トップ動画
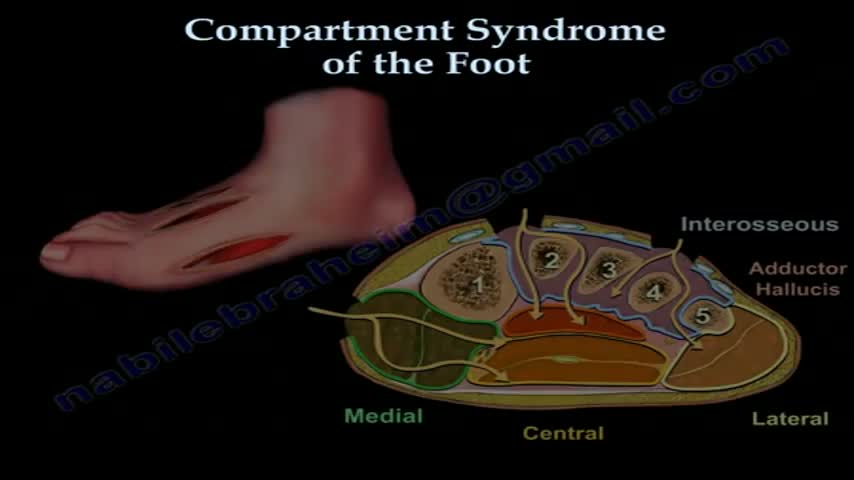
Compartment syndrome can develop in the foot following crush injury or closed fracture. Following some critical threshold of bleeding and/or swelling into the fixed space compartments, arterial pulse pressure is insufficient to overcome the osmotic tissue pressure gradient, leading to cell death. The complicating factor is related to the magnitude of the force of the crush injury. The amount of swelling or bleeding has to be sufficient to impair arterial inflow, while not being of sufficient magnitude to produce an open injury, which decompresses the pressure within the affected compartments. When the injury is open, we then attribute the late disability primarily to the crushing injury to the involved muscles.
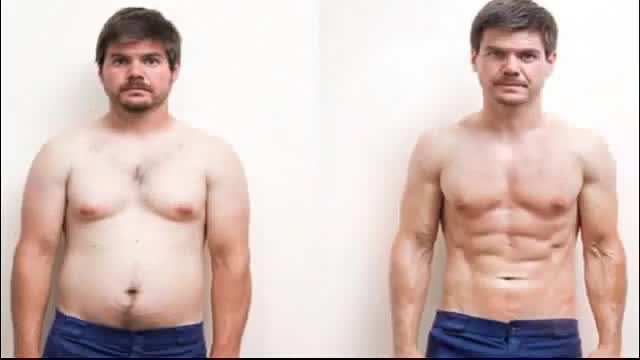
http://segreti-per-dimagrire.plus101.com
---Cerco Una Dieta Per Dimagrire . E' un sistema completo che ti porterà da dove sei ora fin dove vorresti arrivare nel più breve tempo possibile.
Quello che abbiamo sviluppato è un sistema che ti garantisce di bruciare kg su kg di grasso in un programma completo di 30 giorni
Finalmente niente più difficoltà per ottenere il fisico che tanto desideravi. Perderai cosi tanto kg che anche tu farai fatica a crederci! Clicca Qui: http://segreti-per-dimagrire.plus101.com
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=6WXOhZRCwlU
Cerco Una Dieta Per Dimagrire
http://www.youtube.com/user/DietaPanciaPiatta
http://www.youtube.com/user/DietaSettimanale
http://www.youtube.com/user/MetodiPerDimagrire1
http://www.youtube.com/user/ComePossoDimagrire
Cerco Una Dieta Per Dimagrire
Cerco Una Dieta Dimagrire Per
Cerco Una Per Dieta Dimagrire
Cerco Una Per Dimagrire Dieta
Cerco Una Dimagrire Dieta Per
calcolo peso ideale gratis,
calorie dimagrire,
calorie per dieta,
calorie per dimagrire,
calorie per dimagrire un chilo,
calorie per perdere peso,
calorie x dimagrire,
camminare per dimagrire,
camminata veloce per dimagrire,
capsule per dimagrire,
carnitina per dimagrire,
centri dimagrimento,
cerotti dimagranti,
cerotto dimagrante,
che dieta seguire per dimagrire,
cibi per dimagrire,
cibo per dimagrire,
clinica per dimagrire,
cm dimagrire velocemente,
cm perdere peso,

Gonorrhea is a sexually transmitted disease (STD). It’s caused by infection with the bacterium Neisseria gonorrhoeae. It tends to infect warm, moist areas of the body, including the: urethra (the tube that drains urine from the urinary bladder) eyes throat vagina anus female reproductive tract (the fallopian tubes, cervix, and uterus) Gonorrhea passes from person to person through unprotected oral, anal, or vaginal sex. People with numerous sexual partners or those who don’t use a condom are at greatest risk of infection. The best protections against infection are abstinence, monogamy (sex with only one partner), and proper condom usage. Behaviors that make a person more likely to engage in unprotected sex also increase the likelihood of infection. These behaviors include alcohol abuse and illegal drug abuse, particularly intravenous drug use.

Encourage your child to drink lots of fluids to prevent dehydration. Milk and water are both fine. However, if your child refuses solids, give your child just milk, rather than water. ... Keep giving your child table foods while he has diarrhea. Diarrhea is most often spread through fecally contaminated food, hands or surfaces touched by objects or hands put into the mouth (fecal-oral route).Water contaminated by human or animal feces (e.g., swimming pools) or trips to sites with animals (e.g., farms, pet stores, petting zoos) are also possible routes of ... The best foods for your child are easily digestible foods, such as rice cereal, pasta, breads, cooked beans, mashed potatoes, cooked carrots, applesauce, and bananas. Pretzels or salty crackers can help your child replace the salt lost from diarrhea. Foods containing large amounts of sugar or fat should be avoided.
A pneumothorax occurs when some of the tiny air sacs (alveoli) in a baby's lung become overinflated and burst. This causes air to leak into the space between the lung and chest wall (pleural space). The most common cause of pneumothorax is respiratory distress syndrome. This is a condition that occurs in babies who are born too early (premature). The baby's lungs lack the slippery substance (surfactant) that helps them stay open. Therefore, the tiny air sacs are not able to expand as easily. If the baby is put on a breathing machine (mechanical ventilator), there is extra pressure on the baby's lungs, which can sometimes burst the air sacs.

In dark or dim light, the pupil dilates to allow more light into the eye to improve vision. Normal pupil size tends to range between 2.0 and 5.0 millimeters, depending on the lighting. The younger you are, the larger your pupils tend to be.

Pulmonary hypertension is a type of high blood pressure that affects the arteries in your lungs and the right side of your heart. In one form of pulmonary hypertension, tiny arteries in your lungs, called pulmonary arterioles, and capillaries become narrowed, blocked or destroyed. This makes it harder for blood to flow through your lungs, and raises pressure within your lungs' arteries. As the pressure builds, your heart's lower right chamber (right ventricle) must work harder to pump blood through your lungs, eventually causing your heart muscle to weaken and fail. Some forms of pulmonary hypertension are serious conditions that become progressively worse and are sometimes fatal. Although some forms of pulmonary hypertension aren't curable, treatment can help lessen symptoms and improve your quality of life. Pulmonary hypertension care at Mayo Clinic
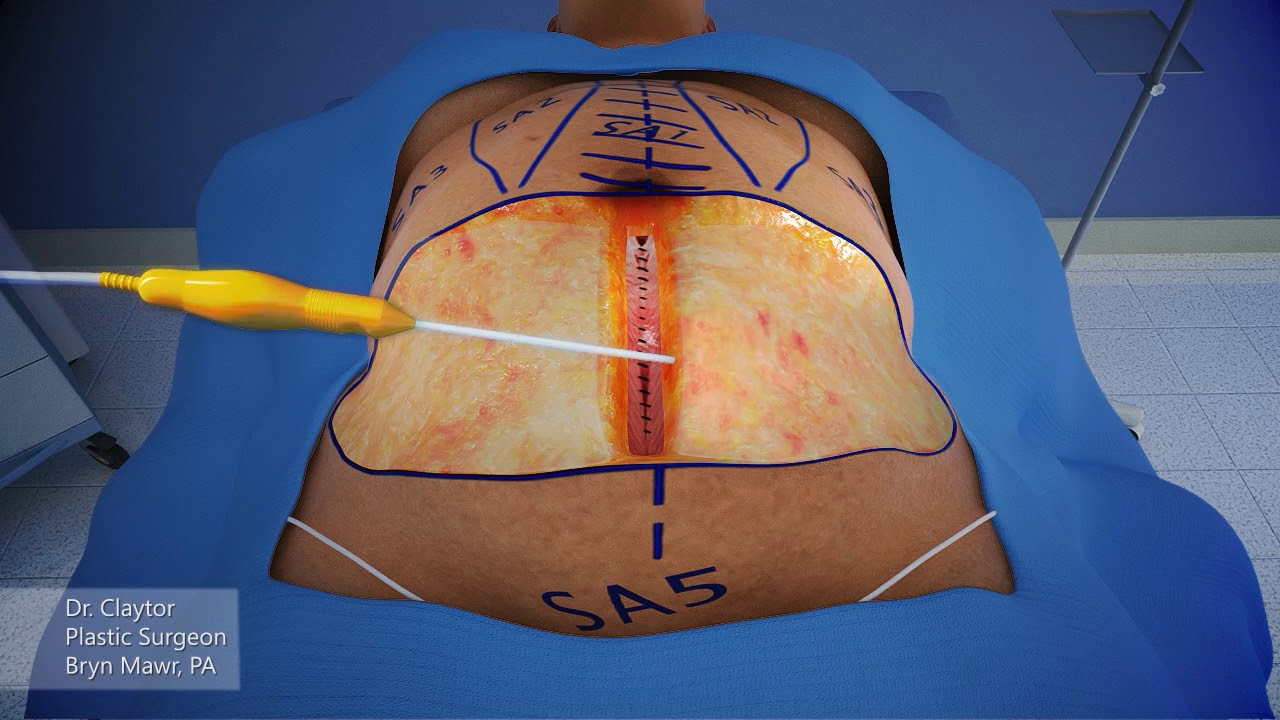
Dr. Claytor uses a 3-D animation to demonstrate how a drainless tummy tuck combined with liposuction can effectively reduce excess skin and fat on the abdomen WITHOUT the need for drains during post-op recovery!
Learn more about Dr. Claytor’s drainless tummy tucks here: https://www.cnplasticsurgery.c....om/procedures/body/t
R. Brannon Claytor, MD, FACS is a renowned double board-certified plastic surgeon and director of Claytor Noone Plastic Surgery, a premium plastic surgery practice in Bryn Mawr, PA that proudly serves the Philadelphia, Main Line, and surrounding areas. Dr. Claytor’s superb skill and results have been recognized for over a decade, earning him numerous awards in both local and national publications, including Philadelphia Magazine, Main Line Today, and Newsweek.
Together, Dr. Claytor and his experienced aesthetics team provide a variety of surgical and non-surgical procedures for the face, breasts, and body to help you look and feel your best. To learn more about how Dr. Claytor and our entire staff can help you reach your goals, please visit our website or give us a call at 610-527-4833.
About Dr. Claytor: https://www.cnplasticsurgery.c....om/our-practice/dr-r
Claytor Noone Plastic Surgery: https://www.cnplasticsurgery.com/
Essential guide to plastic surgery (procedures, costs, planning and more): https://www.cnplasticsurgery.c....om/our-practice/esse
Questions? Contact us online: https://www.cnplasticsurgery.com/contact-us/

http://cfs-cure.plus101.com ----- Chronic Fatigue Syndrome Diet , Cures For Fatigue, Cure For Chronic Fatigue Syndrome. Chronic Fatigue Syndrome Treatment Chronic Fatigue Syndrome (CFS) is variable and unpredictable, and the condition takes its toll on the patient physically, mentally and emotionally. A number of studies have been performed on CFS, with one particular study determining poor early management of the disorder as a primary risk factor for severe CFS. Among the medical community, there is still no consensus on the best course of action for CFS. Most doctors feel that there is no cure for this condition, and limit their treatment to managing the symptoms. There is controversy over different approaches, and main ones being: • Prescription medications • Lifestyle changes • Diet • Nutritional supplements • Graded exercise therapy • Cognitive behavioral therapy • Other alternative/complementary treatments As CFS affects the patients not only physically but also mentally and emotionally, a holistic approach needs to be taken. It is also important that the people around CFS patients understand the condition, and realize that the patient is not just "being lazy" or "constantly feeling down" - chronic fatigue syndrome IS a serious illness and has severe symptoms. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy Cognitive behavioral therapy helps individuals to interpret their symptoms, which in turn helps the patient to shape their behavior in a way to better react to the symptoms. Graded Exercise Therapy A physical therapist can help determine the best exercises for the individual. Programs will start with low levels of exercising, increasing the intensity as the individual gradually builds strength and endurance. Lifestyle Changes Lifestyle changes will also be necessary, including individuals pacing themselves, lowering stress levels, eating a well-balanced diet, engaging in regular moderate exercise, and improving sleep habits. The individual’s work schedule may also need to be modified, as many individuals with CFS find maintaining their regular work schedule too draining. Diet and Chronic Fatigue Syndrome Treatment Diet is crucial in CFS, and dietary supplements may be needed. Certain foods may need to be restricted from the diet, as these may trigger or exacerbate CFS symptoms. A diet-symptom journal can help individuals to identify problem foods. In addition, a significant number of CFS cases may be caused or worsened by un-diagnosed food allergies and intolerances. Therefore, it should be a priority for every patient to check for these using a food-symptom diary and elimination diet, especially if in addition to fatigue you experience gastrointestinal symptoms such as stomach cramps, constipation, or diarrhea. Prescriptions and Medications Depression is often associated with CFS. Antidepressants may be prescribed to treat depression, which in turn will help individuals to cope with CFS-related problems. Studies also show antidepressants administered in low doses may help to relieve pain and improve sleep. Prescription sleep aids may also be prescribed to help individuals improve their sleep. Other drugs that may be prescribed include antiviral drugs, ADD/ADHD medications and anti-anxiety drugs. Alternative/Alternative Chronic Fatigue Syndrome Treatment While the usefulness of alternative/complementary therapy may still be controversial in the scientific community, many patients experience tremendous benefits from these. Main ones include:

Body Mass Index (BMI) is a person's weight in kilograms divided by the square of height in meters. A high BMI can be an indicator of high body fatness. BMI can be used to screen for weight categories that may lead to health problems but it is not diagnostic of the body fatness or health of an individual.May 15, 2015
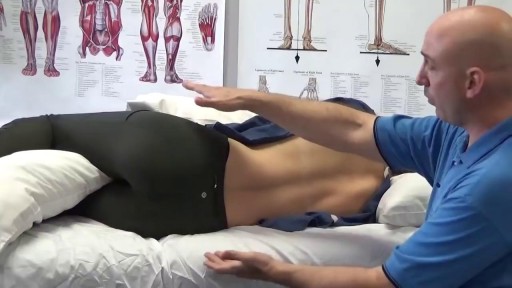
Your sleeping pose can have a major impact on your slumber—as well as your overall health. Poor p.m. posture could potentially cause back and neck pain, fatigue, sleep apnea, muscle cramping, impaired circulation, headaches, heartburn, tummy troubles, and even premature wrinkles