سرفہرست ویڈیوز
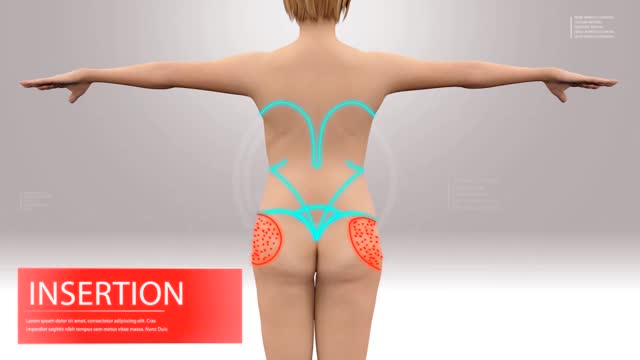
The cause of pectus excavatum is not known however it can run in families, with up to 25 percent of affected patients reporting chest wall abnormalities in other family members. Pectus excavatum occurs in approximately 1 out of 400–1000 children and is three to five times more common in males than females.

The cause of pectus excavatum is not known however it can run in families, with up to 25 percent of affected patients reporting chest wall abnormalities in other family members. Pectus excavatum occurs in approximately 1 out of 400–1000 children and is three to five times more common in males than females.

Interrupted aortic arch (IAA) is the absence or discontinuation of a portion of the aortic arch, the section of the aorta that turns downward toward the lower half of the body. Once the diagnosis of this rare defect is suspected and confirmed, treatment and surgical intervention are vitally important. Heart models and animation were developed by the Cincinn
When you get a kidney transplant, a healthy kidney is placed inside your body to do the work your own kidneys can no longer do. On the plus side, there are fewer limits on what you can eat and drink, but you should follow a heart-healthy diet. Your health and energy should improve. In fact, a successful kidney transplant may allow you to live the kind of life you were living before you got kidney disease. Studies show that people with kidney transplants live longer than those who remain on dialysis. On the minus side, there are the risks of surgery. You will also need to take anti-rejection medicines for as long as your new kidney is working, which can have side effects. You will have a higher risk for infections and certain types of cancer.
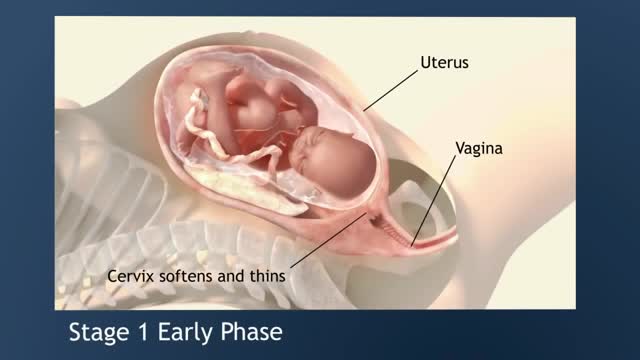
Early labour contractions usually feel like period pain, or you might experience a lower backache at 20 to 30 minute intervals. Sometimes these pains radiate from back to front, or vice versa. There's no need to start timing the contractions straight away – if they are mild contractions, ignore them. The first stage of labor is the longest and involves three phases: Early Labor Phase –The time of the onset of labor until the cervix is dilated to 3 cm. Active Labor Phase – Continues from 3 cm. until the cervix is dilated to 7 cm. Transition Phase – Continues from 7 cm. until the cervix is fully dilated to 10 cm.
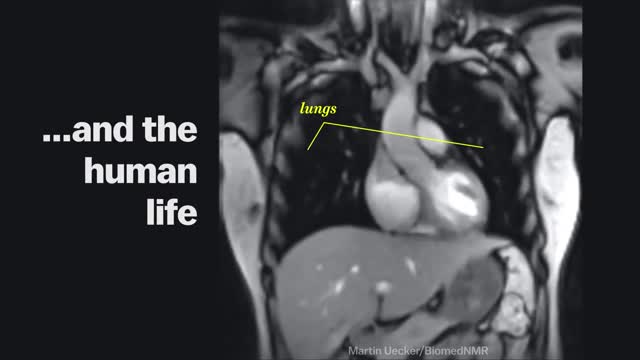
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) "sees" inside the body by mapping the position of water molecules, which exist at different densities in different types of tissue. Watch the video above for a sample of some impressive MRI images of the human body in action.
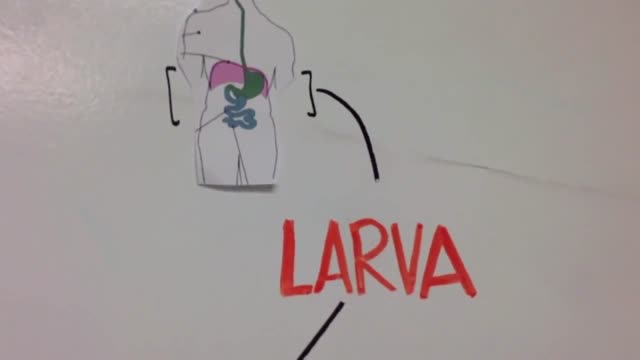
Trichinosis (trik-ih-NO-sis), sometimes called trichinellosis (trik-ih-nuh-LOW-sis), is a type of roundworm infection. Roundworm parasites use a host body to live and reproduce. Occurring primarily among meat-eating animals (carnivores) — especially bears, foxes and walruses — the infection is acquired by eating roundworm larvae in raw or undercooked meat. When humans eat undercooked meat containing trichinella larvae, the larvae mature into adult worms in the intestine over several weeks. The adult worms then produce larvae that travel through various tissues, including muscle. Trichinosis is most widespread in rural areas throughout the world. Trichinosis can be treated with medication, though it's not always necessary. It's also easy to prevent.
Surgery is an alternative for some people whose seizures cannot be controlled by medications. It has been used for more than a century, but its use dramatically increased in the 1980s and 90s, reflecting its effectiveness as an alternative to seizure medicines. The benefits of surgery should be weighed carefully against its risks, however, because there is no guarantee that it will be successful in controlling seizures. People with partial epilepsy who are considered for surgery have difficult-to-control seizures that have not responded to aggressive treatment with medication. In the past, patients usually tried several medications with poor results for many years, even decades, before being considered for surgery. More recently, surgery is being considered sooner. Studies have shown that the earlier surgery is performed, the better the outcome. Surgery is now being performed on some people whose seizures have been uncontrolled for only 1 or 2 years. At least two single drugs and a combination of two or more drugs should be tried before surgery is considered. Epilepsy surgery can be especially helpful to people who have seizures from structural brain problems (such as benign brain tumors, strokes or malformations of blood vessels).

Surgery is an elective procedure done in people who have had extensive testing to decide if they are potential candidates. The following criteria are considered when determining if a person may be a good candidate for surgery. Person has failed adequate trials of two first-line seizure medicines (ones that are commonly effective in controlling the type of seizures the person is experiencing) and one combination of at least two drugs. A trial of a medication is considered adequate when it has been increased gradually to the maximum dosage that does not cause serious side effects. If the person has frequent seizures, any improvement will be obvious after a short time. If the seizures generally occur far apart, however, it may take months to determine whether a medication is helping. At some epilepsy centers, patients are offered additional conventional or experimental medications before surgery is considered. But research suggests that each time a trial of medication fails to control a person's seizures, it becomes less likely that a different medicine or combination will be successful. Since uncontrolled seizures present serious physical risks and social and psychological consequences, the trend these days is to proceed with surgery much sooner than in the past if it seems appropriate for that person.

Broca's Aphasia (expressive) When a stroke injures the frontal regions of the left hemisphere, different kinds of language problems can occur. This part of the brain is important for putting words together to form complete sentences. Injury to the left frontal area can lead to what is called Broca's aphasia.

Impaired awareness of illness (anosognosia) is a major problem because it is the single largest reason why individuals with schizophrenia and bipolar disorder do not take their medications. It is caused by damage to specific parts of the brain, especially the right hemisphere.

Bacterial vaginosis is a type of vaginal inflammation caused by the overgrowth of bacteria naturally found in the vagina, which upsets the natural balance. Women in their reproductive years are most likely to get bacterial vaginosis, but it can affect women of any age. The cause isn't completely understood, but certain activities, such as unprotected sex or frequent douching, increase your risk.
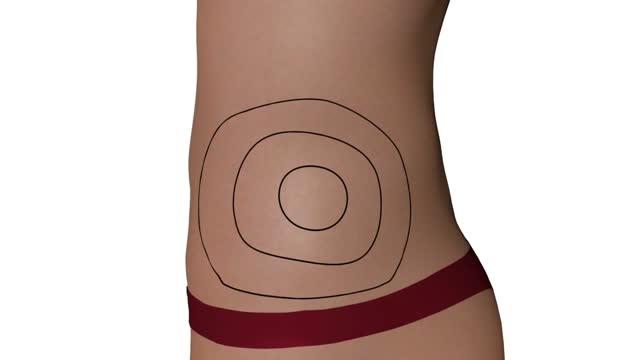
Questo Video 3D illustra la tecnica della Microlipocavitazione: sistema chirurgico ad ultrasuoni per ottenere l'emulsione del grasso in eccesso da eliminare. La Microlipocavitazione è una tecnica di chirurgia ambulatoriale, che richiede una modesta anestesia locale con un recupero delle proprie attività pressoché immediato.
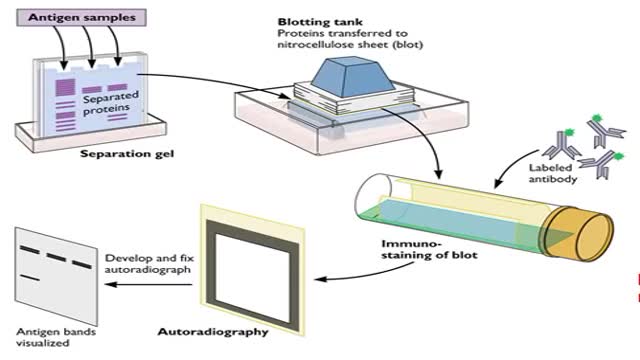
The window period is the time from infection until a test can detect any change. The average window period with HIV-1 antibody tests is 25 days for subtype B. Antigen testing cuts the window period to approximately 16 days and nucleic acid testing (NAT) further reduces this period to 12 days.[2] Performance of medical tests is often described in terms of: sensitivity: The percentage of the results that will be positive when HIV is present specificity: The percentage of the results that will be negative when HIV is not present. All diagnostic tests have limitations, and sometimes their use may produce erroneous or questionable results. False positive: The test incorrectly indicates that HIV is present in a non-infected person. False negative: The test incorrectly indicates that HIV is absent in an infected person.

If you have gestational diabetes, your baby may be at increased risk of: Excessive birth weight. Extra glucose in your bloodstream crosses the placenta, which triggers your baby's pancreas to make extra insulin. This can cause your baby to grow too large (macrosomia).

Phencyclidine (PCP) was developed in the 1950s as an intravenous anesthetic but, due to the side effects of confusion and delirium, its development for human medical use was discontinued. In its pure form, it is a white crystalline powder that readily dissolves in water or alcohol and has a distinctive bitter chemical taste. On the illicit drug market, Phencyclidine contains a number of contaminants as a result of makeshift manufacturing, causing the color to range from tan to brown, and the consistency to range from powder to a gummy mass. It is available in a variety of tablets, capsules, and colored powders, which are either taken orally or snorted. The liquid form of phencyclidine is actually phencyclidine base dissolved most often in ether, a highly flammable solvent. For smoking, phencyclidine is typically sprayed onto leafy material such as mint, parsley, oregano, or marijuana.