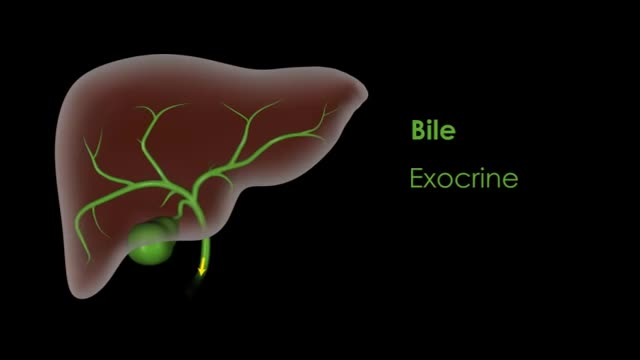
Najnoviji video zapisi
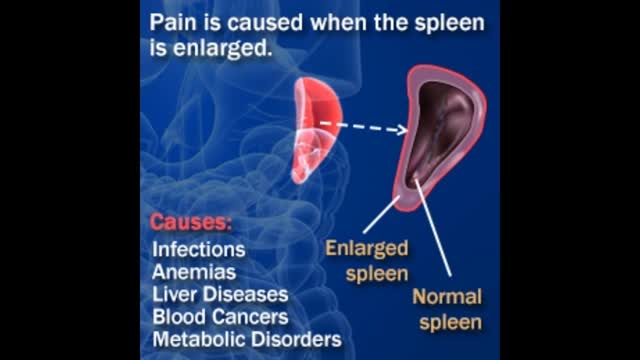
An enlarged spleen can be caused by infections, cirrhosis and other liver diseases, blood diseases characterized by abnormal blood cells, problems with the lymph system, or other conditions. Other causes of an enlarged spleen include: Inflammatory diseases such as sarcoidosis, lupus, and rheumatoid arthritis.

The spleen, a spongy, soft organ about as big as a person’s fist, is located in the upper left part of the abdomen, just under the rib cage. The splenic artery brings blood to the spleen from the heart. Blood leaves the spleen through the splenic vein, which drains into a larger vein (the portal vein) that carries the blood to the liver. The spleen has a covering of fibrous tissue (the splenic capsule) that supports its blood vessels and lymphatic vessels. The spleen is made up of two basic types of tissue, each with different functions: White pulp Red pulp The white pulp is part of the infection-fighting (immune) system. It produces white blood cells called lymphocytes, which in turn produce antibodies (specialized proteins that protect against invasion by foreign substances). The red pulp filters the blood, removing unwanted material. The red pulp contains other white blood cells called phagocytes that ingest microorganisms, such as bacteria, fungi, and viruses. It also monitors red blood cells, destroying those that are abnormal or too old or damaged to function properly. In addition, the red pulp serves as a reservoir for different elements of the blood, especially white blood cells and platelets (cell-like particles involved in clotting). However, releasing these elements is a minor function of the red pulp.

Overactive bladder syndrome is common. Symptoms include an urgent feeling to go to the toilet, going to the toilet frequently and sometimes leaking urine before you can get to the toilet (urge incontinence). Treatment with bladder training often cures the problem. Sometimes medication may be advised in addition to bladder training to relax the bladder.
The urinary bladder is a hollow muscular organ that collects urine from the kidneys before disposal by urination. A hollow muscular, and distensible (or elastic) organ, the bladder sits on the pelvic floor. Urine enters the bladder via the ureters and exits via the urethra.
Pelvic ureter. The ureter enters the pelvis, where it crosses anteriorly to the iliac vessels, which usually occurs at the bifurcation of the common iliac artery into the internal and external iliac arteries. Here, the ureters are within 5 cm of one another before they diverge laterally.
To remove a smaller stone in your ureter or kidney, your doctor may pass a thin lighted tube (ureteroscope) equipped with a camera through your urethra and bladder to your ureter. Once the stone is located, special tools can snare the stone or break it into pieces that will pass in your urine.
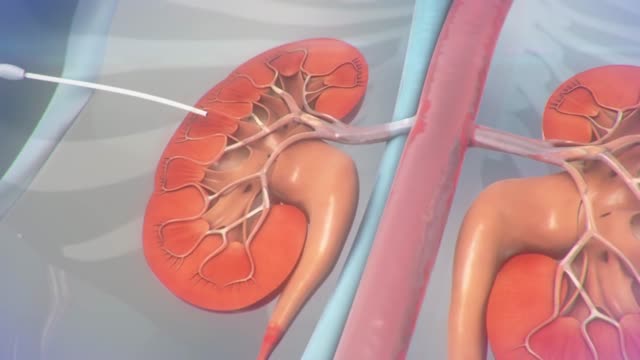
A ureteral stent is a thin, hollow tube that is placed in the ureter to help urine pass from the kidney into the bladder. Ureters are the tubes that connect the kidneys to the bladder. You may have a small amount of blood in your urine for 1 to 3 days after the procedure.

A ventricular septal defect (VSD) is an opening or hole in the wall that separates the two lower chambers of the heart. This wall is called the ventricular septum. The hole causes oxygen-rich blood to leak from the left side of the heart to the right side. This causes extra work for the right side of the heart, since more blood than necessary is flowing through the right ventricle to the lungs. The hole is usually closed with surgery. However, in certain situations, your child's cardiologist and surgeon may think it is best to close the hole with a special device. This procedure is done in the heart catheterization lab.
A ventricular septal defect (VSD) is an opening or hole in the wall that separates the two lower chambers of the heart. This wall is called the ventricular septum. The hole causes oxygen-rich blood to leak from the left side of the heart to the right side. This causes extra work for the right side of the heart, since more blood than necessary is flowing through the right ventricle to the lungs.
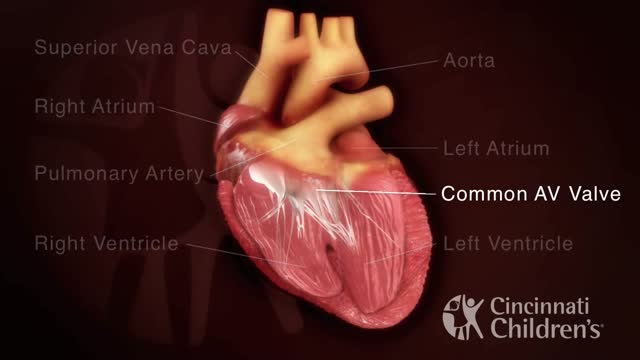
An atrioventricular septal defect (AVSD) is a heart defect in which there are holes between the chambers of the right and left sides of the heart, and the valves that control the flow of blood between these chambers may not be formed correctly
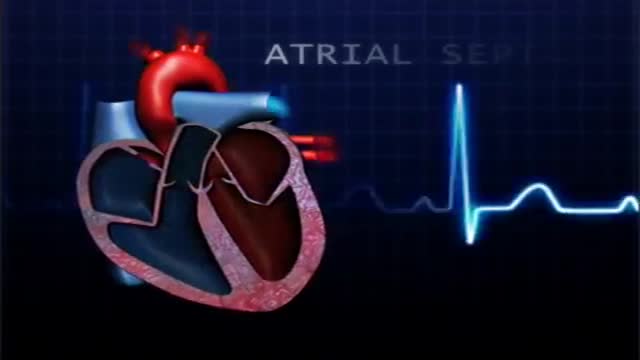
atrial septal defect (ASD) is a hole in the wall between the two upper chambers of your heart (atria). The condition is present from birth (congenital). Small atrial septal defects may close on their own during infancy or early childhood. Large and long-standing atrial septal defects can damage your heart and lungs. Small defects may never cause a problem and may be found incidentally. An adult who has had an undetected atrial septal defect for decades may have a shortened life span from heart failure or high blood pressure that affects the arteries in the lungs (pulmonary hypertension). Surgery may be necessary to repair atrial septal defects to prevent complications
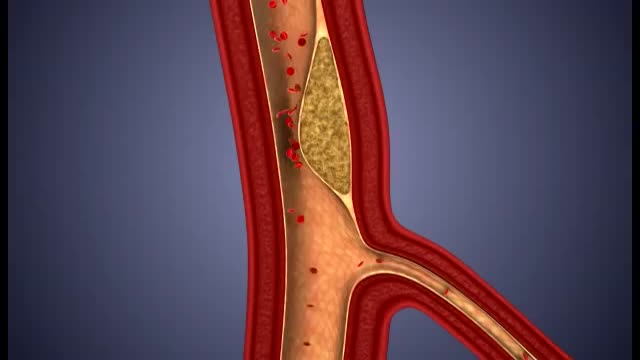
What damage does atherosclerosis cause? Plaque may partially or totally block the blood's flow through an artery in the heart, brain, pelvis, legs, arms or kidneys. Some of the diseases that may develop as a result of atherosclerosis include coronary heart disease, angina (chest pain), carotid artery disease, peripheral artery disease (PAD) and chronic kidney disease.

It is a specialized bodily fluid that supplies essential substances and nutrients, such as sugar, oxygen, and hormones to our cells, and carries waste away from those cells, this waste is eventually flushed out of the body in urine, feces, sweat, and lungs (carbon dioxide). Blood also contains clotting agents.

Blood type (or blood group) is determined, in part, by the ABO blood group antigens present on red blood cells. A blood type (also called a blood group) is a classification of blood based on the presence or absence of inherited antigenic substances on the surface of red blood cells (RBCs).

A central venous catheter, also called a central line, is a long, thin, flexible tube used to give medicines, fluids, nutrients, or blood products over a long period of time, usually several weeks or more. A catheter is often inserted in the arm or chest through the skin into a large vein.

There are two main purposes of an arterial line. Firstly when patients are very sick an arterial line is inserted to provide constant monitoring and recording of the patient's blood pressure. Secondly some patients require frequent blood tests and the arterial line provides easy access to a patient's blood.