Latest videos
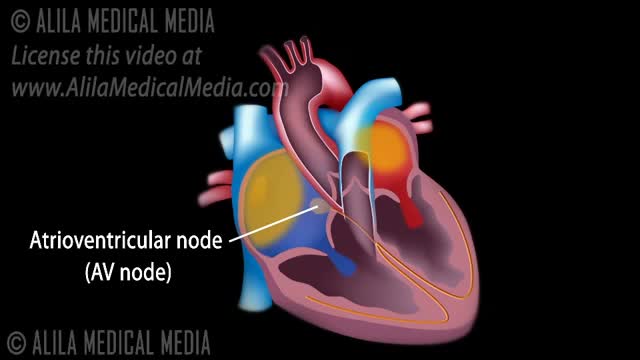
The normal electrical conduction in the heart allows the impulse that is generated by the sinoatrial node (SA node) of the heart to be propagated to (and stimulate) the cardiac muscle (myocardium). The myocardium contracts after stimulation.

Ear irrigation is a routine procedure used to remove excess earwax, called cerumen, or foreign materials from the ear. The ear naturally secretes earwax to protect, lubricate, keep debris out, and regulate bacterial growth. Under normal conditions, the body keeps the amount of earwax in the ears .
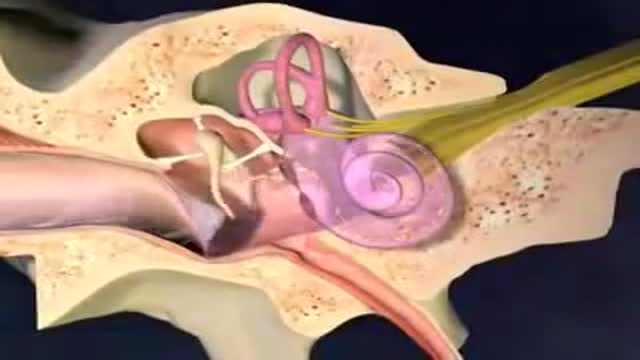
Acute otitis media: Inflammation of the middle ear in which there is fluid in the middle ear accompanied by signs or symptoms of ear infection: a bulging eardrum usually accompanied by pain; or a perforated eardrum, often with drainage of purulent material (pus).

If severe, it can eventually lead to cirrhosis and liver failure. How would you know if you have a fatty liver? ... Luckily fatty liver is reversible. ... Eat less carbohydrate. ... Drink less alcohol. ... Eat more vegetables, protein and the right fats. ... Drink raw vegetable juices. ... Take a good liver tonic.

Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is a very common disorder and refers to a group of conditions where there is accumulation of excess fat in the liver of people who drink little or no alcohol. The most common form of NAFLD is a non serious condition called fatty liver.

Uncontrolled hyperthyroidism during pregnancy can lead to serious health problems in the mother and the unborn baby. During pregnancy, mild hyperthyroidism does not require treatment. More severe hyperthyroidism is treated with antithyroid medications, which act by interfering with thyroid hormone production.

Thyroiditis is a general term that refers to “inflammation of the thyroid gland”. Thyroiditis includes a group of individual disorders causing thyroidal inflammation but presenting in different ways. For example, Hashimoto’s thyroiditis is the most common cause of hypothyroidism in the United States. Postpartum thyroiditis, which causes temporary thyrotoxicosis (high thyroid hormone levels in the blood) followed by temporary hypothyroidism, is a common cause of thyroid problems after the delivery of a baby. Subacute thyroiditis is the major cause of pain in the thyroid. Thyroiditis can also be seen in patients taking the drugs interferon and amiodarone.

Your body's immune system protects you from disease and infection. But if you have an autoimmune disease, your immune system attacks healthy cells in your body by mistake. Autoimmune diseases can affect many parts of the body. No one is sure what causes autoimmune diseases. They do tend to run in families. Women - particularly African-American, Hispanic-American, and Native-American women - have a higher risk for some autoimmune diseases. There are more than 80 types of autoimmune diseases, and some have similar symptoms. This makes it hard for your health care provider to know if you really have one of these diseases, and if so, which one. Getting a diagnosis can be frustrating and stressful. Often, the first symptoms are fatigue, muscle aches and a low fever. The classic sign of an autoimmune disease is inflammation, which can cause redness, heat, pain and swelling. The diseases may also have flare-ups, when they get worse, and remissions, when symptoms get better or disappear. Treatment depends on the disease, but in most cases one important goal is to reduce inflammation. Sometimes doctors prescribe corticosteroids or other drugs that reduce your immune response.
Autoimmune hepatitis is liver inflammation that occurs when your body's immune system turns against liver cells. The exact cause of autoimmune hepatitis is unclear, but genetic and environmental factors appear to interact over time in triggering the disease. Untreated autoimmune hepatitis can lead to scarring of the liver (cirrhosis) and eventually to liver failure. When diagnosed and treated early, however, autoimmune hepatitis often can be controlled with drugs that suppress the immune system. A liver transplant may be an option when autoimmune hepatitis doesn't respond to drug treatments or when liver disease is advanced.

Fulminant hepatic failure (FHF) or acute liver failure (ALF) is defined as the rapid development of acute liver injury with severe impairment of the synthetic function and hepatic encephalopathy in a patient without obvious, previous liver disease.
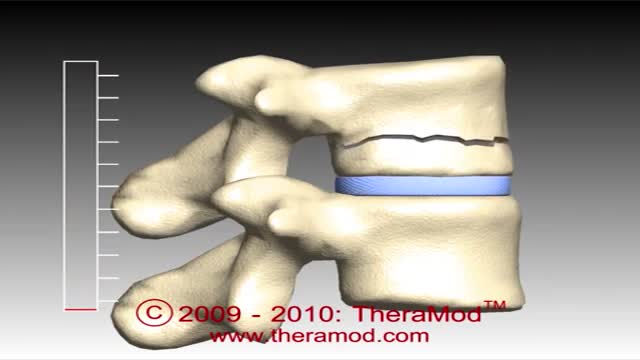
The vertebrae are the bony building blocks of the spine. Between each of the largest parts (bodies) of the vertebrae are the discs. Ligaments are situated around the spine and discs. The spine has seven vertebrae in the neck (cervical vertebrae), 12 vertebrae in the mid-back (thoracic vertebrae), and five vertebrae in the low back (lumbar vertebrae). In addition, in the mid-buttock, beneath the fifth lumbar vertebra, is the sacrum, followed by the tailbone (coccyx).

How to Use Wash your hands. Check the drug label to be sure it is what your doctor prescribed. ... Remove pen cap. Look at the insulin. Wipe the tip of the pen where the needle will attach with an alcohol swab or a cotton ball moistened with alcohol.

Insert the needle into the rubber stopper of the insulin bottle. Push the plunger down to inject air into the bottle (this allows the insulin to be drawn more easily). Leave the needle in the bottle. Turn the bottle and syringe upside-down.
This short course reviews the main features of EKG tracings. A method for analyzing EKGs is also presented. This method includes assessment of rhythm, calculating heart rate, observing P-wave forms, measurement of EKG intervals and segments and the evaluation of other relevant waves.
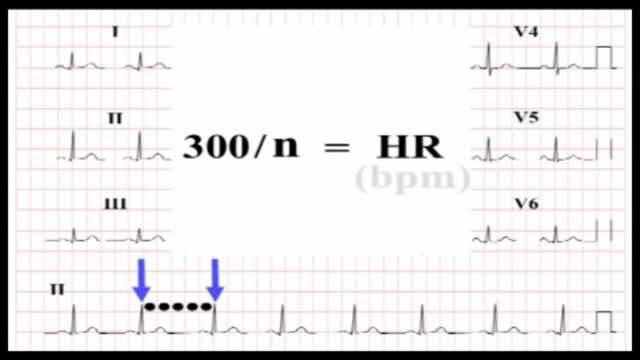
Basic ECG Interpretation Our ECG Interpretation Training and Reference Guides provide basic lessons for ECG analysis as well as a quick reference guide for over 40 types of ECG tracings. The arrhythmia drills and quizzes allow you to practice ECG interpretation. What is ECG Interpretation? An electrocardiogram or ECG, records electrical activity in the heart. An ECG machine records these electrical signals across multiple heart beats and produces an ECG strip that is interpreted by a healthcare professional. How Electrocardiograms Work - ECG Strips To briefly summarize the components of a normal ECG tracings, it consist of waveform components which indicate electrical events during one heart beat. These waveforms are labeled P, Q, R, S, T and U. P wave is the first short upward movement of the ECG tracing. It indicates that the atria are contracting, pumping blood into the ventricles. The QRS complex, normally beginning with a downward deflection, Q; a larger upwards deflection, a peak (R); and then a downwards S wave. The QRS complex represents ventricular depolarization and contraction. The PR interval indicates the transit time for the electrical signal to travel from the sinus node to the ventricles. T wave is normally a modest upwards waveform representing ventricular repolarization. ECG Interpretation illustration spacer image ECG Training - Introduction The focus of this introductory ECG course is to provide a tutorial about the main features of ECGs along with a method for analyzing ECGs. This method includes assessment of rhythm, calculating heart rate, observing P-wave forms, measurement of intervals and segments and the evaluation of other relevant waves. ECG practice exercises serve to reinforce the lesson content.

The 12-lead ECG is a vital tool for EMT’s and paramedics in both the prehospital and hospital setting. It is extremely important to know the exact placement of each electrode on the patient. Incorrect placement can lead to a false diagnosis of infarction or negative changes on the ECG.

Invasive intracranial pressure monitoring. The most common surgically placed monitors for ICP measurement are intraventricular catheters (external ventricular drain [EVD] or a ventriculostomy drain) and fiberoptic ICP monitors implanted into the parenchyma of the brain.
Good abdominal wall closure is one of the basic surgical skills and is a common feature of almost all modern-day CSF shunt operations. The fact that some patients require multiple abdominal operations highlights the need for a simple and effective technique for peritoneal catheter insertion through the abdominal wall and abdominal wall closure. Although technically simple, abdominal wall closure becomes more complex when combined with the requirement to maintain CSF shunt function in cases in which the shunt catheter passes through the abdominal wall into the peritoneal cavity. In this report, the authors describe a simple technique for passing the peritoneal catheter of a ventriculoperitoneal shunt through the abdominal wall on a pathway separate from the fascial opening. This technique minimizes the risk of abdominal wall-related complications and is especially important in high-risk patients such as those with obesity and/or diabetes and in children.
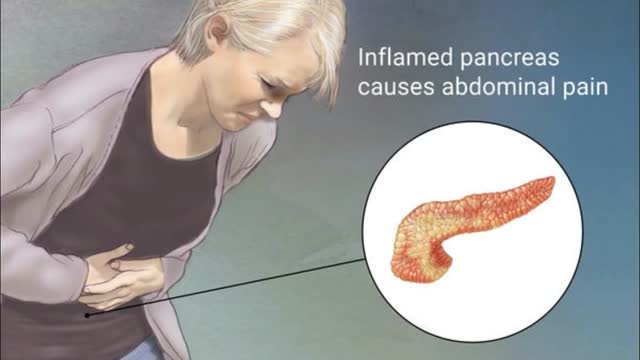
Pancreatitis is inflammation of the pancreas. The pancreas is a large gland behind the stomach and close to the duodenum—the first part of the small intestine. The pancreas secretes digestive juices, or enzymes, into the duodenum through a tube called the pancreatic duct. Pancreatic enzymes join with bile—a liquid produced in the liver and stored in the gallbladder—to digest food. The pancreas also releases the hormones insulin and glucagon into the bloodstream. These hormones help the body regulate the glucose it takes from food for energy. Normally, digestive enzymes secreted by the pancreas do not become active until they reach the small intestine. But when the pancreas is inflamed, the enzymes inside it attack and damage the tissues that produce them. Pancreatitis can be acute or chronic. Either form is serious and can lead to complications. In severe cases, bleeding, infection, and permanent tissue damage may occur.
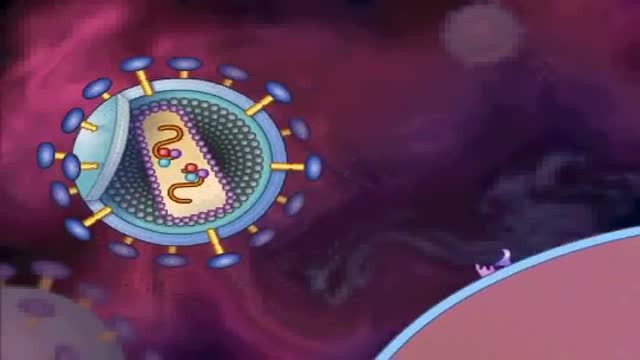
HIV stands for human immunodeficiency virus. If left untreated, HIV can lead to the disease AIDS (acquired immunodeficiency syndrome). Unlike some other viruses, the human body can’t get rid of HIV completely. So once you have HIV, you have it for life. HIV attacks the body’s immune system, specifically the CD4 cells (T cells), which help the immune system fight off infections. If left untreated, HIV reduces the number of CD4 cells (T cells) in the body, making the person more likely to get infections or infection-related cancers. Over time, HIV can destroy so many of these cells that the body can’t fight off infections and disease. These opportunistic infections or cancers take advantage of a very weak immune system and signal that the person has AIDS, the last state of HIV infection. No effective cure for HIV currently exists, but with proper treatment and medical care, HIV can be controlled. The medicine used to treat HIV is called antiretroviral therapy or ART. If taken the right way, every day, this medicine can dramatically prolong the lives of many people with HIV, keep them healthy, and greatly lower their chance of transmitting the virus to others. Today, a person who is diagnosed with HIV, treated before the disease is far advanced, and stays on treatment can live a nearly as long as someone who does not have HIV.

