Últimos vídeos

The lumps may be hard or rubbery and can appear as a single breast lump that may be large or small. Fibrocystic changes also can appear as thickening of the breast tissue. Fibrocystic changes can occur in one or both breasts and are the most common cause of benign breast lumps in women age 35 to 50.

Breast lumps facts Breast lumps can be caused by infections, injuries, non-cancerous growths, and cancer. Breast cancer usually causes no pain in the breast. The symptoms of breast cancer include painless breast lumps, nipple discharge, and inflammation of the skin of the breast. The chances that a particular breast lump could be cancerous depends on many factors, including past medical history, physical examination, as well as genetic and other risk factors. The only way to be certain that a lump is not cancerous is to have a tissue sampling (biopsy). There are several ways to do the biopsy. The treatment of a breast lump depends on its cause.
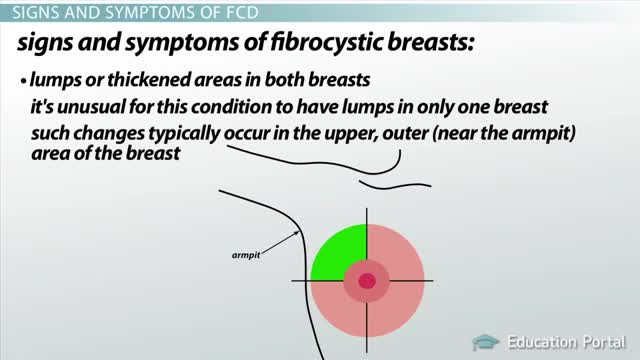
Fibrocystic breasts are composed of tissue that feels lumpy or rope-like in texture. Doctors call this nodular or glandular breast tissue. It's not at all uncommon to have fibrocystic breasts. More than half of women experience fibrocystic breast changes at some point in their lives. In fact, medical professionals have stopped using the term "fibrocystic breast disease" and now simply refer to "fibrocystic breasts" or "fibrocystic breast changes" because having fibrocystic breasts isn't really a disease. Breast changes categorized as fibrocystic are considered normal. Although many women with fibrocystic breasts don't have symptoms, some women experience breast pain, tenderness and lumpiness — especially in the upper, outer area of the breasts. Breast symptoms tend to be most bothersome just before menstruation. Simple self-care measures can usually relieve discomfort associated with fibrocystic breasts.
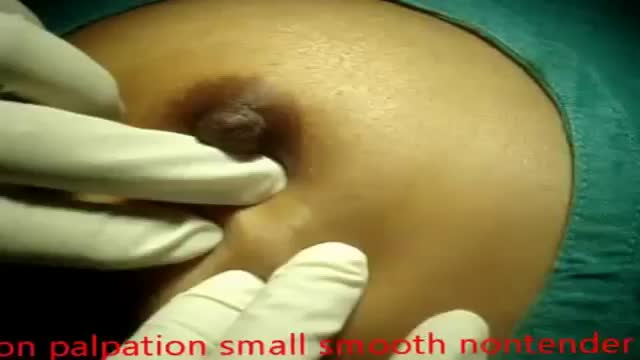
Fibroadenomas (fy-broe-ad-uh-NO-muhz) are solid, noncancerous breast tumors that occur most often in adolescent girls and women under the age of 30. You might describe a fibroadenoma as firm, smooth, rubbery or hard with a well-defined shape. Usually painless, a fibroadenoma might feel like a marble in your breast, moving easily under your skin when touched. Fibroadenomas vary in size, and they can get bigger or even shrink on their own. Fibroadenomas are among the most common breast lumps in young women. Treatment may include monitoring to detect changes in the size or feel of the fibroadenoma, a biopsy to evaluate the lump, or surgery to remove it.
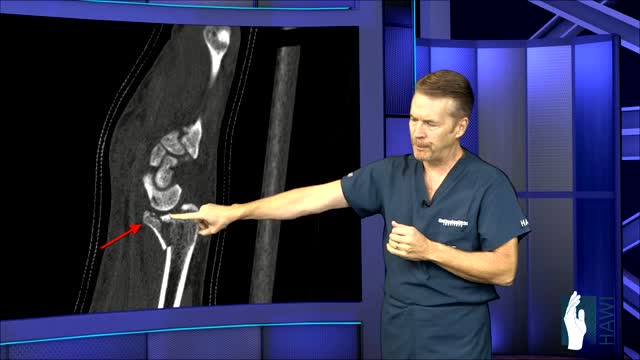
A distal radius fracture almost always occurs about 1 inch from the end of the bone. The break can occur in many different ways, however. One of the most common distal radius fractures is a Colles fracture, in which the broken fragment of the radius tilts upward. This fracture was first described in 1814 by an Irish surgeon and anatomist, Abraham Colles -- hence the name "Colles" fracture.
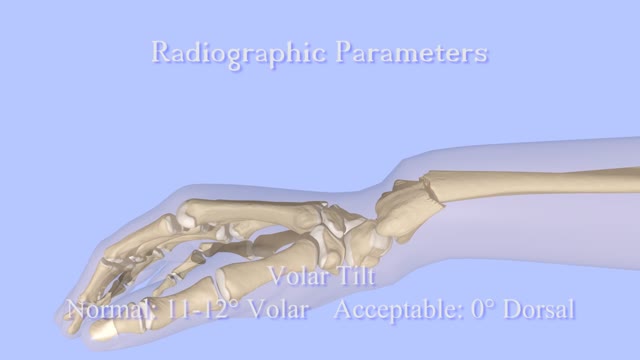
Closed Reduction of Distal Radius Fractures - Discussion: (distal radius fracture menu) - closed reduction & immobilization in plaster cast remains accepted method of treatment for majority of stable distal radius frx; - unstable fractures will often lose reduction in the cast and will slip back to the pre-reduction position; - patients should be examined for carpal tunnel symptoms before and after reduction; - carpal tunnel symptoms that do not resolve following reduction will require carpal tunnel release; - cautions: - The efficacy of closed reduction in displaced distal radius fractures. - Technique: - anesthesia: (see: anesthesia menu) - hematoma block w/ lidocaine; - w/ hematoma block surgeon should look for "flash back" of blood from hematoma, prior to injection; - references: - Regional anesthesia preferable for Colles' fracture. Controlled comparison with local anesthesia. - Neurological complications of dynamic reduction of Colles' fractures without anesthesia compared with traditional manipulation after local infiltration anesthesia. - methods of reduction: - Jones method: involves increasing deformity, applying traction, and immobilizing hand & wrist in reduced position; - placing hand & wrist in too much flexion (Cotton-Loder position) leads to median nerve compression & stiff fingers; - Bohler advocated longitudinal traction followed by extension and realignment; - consider hyper-extending the distal fragment, and then translating it distally (while in extended position) until it can be "hooked over" proximal fragment; - subsequently, the distal fragment can be flexed (or hinged) over the proximal shaft fragment; - closed reduction of distal radius fractures is facilitated by having an assistant provide counter traction (above the elbow) while the surgeon controls the distal fragment w/ both hands (both thumbs over the dorsal surface of the distal fragment); - flouroscopy: - it allows a quick, gentle, and complete reduction; - prepare are by prewrapping the arm w/ sheet cotton and have the plaster or fibroglass ready; - if flouroscopy is not available, then do not pre-wrap the extremity w/ cotton; - it will be necessary to palpate the landmarks (outer shaped of radius, radial styloid, and Lister's tubercle, in order to judge success of reduction; - casting: - generally, the surgeon will use a pre-measured double sugar sugar tong splint, which is 6-8 layers in thickness; - more than 8 layers of plaster can cause full thickness burns: - reference: Setting temperatures of synthetic casts. - position of immobilization - follow up: - radiographs: - repeat radiographs are required weekly for 2-3 weeks to ensure that there is maintenance of the reduction; - a fracture reduction that slips should be considered to be unstable and probably require fixation with (pins, or ex fix ect.) - there is some evidence that remanipulation following fracture displacement in cast is not effective for these fractures; - ultimately, whether or not a patient is satisfied with the results of non operative treatment depends heavily on th

Pancreatic cysts are saclike pockets of fluid on or in your pancreas, a large organ behind the stomach that produces hormones and enzymes that help digest food. Most pancreatic cysts aren't cancerous, and many don't cause symptoms. They're typically found during imaging testing for another problem. Some are actually noncancerous (benign) pockets of fluids lined with scar or inflammatory tissue, not the type of cells found in true cysts (pseudocysts). But some pancreatic cysts can be or can become cancerous. Your doctor might take a sample of the pancreatic cyst fluid to determine if cancer cells are present. Or your doctor might recommend monitoring a cyst over time for changes that indicate cancer.

Epididymitis is infection or less frequently, inflammation of the epididymis (the coiled tube on the back of the testicle). The majority of men that develop epididymitis develop it because of a bacterial infection. Although males of any age can develop epididymitis, it occurs most frequently between ages of 20 to 39.

Testicular torsion occurs when a testicle rotates, twisting the spermatic cord that brings blood to the scrotum. The reduced blood flow causes sudden and often severe pain and swelling. Testicular torsion is most common between ages 12 and 16, but it can occur at any age, even before birth. Testicular torsion usually requires emergency surgery. If treated quickly, the testicle can usually be saved. But when blood flow has been cut off for too long, a testicle might become so badly damaged that it has to be removed.
Pruritis is itchy skin that makes you want to scratch. It can be caused by many things. Normally, itchy skin isn't serious, but it can make you uncomfortable. Sometimes, itchy skin is caused by a serious medical condition. It can occur in association with a primary rash (e.g. dermatitis) or may occur because of hypersensitive nerves in the skin (neuropathic pruritus). ... Scratching a localised itch may lead to lichen simplex, prurigo or prurigo nodularis. Systemic causes of pruritus. Sytemic diseases may cause generalised pruritus.

The long-standing answer has been that sneezing is a reflex. When irritants — such as germs, dust, pollen, animal dander, or pollutants, just to name just a few — infiltrate the nose lining, the brain sends out a signal to get rid of it. That triggers a deep breath, which gets held in the lungs.

Hodgkin's lymphoma — formerly known as Hodgkin's disease — is a cancer of the lymphatic system, which is part of your immune system. In Hodgkin's lymphoma, cells in the lymphatic system grow abnormally and may spread beyond the lymphatic system. As Hodgkin's lymphoma progresses, it compromises your body's ability to fight infection. Hodgkin's lymphoma is one of two common types of cancers of the lymphatic system. The other type, non-Hodgkin's lymphoma, is far more common. Advances in diagnosis and treatment of Hodgkin's lymphoma have helped give people with this diagnosis the chance for a full recovery. The prognosis continues to improve for people with Hodgkin's lymphoma.

Non-Hodgkin's lymphoma, also called non-Hodgkin lymphoma, is cancer that originates in your lymphatic system, the disease-fighting network spread throughout your body. In non-Hodgkin's lymphoma, tumors develop from lymphocytes — a type of white blood cell. Non-Hodgkin's lymphoma is more common than the other general type of lymphoma — Hodgkin lymphoma. Many different subtypes of non-Hodgkin's lymphoma exist. The most common non-Hodgkin's lymphoma subtypes include diffuse large B-cell lymphoma and follicular lymphoma.

Arthritis is inflammation of one or more of your joints. The main symptoms of arthritis are joint pain and stiffness, which typically worsen with age. The most common types of arthritis are osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis. Osteoarthritis causes cartilage — the hard, slippery tissue that covers the ends of bones where they form a joint — to break down. Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disorder that first targets the lining of joints (synovium). Uric acid crystals, infections or underlying disease, such as psoriasis or lupus, can cause other types of arthritis. Treatments vary depending on the type of arthritis. The main goals of arthritis treatments are to reduce symptoms and improve quality of life.

Fibromyalgia syndrome (FMS) is a form of fibromyalgia where pain and stiffness occurs in muscles, tendons, and ligaments throughout the body, accompanied by other generalized symptoms such as fatigue, sleep disruption or unrefreshing sleep, mood disorder, and cognitive difficulties such as poor memory or mental ...
Memory Loss & the Brain. It's not just a movement disorder. Besides causing tremors and other motion-related symptoms, Parkinson's disease affects memory, learning, and behavior. Parkinson's disease is notorious for so-called motor symptoms like muscle rigidity, tremor, slowed movement, and unsteady posture and gait.

The arm and leg muscles are affected later. Myasthenia gravis (MG) is an autoimmune disease — a disease that occurs when the immune system attacks the body's own tissues. In MG, that attack interrupts the connection between nerve and muscle — the neuromuscular junction.
Myasthenia gravis is a chronic autoimmune neuromuscular disease characterized by varying degrees of weakness of the skeletal (voluntary) muscles of the body. The name myasthenia gravis, which is Latin and Greek in origin, literally means "grave muscle weakness."
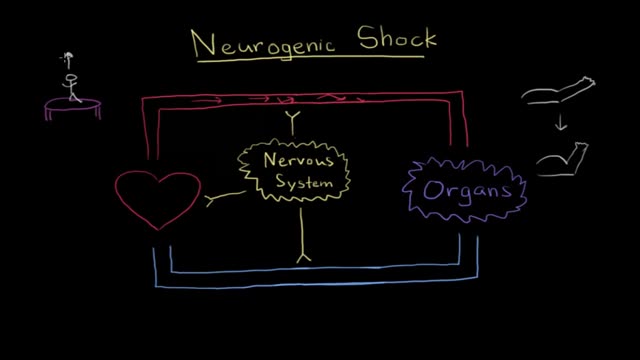
Neurogenic shock is a distributive type of shock resulting in low blood pressure, occasionally with a slowed heart rate, that is attributed to the disruption of the autonomic pathways within the spinal cord. It can occur after damage to the central nervous system such as spinal cord injury.
Anaphylaxis is a severe, potentially life-threatening allergic reaction. It can occur within seconds or minutes of exposure to something you're allergic to, such as a peanut or the venom from a bee sting. The flood of chemicals released by your immune system during anaphylaxis can cause you to go into shock; your blood pressure drops suddenly and your airways narrow, blocking normal breathing. Signs and symptoms of anaphylaxis include a rapid, weak pulse, a skin rash, and nausea and vomiting. Common triggers of anaphylaxis include certain foods, some medications, insect venom and latex. Anaphylaxis requires an immediate trip to the emergency department and an injection of epinephrine. If anaphylaxis isn't treated right away, it can lead to unconsciousness or even death.

