Top videos

The colonoscope is slowly withdrawn during this screening colonoscopy down from the transverse colon, back around the splenic flexure, and down the descending colon, and reveals this finding a colonic diverticula. Diverticulosis is a common, acquired, age-related occurrence affecting over 50% of the... western adult population over the age of 50. It is seen rarely in Africa and Asia where the dietary fiber content is traditionally higher. Thus most investigators feel that low fiber diets are related to the development of this condition. Ironically, colonic diverticula are not true diverticula but rather pseudodiverticula in that the sac includes layers of the mucosa and submucosa that push through rather than include the outer muscular layer. As with the small bowel the colon has an inner circular muscular layer, but the outer longitudinal layer is composed of three bands of muscle that run the length of the colon known as teniae. Diverticula occur in rows between the mesenteric and two antimesenteric teniae where the colonic wall is further weakened by the defect caused by the perforating vasa recti artery which supplies the colonic mucosa. Occasionally, the anatomic propensity of diverticula to form in rows is quite apparent as seen when this clip is replayed in slow motion. Most often, however, the arrangement of the diverticula appears random due to the angulation of the bowel and thickening of the semi lunar folds. The conditions that cause these pulsion diverticula are not know with certainty but may include high intrahaustral pressures, muscular hypertrophy, and age related alterations in collagen cross linking. Diverticula can bleed or can abscess and perforate. The incidence of diverticulitis or diverticular bleeding is in the range of 1:1,000 patients with diverticulosis.

Image result for Stop Arterial Bleeding The Femoral Artery is located in the crease of the groin area. Pressure placed here will stop bleeding in leg wounds. Direct Pressure and Elevation should be continued while applying pressure to pressure points. Finally, A pressure bandage should be placed over the dressing and wound
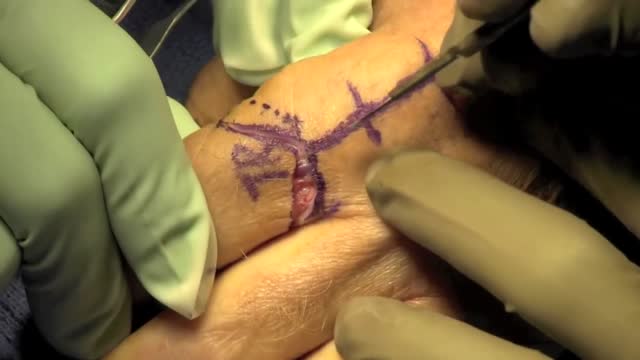
An amputation is the removal of an extremity or appendage from the body. Amputations in the upper extremity can occur as a result of trauma, or they can be performed in the treatment of congenital or acquired conditions. Although successful replantation represents a technical triumph to the surgeon, the patient's best interests should direct the treatment of amputations. The goals involved in the treatment of amputations of the upper extremity include the following : Preservation of functional length Durable coverage Preservation of useful sensibility Prevention of symptomatic neuromas Prevention of adjacent joint contractures Early return to work Early prosthetic fitting These goals apply differently to different levels of amputation. Treatment of amputations can be challenging and rewarding. It is imperative that the surgeon treat the patient with the ultimate goal of optimizing function and rehabilitation and not become absorbed in the enthusiasm of the technical challenge of the replantation, which could result in poorer outcome and greater financial cost due to lost wages, hospitalization, and therapy.
Identify the anatomy and explain the physiology of the breast on diagrams and sonograms.
Describe and demonstrate the protocol for sonographic scanning of the breast, including the clock and quadrant methods, and targeted examinations based on mammographic findings.
Describe the various diagnostic pathways that may lead to a sonographic breast examination, and explain how the ultrasound findings are correlated with other imaging modalities.
Identify and describe sonographic images of benign and malignant features and common breast pathologies.
Explain biopsy techniques for breast tumors.
Define and use related medical terminology.
Explain the Patient Privacy Rule (HIPAA) and Patient Safety Act (see reference

In as many as 80% of cases, doctors don’t find the exact reason for a curved spine. Scoliosis without a known cause is what doctors call “idiopathic.” Some kinds of scoliosis do have clear causes. Doctors divide those curves into two types -- structural and nonstructural. In nonstructural scoliosis, the spine works normally, but looks curved. Why does this happen? There are a number of reasons, such as one leg’s being longer than the other, muscle spasms, and inflammations like appendicitis. When these problems are treated, this type of scoliosis often goes away.
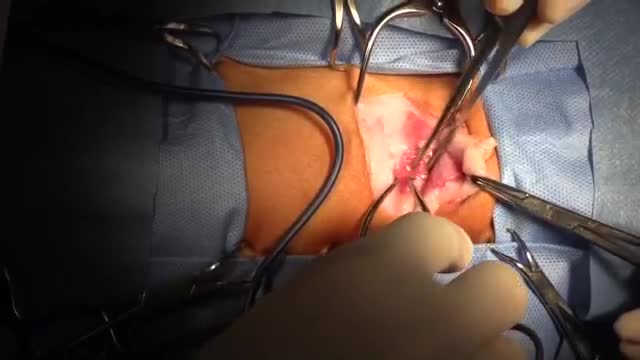
This video: Patent ductus arteriosus (PDA) is a persistent opening between two major blood vessels leading from the heart. The opening, called the ductus arteriosus, is a normal part of a baby's circulatory system before birth that usually closes shortly after birth. If it remains open, however, it's called a patent ductus arteriosus. A small patent ductus arteriosus often doesn't cause problems and might never need treatment. However, a large patent ductus arteriosus left untreated can allow poorly oxygenated blood to flow in the wrong direction, weakening the heart muscle and causing heart failure and other complications. Treatment options for a patent ductus arteriosus include monitoring, medications and closure by cardiac catheterization or surgery.