Top videos
Cosmetic facial plastic surgery is surgery performed to enhance visual appearance of the facial structures and features. Common procedures include facelifts, eye lifts, rhinoplasty, chin and cheek implants, liposuction, and procedures to correct facial wrinkles.
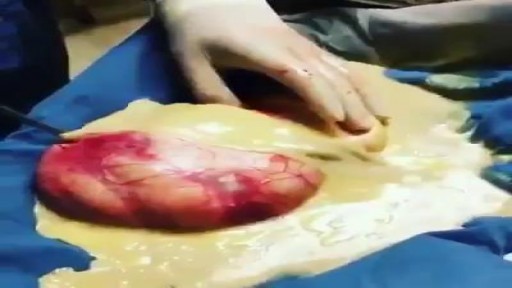
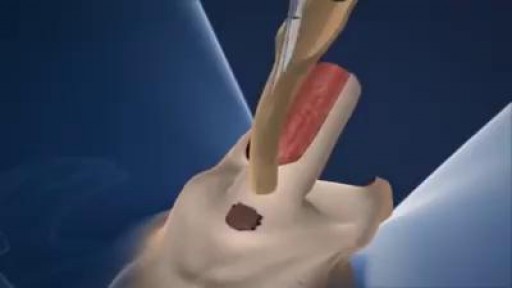
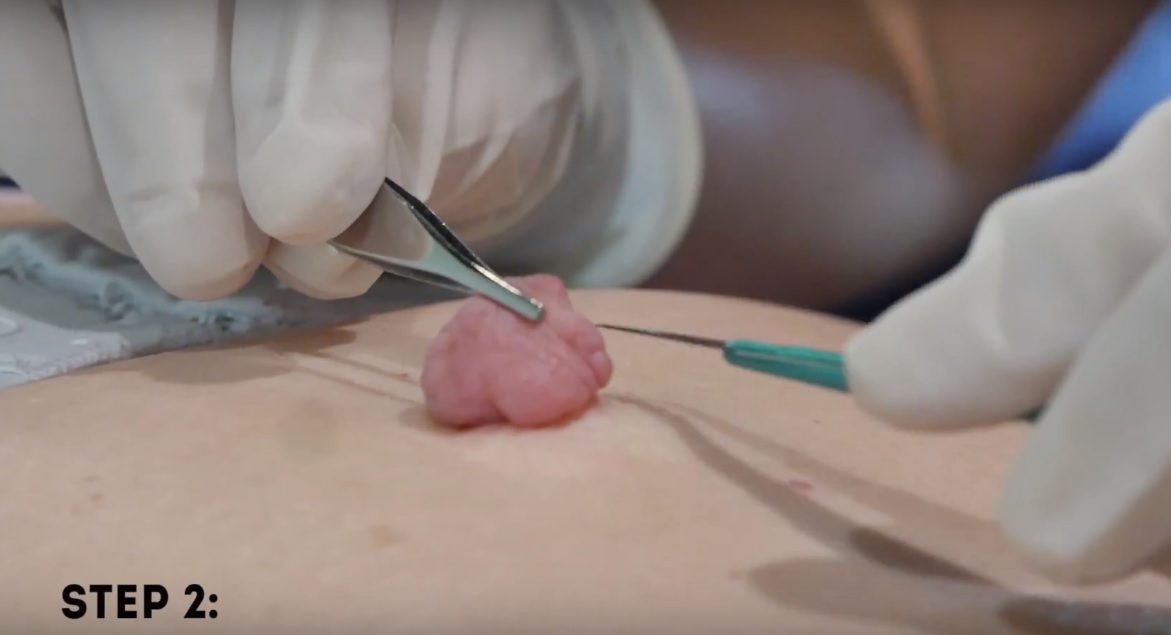
Teratomas are tumors made up of tissues, such as hair, muscle, and bone. They occur most often in the ovaries in women, and the testicles in men. They may be benign or malignant. Symptoms vary depending on the location. A painful lump or swelling may be apparent. Some babies have a mass that can be seen on an ultrasound before birth. Treatment often involves surgery. In rare cases when a teratoma is malignant, chemotherapy or radiation may be needed.
Alagille syndrome (AS) is an autosomal dominant disorder (OMIM 118450) associated with abnormalities of the liver, heart, skeleton, eye, and kidneys and a characteristic facial appearance. In 1973, Watson and Miller reported 9 cases of neonatal liver disease with familial pulmonary valvular stenosis.
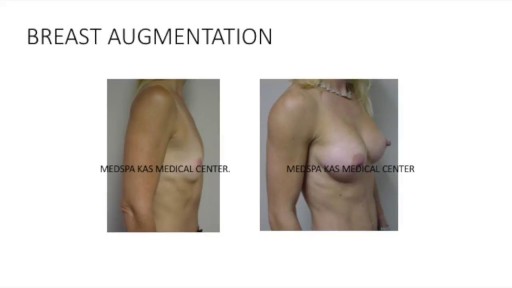
This is a complete video of breast augmentation procedure with implants also includes some before after photographs of breast augmentation surgery by Dr. Ajaya Kashyap at MedSpa Clinic, Delhi, India. source: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=tRg3RkvCvOE Get more information: www.bestbreastsurgeryindia.com Get more information: www.themedspa.us Email at: info@themedspa.us Call/WhatsApp on:+91-9818369662, 9958221983/82/81

very day, specialists deliver high-quality care in 68 disciplines in health centres across Canada. Yet many Canadians know very little about what many specialists actually do, and the important role these disciplines play in Canada’s health care system. This video provides a brief high-level overview of what Internal Medicine Specialists actually do, their training, and their role in Canadian health care.

http://skin-whitening.good-info.co ---- Skin Whitening Pills, Best Skin Whitening Pills, Best Skin Whitening Products For Asians, Whitening. How to Take Care of Your Skin after a Skin Whitening Treatment No matter if you go for laser skin whitening treatment or you choose to use a bleaching cream in the comfort of your home, your skin needs to be well taken care of before, during and after the skin whitening treatment. You do not want to further damage your skin instead of making it look better, do you? This is why it is absolutely necessary to understand which are the things which should be done and what are the things which are totally prohibited once you have done a skin whitening treatment. The first thing on the list is by far avoiding exposure to sun. No matter what type of skin whitening treatment you choose, the skin will be more sensitive to the solar rays and the prolonged exposure to sun can provoke sunburns or even further skin darkening. If you must go out of the house when the sun is up, choose a good sunscreen lotion and wear a hat on your head to prevent the sunrays to reach your skin. As important as avoiding sun exposure is maintaining your skin moisturized. This can be done by two ways: drinking plenty of water all day long and using special products such as moisturizing creams and lotions that will further increase the moisture and help your skin heal faster and look much better in a shorter period of time. Here you will find out everything you need to know about skin color as well as some natural recipes for homemade products that will remove your spots in a matter of weeks! Click Here. http://skin-whitening.good-info.co