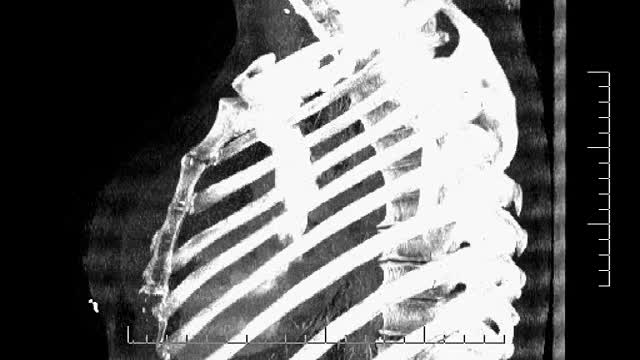
سرفہرست ویڈیوز

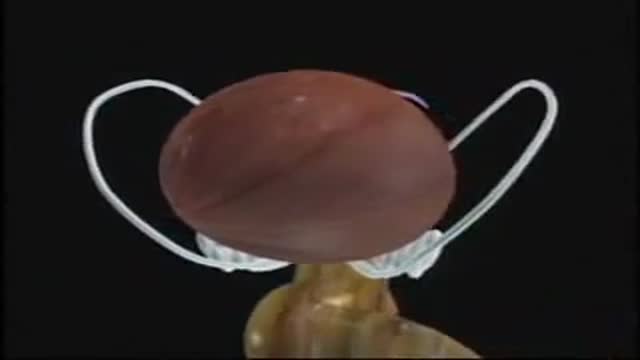
A visual prosthesis, often referred to as a bionic eye, is an experimental visual device intended to restore functional vision in those suffering from partial or total blindness. In 1983 Joao Lobo Antunes, a Portuguese doctor, implanted a bionic eye in a person born blind.

When food is taken, it is broken down into smaller components. Sugars and carbohydrates are thus broken down into glucose for the body to utilize them as an energy source. The liver is also able to manufacture glucose. In normal persons the hormone insulin, which is made by the beta cells of the pancreas, regulates how much glucose is in the blood. When there is excess of glucose in blood, insulin stimulates cells to absorb enough glucose from the blood for the energy that they need. Insulin also stimulates the liver to absorb and store any excess glucose that is in the blood. Insulin release is triggered after a meal when there is a rise in blood glucose. When blood glucose levels fall, during exercise for example, insulin levels fall too. High insulin will promote glucose uptake, glycolysis (break down of glucose), and glycogenesis (formation of storage form of glucose called glycogen), as well as uptake and synthesis of amino acids, proteins, and fat. Low insulin will promote gluconeogenesis (breakdown of various substrates to release glucose), glycogenolysis (breakdown of glycogen to release gluose), lipolysis (breakdown of lipids to release glucose), and proteolysis (breakdown of proteins to release glucose). Insulin acts via insulin receptors.
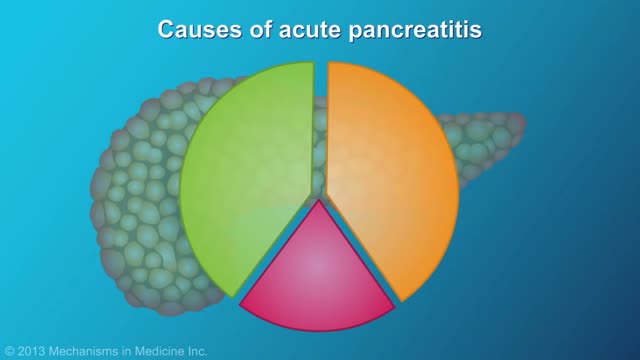
Pancreatitis is inflammation in the pancreas. The pancreas is a long, flat gland that sits tucked behind the stomach in the upper abdomen. The pancreas produces enzymes that assist digestion and hormones that help regulate the way your body processes sugar (glucose). Pancreatitis can occur as acute pancreatitis — meaning it appears suddenly and lasts for days. Or pancreatitis can occur as chronic pancreatitis, which describes pancreatitis that occurs over many years. Mild cases of pancreatitis may go away without treatment, but severe cases can cause life-threatening complications.
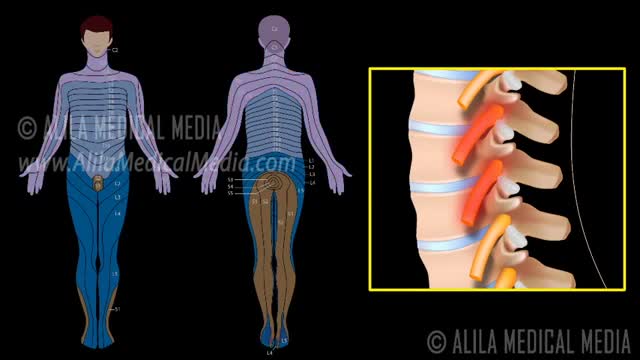
A nerve root block is an injection of local anesthetic (numbing medicine) and steroid injected under X-ray guidance into the area where the nerve exits the spinal column. A nerve root block is usually ordered by your doctor for pain in the arm or leg that follows the path of a single nerve. A nerve root block may be diagnostic (a test to determine the source of your pain) and/or therapeutic (to relieve your pain). If you get a period of sustained pain relief from the injection, the block may be repeated. Sometimes the block is done to help identify whether or not surgery might be helpful and at what level such surgery might be most helpful.
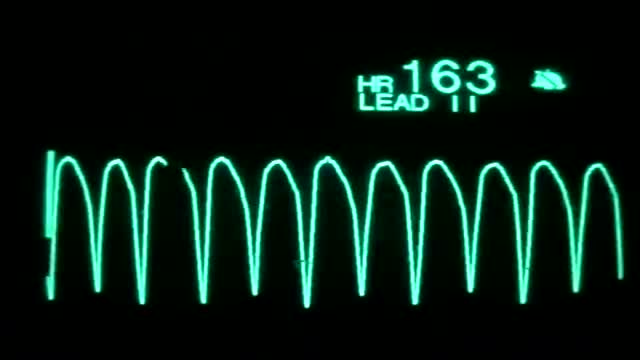
On the rhythm strip, the QRS might be somewhat taller or wider. One commonly seen type of polymorphic ventricular tachycardia is torsades de pointes. Torsades and other polymorphic VT are advanced rhythms which require additional expertise and expert consultation is advised.
Sickle cell anemia (sickle cell disease) is a disorder of the blood caused by an inherited abnormal hemoglobin (the oxygen-carrying protein within the red blood cells). The abnormal hemoglobin causes distorted (sickled) red blood cells.