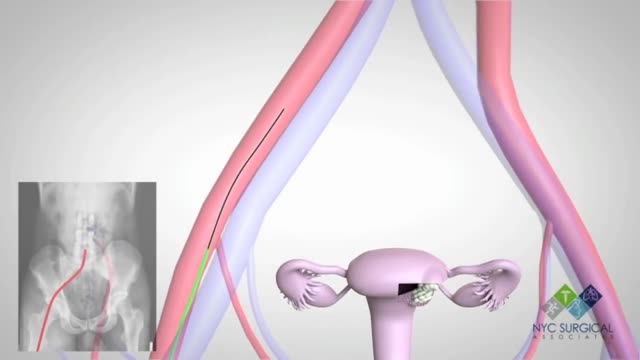
There's no single best approach to uterine fibroid treatment — many treatment options exist. If you have symptoms, talk with your doctor about options for symptom relief. Watchful waiting Many women with uterine fibroids experience no signs or symptoms, or only mildly annoying signs and symptoms that they can live with. If that's the case for you, watchful waiting could be the best option. Fibroids aren't cancerous. They rarely interfere with pregnancy. They usually grow slowly — or not at all — and tend to shrink after menopause, when levels of reproductive hormones drop. Medications Medications for uterine fibroids target hormones that regulate your menstrual cycle, treating symptoms such as heavy menstrual bleeding and pelvic pressure. They don't eliminate fibroids, but may shrink them. Medications include: Gonadotropin-releasing hormone (Gn-RH) agonists. Medications called Gn-RH agonists (Lupron, Synarel, others) treat fibroids by blocking the production of estrogen and progesterone, putting you into a temporary postmenopausal state. As a result, menstruation stops, fibroids shrink and anemia often improves. Your doctor may prescribe a Gn-RH agonist to shrink the size of your fibroids before a planned surgery. Many women have significant hot flashes while using Gn-RH agonists. Gn-RH agonists typically are used for no more than three to six months because symptoms return when the medication is stopped and long-term use can cause loss of bone. Progestin-releasing intrauterine device (IUD). A progestin-releasing IUD can relieve heavy bleeding caused by fibroids. A progestin-releasing IUD provides symptom relief only and doesn't shrink fibroids or make them disappear. It also prevents pregnancy. Tranexamic acid (Lysteda). This nonhormonal medication is taken to ease heavy menstrual periods. It's taken only on heavy bleeding days. Other medications. Your doctor might recommend other medications. For example, oral contraceptives or progestins can help control menstrual bleeding, but they don't reduce fibroid size. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), which are not hormonal medications, may be effective in relieving pain related to fibroids, but they don't reduce bleeding caused by fibroids. Your doctor may also suggest that you take vitamins and iron if you have heavy menstrual bleeding and anemia