Top videos
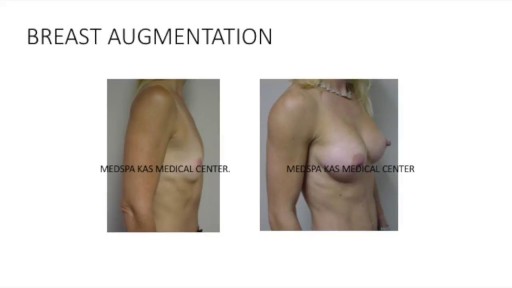
This is a complete video of breast augmentation procedure with implants also includes some before after photographs of breast augmentation surgery by Dr. Ajaya Kashyap at MedSpa Clinic, Delhi, India. source: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=tRg3RkvCvOE Get more information: www.bestbreastsurgeryindia.com Get more information: www.themedspa.us Email at: info@themedspa.us Call/WhatsApp on:+91-9818369662, 9958221983/82/81

http://skin-whitening.good-info.co ---- Skin Whitening Pills, Best Skin Whitening Pills, Best Skin Whitening Products For Asians, Whitening. How to Take Care of Your Skin after a Skin Whitening Treatment No matter if you go for laser skin whitening treatment or you choose to use a bleaching cream in the comfort of your home, your skin needs to be well taken care of before, during and after the skin whitening treatment. You do not want to further damage your skin instead of making it look better, do you? This is why it is absolutely necessary to understand which are the things which should be done and what are the things which are totally prohibited once you have done a skin whitening treatment. The first thing on the list is by far avoiding exposure to sun. No matter what type of skin whitening treatment you choose, the skin will be more sensitive to the solar rays and the prolonged exposure to sun can provoke sunburns or even further skin darkening. If you must go out of the house when the sun is up, choose a good sunscreen lotion and wear a hat on your head to prevent the sunrays to reach your skin. As important as avoiding sun exposure is maintaining your skin moisturized. This can be done by two ways: drinking plenty of water all day long and using special products such as moisturizing creams and lotions that will further increase the moisture and help your skin heal faster and look much better in a shorter period of time. Here you will find out everything you need to know about skin color as well as some natural recipes for homemade products that will remove your spots in a matter of weeks! Click Here. http://skin-whitening.good-info.co

http://tinnitus-solution.info-pro.co --- Ear Infection, Loud Ringing In Ears, Tinnitus Suicide, Ear Is Ringing, Tinnitus One Ear, Tinnitus. Do you suddenly get up in the middle of the night hearing strange noises? Yes it can definitely be frightening, more so when you cannot find the source. Now consider for a moment that these sounds are coming from within you. Most people would be stunned to know that. Many of us do not even know that our internal organs can make sounds. Let us try to see whether you actually heard these noises or not, and if you did, where did they come from. Now before anything, let us get this straight - yes, you actually heard those noises. No, they are not a result of a creative mind that imagined things in slumber. But having said that, it is also true that there is indeed no source of the sounds you heard. So what is it? Confused? This is a classic case of tinnitus. What is tinnitus? What you experienced last night (or did you just get up from sleep and switch on the computer) is a classic case of tinnitus. This is a medical condition wherein a person hears all kinds of strange clicking, ringing, buzzing, whistling or hissing sounds within the ear. What's so worrisome about this condition for a lot of people is that, there's actually no physical source of these sounds. What makes it even worse is that, no one else seems to hear them. Frankly, these people cannot be really blamed. Naturally, if you cannot see where the sound is coming from, and if you keep hearing it, you are bound to get worried. In tinnitus, the sounds a person hears are actually perceptions. Since there's no actual source, they are often referred to as "phantom noises". Will it help you if you knew that about 8% of all people in the US suffer from tinnitus? Perhaps not, but at least now you know that you are not alone who hears these strange noises. Cure tinnitus. this simple, but effective system to erasing Tinnitus out of your life for good has now helped cure over 105,302 people of all the frustrating ringing, hissing, buzzing. Even if you’ve tried every single tinnitus treatment or remedy under the sun. 100% natural tinnitus cure click here: http://tinnitus-solution.info-pro.co

Suppurativa Hidradenitis, Hidradenitis Suppurativa Support, Hidradenitis Suppurativa Cures.--- http://hidradenitis-suppurativa-cure.good-info.co --- Causes of hidradenitis suppurativa Now that we know the symptoms, we must look deeper into the causes so as to get to the root of the problem Caused when hair follicles are blocked or inflamed When hair follicles are blocked due to smoking When hair follicles are blocked due to excess weight Hormonal fluctuations May be caused due to hyper active immune system Causes are sometimes also genetic Severe effects of hidradenitis suppurativa Smells, scars, itches and pains Fear of isolation due to stigmatization Overtime leading to depression Debility and strike on self esteem More information in. http://hidradenitis-suppurativa-cure.good-info.co

Home Remedies For Acid Reflux, Ginger For Acid Reflux, Heartburn After Gallbladder Removal --- http://heartburn-acid-reflux.info-pro.co --- Stop using Pepto Bismol until you read the following… There is BREAKING scientific news reporting that many of America’s most popular antacids – both the ones you buy at the drug store and the ones you need prescriptions for… Are linked to more than a dozen forms of potentially DEADLY cancers. Click this link now to get the full story and see if you’re at risk. You’ll find out about a “just discovered” alternative to antacids…. Something that can permanently cure even the worst cases of acid reflux in as little few days, and that doesn’t require any pills or medications. Click Here: http://heartburn-acid-reflux.info-pro.co

Acid Reflux Home Remedies, Acid Reflux Shortness Of Breath, Heartburn Nausea Fatigue, Acid Reflux. http://heartburn-acid-reflux.info-pro.co --- If you think the worst part about having Acid Reflux is heartburn and mild discomfort… You need to watch this video below IMMEDIATELY. In it, you’ll be shown the much darker side to your acid reflux… Something that over-the-counter and prescription drug manufacturers alike are spending billions to keep hidden from you… But that could soon cost you your LIFE...like it almost did to me. There are even over a dozen forms of cancer that can be traced back to your Acid Reflux, but the situation is not hopeless. Use this link now to see exactly what your biggest risk is…and how a highly unconventional method can rapidly and naturally CURE your Acid Reflux forever. Click Here: http://heartburn-acid-reflux.info-pro.co