Top videos
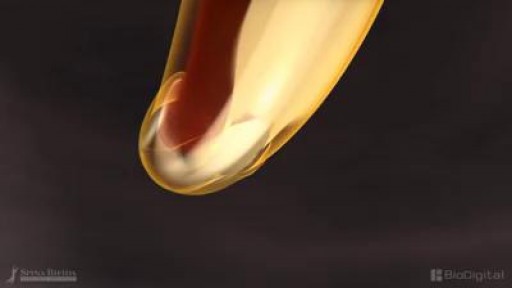
Spina bifida is a condition that affects the spine and is usually apparent at birth. It is a type of neural tube defect (NTD). Spina bifida can happen anywhere along the spine if the neural tube does not close all the way. When the neural tube doesn’t close all the way, the backbone that protects the spinal cord doesn’t form and close as it should. This often results in damage to the spinal cord and nerves. Spina bifida might cause physical and intellectual disabilities that range from mild to severe. The severity depends on: The size and location of the opening in the spine. Whether part of the spinal cord and nerves are affected.

People with serious comprehension difficulties have what is called Wernicke’s aphasia and: Often say many words that don’t make sense. May fail to realize they are saying the wrong words; for instance, they might call a fork a “gleeble.” May string together a series of meaningless words that sound like a sentence but don’t make sense. Have challenges because our dictionary of words is shelved in a similar region of the left hemisphere, near the area used for understanding words.
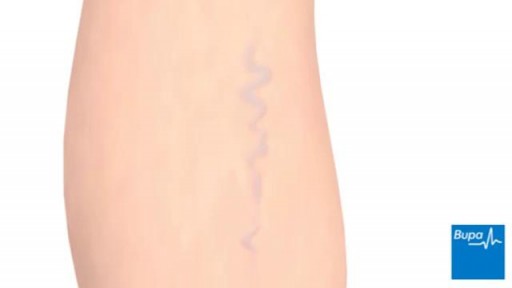
Varicose veins are generally benign. The cause of this condition is not known. For many people, there are no symptoms and varicose veins are simply a cosmetic concern. In some cases, they cause aching pain and discomfort or signal an underlying circulatory problem. Treatment involves compression stockings, exercise, or procedures to close or remove the veins.

Is that knee pain just a sprain or a more serious ACL injury? Orthopedic surgeon Paul Fadale, M.D., offers tips on how to tell the difference. http://www.orthopedicsri.org/

Hysteroscopy is a procedure that allows your doctor to look inside your uterus in order to diagnose and treat causes of abnormal bleeding. Hysteroscopy is done using a hysteroscope, a thin, lighted tube that is inserted into the vagina to examine the cervix and inside of the uterus.
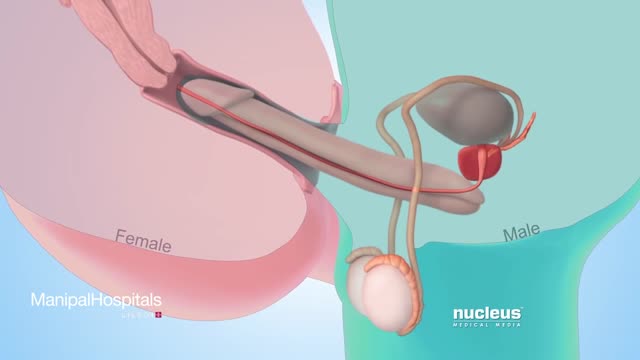
Testicular sperm aspiration (TESA) is a procedure performed for men who are having sperm retrieved for in vitro fertilization/intracytoplasmic sperm injection (IVF/ICSI). It is done with local anesthesia in the operating room or office and is coordinated with their female partner's egg retrieval.
Methotrexate anti-tumor activity is a result of the inhibition of folic acid reductase, leading to inhibition of DNA synthesis and inhibition of cellular replication. The mechanism involved in its activity against rheumatoid arthritis is not known.
Classical PKU is an autosomal recessive disorder, caused by mutations in both alleles of the gene for phenylalanine hydroxylase (PAH), found on chromosome 12. In the body, phenylalanine hydroxylase converts the amino acid phenylalanine to tyrosine, another amino acid.

Pregnancy occurs when an egg is fertilized by a sperm, grows inside a woman's uterus (womb), and develops into a baby. In humans, this process takes about 264 days from the date of fertilization of the egg, but the obstetrician will date the pregnancy from the first day of the last menstrual period (280 days 40 weeks).