Top videos
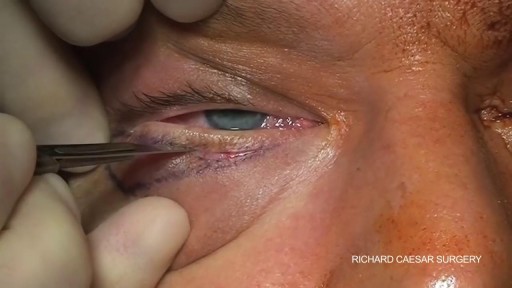
Many people have baggy and puffy lower eyelids. Lower Eyelid Surgery (Blepharoplasty) is the removal of excess fat and tightening of the skin, which can drastically minimize the appearance of baggy and puffy lower eyelids that makes everyone look tired and worn down. This procedure is just as popular with men as with women. A sense of well-being and alertness is the reason why most people elect to have this procedure. Lower lids surgery is a procedure that the best results are achieved when performed earlier than later. Dr. Lee has performed this surgery on patients who are 18 yrs old to 82 yrs old- all very happy with their results. The cause of baggy and puffy lower eyelid is due to a combination of herniating fat, excessive skin, and edema (water retention).
surgical procedure used to remove excess skin and fat from the abdomen and to tighten the muscles of the abdominal wall. Most tummy tuck patients are dealing with the effects of pregnancies and weight loss and find themselves with loose skin in spite of exercise and weight control. Each year, thousands of Americans undergo a tummy tuck to tone, firm and define the abdominal area.

Cases of some sexually transmitted diseases have reached an all-time high, according to a new report from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. From 2014 to 2015, there was a 6% increase in diagnosed cases of chlamydia and a 13% increase in gonorrhea.

1. What is hemodialysis?
2. Why do you do hemodialysis?
3. How does hemodialysis remove body waste?
4. What are the symptoms and side effects of hemodialysis?
5. How should I eat food when I do hemodialysis?
6. What are some precautions for patients during hemodialysis?
► If you have any health issues contact us anytime, we here to help at CloudHospital – https://icloudhospital.com/
► Subscribe: https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCmk5... to learn more about various health and beauty topics.
► Find us on Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/icloudhospital/
► On Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/cloudhospit...
► On LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/company/clou...
► On Twitter: https://twitter.com/CloudhospitalI
#hemodialysis #cloudhospital #koreahospital

Cathy covers hemodialysis, including nursing care before, during, and after the procedure. Peritoneal dialysis, including nursing associated with the procedure. Key complications of hemodialysis, including disequilibrium syndrome and hypotension. Peritonitis, which is a key complication of peritoneal dialysis. Post-op nursing care and patient teaching associated with a kidney transplant.
Our Medical-Surgical video tutorial series is taught by Cathy Parkes BSN, RN, CWCN, PHN and intended to help RN and PN nursing students study for their nursing school exams, including the ATI, HESI and NCLEX.
#NCLEX #KidneyTransplant #HESI #Kaplan #ATI #NursingSchool #NursingStudent #Nurse #RN #PN #Education #LVN #LPN #Renal #Hemodialysis
0:00 What to Expect
0:31 Hemodialysis
2:06 Nursing Care
2:47 Peritoneal Dialysis
3:23 Nursing Care
4:09 Dialysis Complications
4:19 Disequilibrium Syndrome
4:55 Hypotension
5:26 Peritonitis
5:57 Kidney Transplant
6:17 Nursing Care
6:40 Signs and Symptoms
6:51 Patient Teaching
7:17 Quiz Time!
8:27 Bloopers
🚨Head over to our interactive study guide and index ANYTIME and find out exactly which card we’re referencing. https://bit.ly/MedSurgIndex
🚨 Reminder: shipping deadlines are looming 👀
🎁 Regular Shipping: Order by Friday, December 15
🚀 Expedited Shipping: Order by Monday, December 18
🔍 Still searching for last-minute gifts? Consider a Level Up RN Gift Card! 💌 It’s not only a thoughtful present but also the perfect way to share treasures like Pharmacology Flashcards OR digital treasures like Flashables Digital Nursing Flashcards & the Level Up RN membership. Give the gift of knowledge this holiday season! 🧠⚡️💖 bit.ly/LevelUpRNGC
🚪 Access our Cram Courses, Quizzes and Videos all in one ad free space with Level Up RN Membership https://bit.ly/LevelUpRNMembership
Want more ways to MASTER Medical-Surgical Nursing? Check out our flashcards, review games, videos, tips & more!
👇👇👇👇👇👇👇👇👇👇
👉 https://bit.ly/AllMedSurg 👈
☝️👆☝️👆☝️👆☝️👆☝️👆
This is your one-stop-shop for materials to help you LEARN & REVIEW so you can PASS Nursing School.
🤔🤔🤔 DO YOU WANT TO PASS your classes, proctored exams and the NCLEX? 🤔🤔🤔 Our resources are the best you can buy. They are built with a single goal: help you pass with no fluff. Everything you need, and nothing you don’t. Don’t take our word for it, though! Check out our hundreds of ⭐️⭐️⭐️⭐️⭐️ reviews from nurses who passed their exams and the NCLEX with Level Up RN.
🗂️ Our Ultimate Nursing School Survival kit is your number 1 resource to get through nursing school and to pass the NCLEX. Whether you're just starting school or you’re already prepping for the NCLEX, this bundle of flashcards is the best you can buy. It covers all the information you need to know to pass all your exams and it has FREE shipping!
➡️ https://bit.ly/TUNSSK ⬅️
L👀king for EVEN MORE resources to survive Nursing School? Make your Nursing School experience your own! Life’s difficult enough—learning shouldn’t be.
🪅 Games https://nursesquad.com
💻 Digital resources https://bit.ly/NursingStudyCourses
📅 Organizational tools https://bit.ly/OrganizingSchool
✨Want perks? Join our channel!
https://youtube.com/leveluprn/join
🏷 Head to https://leveluprn.com/specials for all our latest deals!🥳️
📧 LOOKING FOR FREE RESOURCES TO HELP WITH YOUR EXAMS? Get exclusive tips, latest video releases and more delivered to your email!
➡️ https://leveluprn.com/signup ⬅️
⚕ 👩 LEVEL UP NURSE SQUAD 👩⚕️
All of the nurses at Level Up RN are here to help! Cathy Parkes started helping her fellow classmates back when she was in nursing school, tutoring so they could pass their exams and graduate. After she got her BSN and started working as an RN at Scripps Encinitas Hospital, she started this YouTube channel to help nursing students around the world. Since then she has built a team of top-notch dedicated nurses and nurse educators who are focused on improving nursing education and supporting career advancement for nurses everywhere. With flashcards, videos, courses, organizational tools and more, we are singularly focused on helping students and nurses Level Up on their exams and nursing careers.
What is vascular access? What are the different types of accesses for hemodialysis? Does vascular access require surgery? Adina Voiculescu, M.D., FASDIN, General and Interventional Nephrologist at Brigham and Women's Hospital and Assistant Professor at Harvard Medical School, discusses the different types of vascular access, such as AV fistulas and AV grafts, and how to stay healthy while on hemodialysis.
Subscribe Link: https://www.youtube.com/channe....l/UCYrLjATd88gPwIKnt
0:00 - Intro
0:29 - Peritoneal dialysis & Hemodialysis
0:44 - Types of access to perform dialysis
1:48 - Recommendations
About Mass General Brigham:
Mass General Brigham combines the strength of two world-class academic medical centers, five nationally ranked specialty hospitals, 11 community hospitals, and dozens of health centers. Our doctors and researchers accelerate medical breakthroughs and drive innovations in patient care. They are leaders in medical education, serving as Harvard Medical School faculty and training the next generation of physicians. Mass General Brigham’s mission is to deliver the best, affordable health care to patients everywhere. Together, we transform the health of our communities and beyond.
#MassGeneralBrigham #MGB #Hemodialysis
Visit Mass General Brigham: https://www.massgeneralbrigham.org/
Find us on social:
Twitter: https://twitter.com/MassGenBrigham
Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/massgeneralbrigham/
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/MassGeneralBrigham/
LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/compa....ny/mass-general-brig
Mass General Brigham:
https://www.youtube.com/massgeneralbrigham
Hemodialysis: Types of Accesses for Kidney Dialysis and How to Stay Healthy | Mass General Brigham
https://youtu.be/_bxLpudpqnc

What is hemodiafiltration? Hemodiafiltration, or HDF, is a renal replacement modality that combines diffusion and convection to improve removal of molecules in the middle molecular weight range versus hemodialysis.
Find our full video library only on Osmosis Prime: http://osms.it/more.
Join over 3 million current & future clinicians who learn by Osmosis, and over 130 universities around the world who partner with us to make medical and health education more engaging and efficient. We have unparalleled tools and materials to prepare you to succeed in school, on board exams, and as a future clinician. Sign up for a free trial at http://osms.it/more. If you're interested in exploring an institutional partnership, visit osmosis.org/educators to request a personalized demo.
Follow us on social:
Facebook: http://osms.it/facebook
Twitter: http://osms.it/twitter
Instagram for med: http://osms.it/instagram
Instagram for nursing: https://osms.it/ignursing
Linkedin: https://osms.it/linkedin
Our Vision: Everyone who cares for someone will learn by Osmosis.
Our Mission: To empower the world’s clinicians and caregivers with the best learning experience possible. Learn more here: http://osms.it/mission
Medical disclaimer: Knowledge Diffusion Inc (DBA Osmosis) does not provide medical advice. Osmosis and the content available on Osmosis's properties (Osmosis.org, YouTube, and other channels) do not provide a diagnosis or other recommendation for treatment and are not a substitute for the professional judgment of a healthcare professional in diagnosis and treatment of any person or animal. The determination of the need for medical services and the types of healthcare to be provided to a patient are decisions that should be made only by a physician or other licensed health care provider. Always seek the advice of a physician or other qualified healthcare provider with any questions you have regarding a medical condition. © 2023 Elsevier. All rights reserved.
Suspect that a patient has a subphrenic abscess if he deteriorates, or recovers and then deteriorates, between the 14th and the 21st day after a laparotomy, with a low, slowly increasing, swinging fever, sweating, and a tachycardia. This, and a leucocytosis, show that he has ''pus somewhere', which is making him anorexic, wasted, and ultimately cachectic. If he has no sign of a wound infection, a rectal examination is negative, and his abdomen is soft and relaxed, the pus is probably under his diaphragm. The pus might be between his diaphragm and his liver, in (1) his right or (2) his left subphrenic space, or under his liver in (3) his right or (4) his left subhepatic space in his lesser sac. He may have pus in more than one of these spaces. Explore him on the suspicion that he might have a subphrenic abscess. Exploration is not a major operation; the difficulty is knowing where to explore, so refer him if you can. If you cannot refer him, explore him yourself. If you fail to find pus, you have done him no harm; missing a subphrenic abscess is far worse. If it is anterior, you can drain it by going under his costal margin anteriorly. If it is posterior, you can go through the bed of his 12th rib posteriorly.
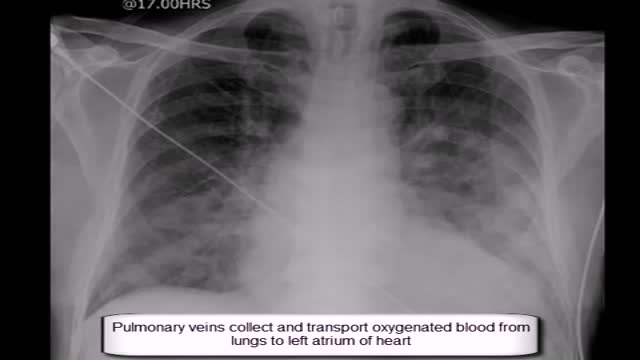
Expand Section. Pulmonary edema is often caused by congestive heart failure. When the heart is not able to pump efficiently, blood can back up into the veins that take blood through the lungs. As the pressure in these blood vessels increases, fluid is pushed into the air spaces (alveoli) in the lungs.
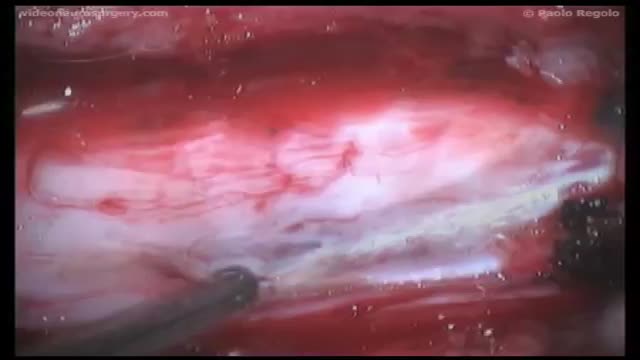
Syringomyelia is a cystic cavitation of the spinal cord associated with Chiari I malformation (70%) or basilar invagination (10%) or tumor. It may be a post-traumatic condition. There are 2 main forms: communicating with the central canal or subarachnoid spaces (Chiari I malformation); non communicating (trauma, tumors).
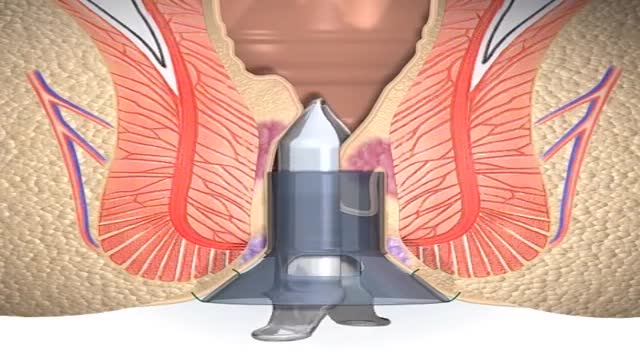
A stapled haemorrhoidopexy is an operation to return the haemorrhoids to a normal. position inside the rectum (back passage). A circular shaped stapling device is gently. inserted in the back passage. The surgeon is then able to use the device to remove.
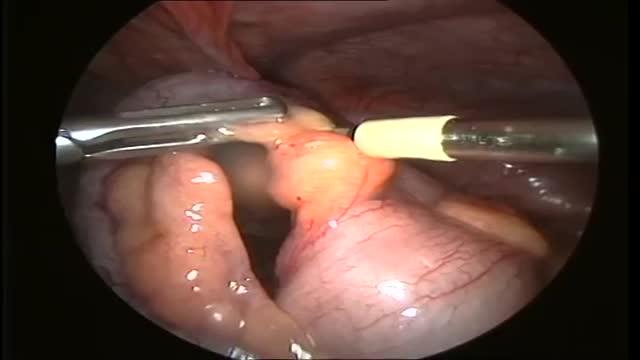
One thing we do know: We can live without it, without apparent consequences. Appendicitis is a medical emergency that requires prompt surgery to remove the appendix. Left untreated, an inflamed appendix will eventually burst, or perforate, spilling infectious materials into the abdominal cavity.
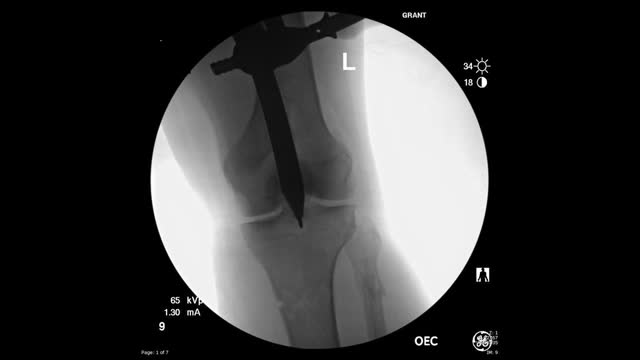
This video shows the technique of suprapatellar tibial nailing as used for a segmental tibia fracture. The broken leg was treated with the nail to allow immediate mobility and range of motion; no cast was needed for this injury.
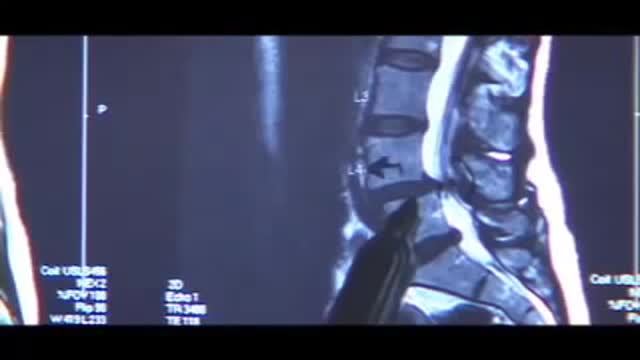
Instead of permanently joining (fusing) vertebrae with metal rods and screws, and therefore restricting movement, the new procedure uses the Anatomic Facet Replacement System (AFRS) device that attaches to each of two adjacent vertebrae with a movable joint that mimics the spine's natural joint.