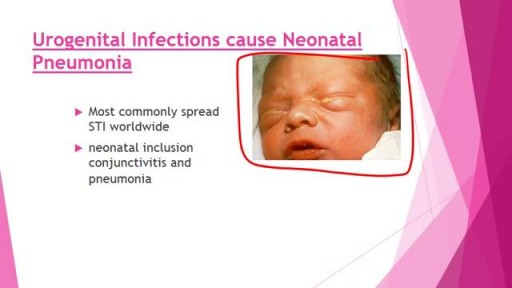
Top videos

URBN Dental is here not only to take care of your tooth decay and prevent gingivitis, but also to give you the best at home dental care instructions as well. Do you find brushing your teeth confusing, or are you unsure whether or not you are brushing correctly? The golden standard when it comes to brushing teeth is brushing twice a day for two minute sessions each. You can break down the mouth into four quadrants: upper right, upper left, lower left, and lower right. By doing this, it will be easier for you to brush for thirty seconds in each area and focus on the correct movement instead of location. It is very important to angle the toothbrush at a forty five degree angle to the tooth and gums while using circular motions to remove food debris and plaque. When it comes to your front teeth, using the brush in a vertical position and combining it with circular motions is effective. Using the dental techniques will ensure healthier teeth that are cavity free and less bleeding gums.

Cameron Underwood Face Transplant Surgical Animation 2018 Eduardo D. Rodriguez, MD, DDS, chair of the Hansjörg Wyss Department of Plastic Surgery, and the Helen L. Kimmel Professor of Reconstructive Plastic Surgery, details the recent face transplant he performed on Cameron Underwood in January 2018 at NYU Langone Health.

For more information:
http://www.7activestudio.com
info@7activestudio.com
http://www.7activemedical.com/
info@7activemedical.com
7activestudio@gmail.com
Contact: +91- 9700061777,
+91- 9100061777
7 Active Technology Solutions Pvt.Ltd. is an educational 3D digital content provider for K-12. We also customize the content as per your requirement for companies platform providers colleges etc . 7 Active driving force "The Joy of Happy Learning" -- is what makes difference from other digital content providers. We consider Student needs, Lecturer needs and College needs in designing the 3D & 2D Animated Video Lectures. We are carrying a huge 3D Digital Library ready to use.
Kidney is most essential organ to remove nitrogenous waste materials from the body. Kidney was damaged by several human activities leads to kidney failure. Once it is damaged it cannot perform basic functions. To overcome this problem one of the best method we follows called hemodialysis. Hemodialysis is a process of removing of nitrogenous waste materials and excess fluids from the blood (collecting from arteries) through tubes containing semi permeable linings in the dialyzer and sending purified blood to the patient's body through veins. It covers the process of hemodialysis in step wise manner. Hemodialysis only performs some basic functions not all those which are performed by natural kidney like reabsorption etc..

Dialysis patients need to choose their heart medicine carefully, as Canadian researchers say that some beta blockers are easily removed from the blood during treatment. Also, people who eat a Mediterranean diet may decrease their risk of developing kidney problems. Eboni Williams reports on the day's top health news.

Rafael Nadal missed seven months last year with a knee injury. That knee will face its toughest test when he plays in the French Open, his first Grand Slam event since his return.
Subscribe to the Times Video newsletter for free and get a handpicked selection of the best videos from The New York Times every week: http://bit.ly/timesvideonewsletter
Subscribe on YouTube: http://bit.ly/U8Ys7n
Watch more videos at: http://nytimes.com/video
---------------------------------------------------------------
Want more from The New York Times?
Twitter: https://twitter.com/nytvideo
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/nytimes
Google+: https://plus.google.com/+nytimes/
Whether it's reporting on conflicts abroad and political divisions at home, or covering the latest style trends and scientific developments, New York Times video journalists provide a revealing and unforgettable view of the world. It's all the news that's fit to watch. On YouTube.
Analysis of Rafael Nadal's Knee Injury (Computer Animation)
http://www.youtube.com/user/TheNewYorkTimes

How to Know If You Have a Serious Knee Injury or Problem
Youtube Channel: https://www.youtube.com/user/physicaltherapyvideo
Website: https://bobandbrad.com/
Bob & Brad discuss how to know if you have a serious knee injury. They show you what to look for and what you should do.
This Week's Giveaway:
This month we are giving away a grand prize of a Sleepovation mattress and two pillows!
BONUS: 2 runners-up will receive a Sleepovation pillow!
December Giveaway link: https://shrsl.com/2ob0e
Purchase Mattress: http://shrsl.com/1n2e2
Purchase Pillow: http://shrsl.com/1xch4
Discount: Make sure to use the discount code FAMOUSPT to receive 15% off of your purchase of a mattress or use FAMOUSPTPIL for 25% off of their pillows! This is the biggest discount of the year!
Sleepovation will reimburse winners of the giveaway if they have already purchased, so no need to wait to buy Bob & Brad's favorite mattress and pillow!
Our videos offer the best "get fit , stay healthy, and pain-free" information directed toward people 0 to 101 years old. Physical Therapists Bob Schrupp and Brad Heineck have over 50 years of combined. We try to add a twist of our humor into each video in our quest to be the "Most Famous Physical Therapists on the Internet" In our opinion of course!!! Subscribe to us now and join the fun. Not only will these videos provide outstanding health information on treating yourself at home, we also do product reviews.
For our favorite products on Amazon click on this link: https://www.amazon.com/shop/physicaltherapyvideo
Visit us on our other social media platforms:
Website: https://bobandbrad.com/
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/BobandBrad/
Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/officialbobandbrad/
Twitter: https://twitter.com/ptfamous
Bob and Brad’s Products:
Grip and Forearm Strengthener: https://store.bobandbrad.com
Wall Anchor: https://store.bobandbrad.com
Booyah Stik: https://store.bobandbrad.com
Knee Glide: https://store.bobandbrad.com
Fit Glide: https://store.bobandbrad.com
Massage Gun: https://amzn.to/36pMekg
Hanging Handles: https://amzn.to/2RXLVFF
Resistance Bands: https://amzn.to/36uqnbr
Pull Up Bands: https://amzn.to/3qmI4Rv
If you order from the Bob and Brad Store Links, you will receive 15% off your purchase.
Check out our shirts, mugs, bags and more in our Bob and Brad merchandise shop here: https://shop.spreadshirt.com/bob-brad
Bob & Brad Amazon Store: https://amzn.to/2RTSLLh
Other Products We Love: https://www.amazon.com/shop/physicaltherapyvideo?listId=3581Z1XUVFAFY
Check out The Bob & Brad Crew on YouTube by clicking here: https://www.youtube.com/c/thebobbradcrew
Want to help translate our videos? We would so love the help! http://www.youtube.com/timedtext_cs_panel?c=UCmTe0LsfEbpkDpgrxKAWbRA&tab=2
Medical Disclaimer All information, content, and material of this website is for informational purposes only and are not intended to serve as a substitute for the consultation, diagnosis, and/or medical treatment of a qualified physician or healthcare provider.
Affiliate disclaimer: Keep in mind that we may receive commissions when you click our links and make purchases. However, this does not impact our reviews and comparisons. We are highly selective in our products and try our best to keep things fair and balanced in order to help you make the best choice for you.

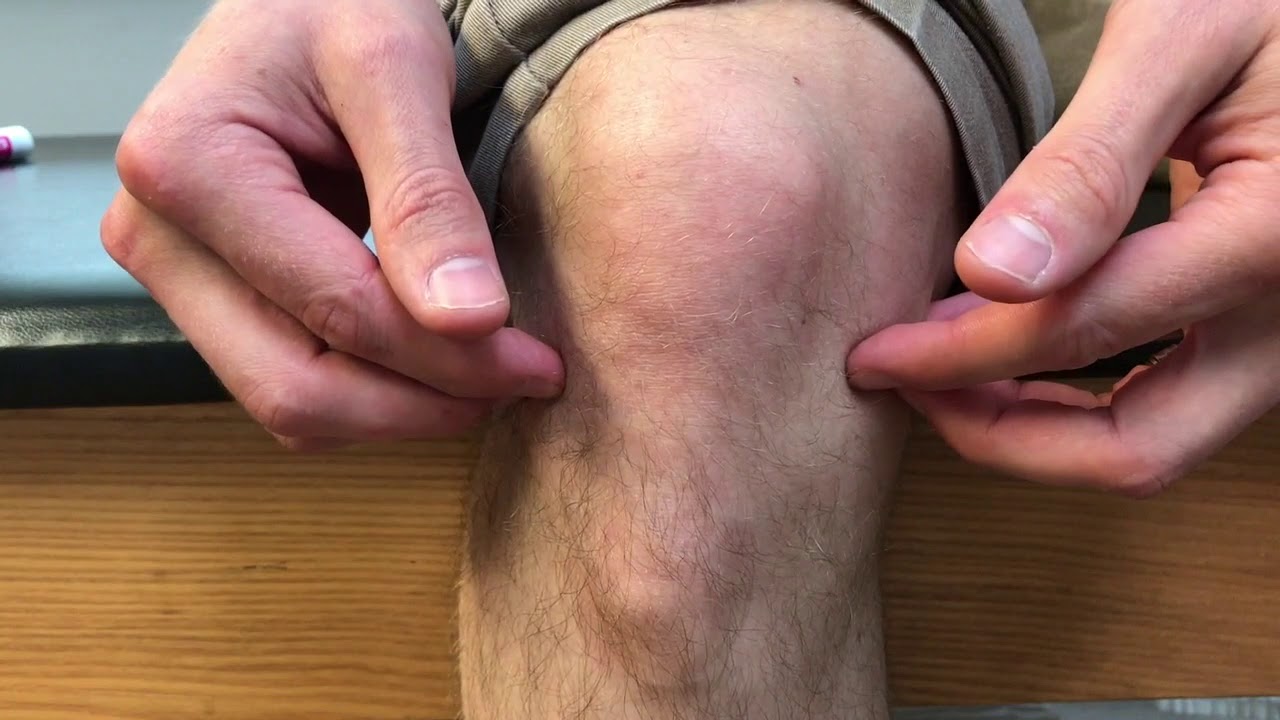
Common causes of the knee pain
Knee pain is very common and in this video we will present the most common problems that can cause pain in the knee. (Patella) itself, which is in front of the knee, or from the tendons that are attached to the kneecap (patellar tendon and quadricep tendon). One of the most common problems is patellar chondromalacia which is chronic pain due to the softening of the cartilage beneath the kneecap. The cartilage of the kneecap will have some erosions, defects, or holes from mild to complete inside the joint (exactly in the back of the kneecap).
• Pain in the front of the knee
• Occurs more in young people
• Becomes worse from climbing up stairs and going downstairs
Treatment is usually nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medication, physical therapy, and surgery is very rare. Also in front of the kneecap, the patient may get pain due to prepatellar bursitis.
When there is prepatellar bursitis, the patient will see that the swelling, the inflammation, and the pain is located over the front of the kneecap. The bursa becomes inflamed and fills with fluid at the top of the knee, causing pain, swelling, tenderness and a lump in that area on top of the kneecap. If the pain is in front of the knee but below or above the patella, this may indicate that the patient has tendonitis. Patellar tendonitis is an overuse condition that often occurs in athletes who perform repetitive jumping activities. Patellar tendonitis is a knee pain that is associated with focal patellar tendon tenderness and it is usually activity related. It is located below the kneecap and is called "jumper's knee". Patellar tendonitis affects approximately 20% of jumping athletes. There will be tenderness to palpation at the distal pole of the patella in extension and not in flexion. Quadriceps inflexibility, atrophy and hamstring tightness are predisposing factors for this condition. Treatment is rest, anti-inflammatory medication, stretching and strengthening of the hamstrings and quadriceps. Use an eccentric exercise program. The early stages of patellar tendonitis will respond well to nonoperative treatment. Another important cause of knee pain is a meniscal tear. The meniscus is the cushion that protects the cartilage in the knee. Injury will cause pain on the medial or the lateral side of the knee exactly at the level of the joint. The patient will complain of a history of locking, instability and swelling of the knee. McMurray test will be positive. A painful pop or click is obtained as the knee is brought from flexion to extension with either internal or external rotation of the knee. Arthritis of the knee Knee arthritis is very common. The cartilage cells die with age and its repair response decreases in the joint collapses with increased breakdown of the framework of the cartilage. The patient will have progressive blurring away of the cartilage of the joint with decreased joint space as seen on x-rays. Another source of pain is the Baker's cyst. The cyst is in the back of the knee between the semimembranosus yes and the medial gastrocnemius muscles. Another important source of knee pain is a ligament injury. Here is a normal knee without a ligament injury. Here you can see from the front, you can see the lateral and medial collateral ligament. You can see the ACL and PCL from the side view. These ligaments are usually injured as a result of a sports activity. Here is an example of a sports knee injury. Here is an example of the medial collateral ligament injury. This is the most commonly injury knee ligament injury to this ligament is on the inner part of the knee. Here is an example of an injury of the anterior cruciate ligament. It involves a valgus stress to the knee. Lachman test is usually positive, and MRI is diagnostic. Another important cause of knee pain is iliotibial band syndrome of the knee. Inflammation of the thickening of the iliotibial band results from excessive friction as the iliotibial band slides over the lateral femoral condyle. The iliotibial band is a thick band of fascia that extends along the lateral thigh from the iliac crest to the knee. And as the knee moves, the IT band was repeatedly shifted forwards and backwards across the lateral femoral condyle. The patient will complain of swelling, tenderness, and crepitus over the lateral femoral condyle. The condition occurs in the ITB S occurs in runners, cyclist and athletes that require repeated knee flexion and extension. The pain may be reproduced by doing a single-leg squat. The Ober's test is used to at assess tightness of the iliotibial band. MRI may show edema in the area of the ITB. Treatment is usually nonoperative with rest and ice, physical therapy, with stretching, proprioception, and improvement in neuromuscular coordination. Training modification and injections may be helpful. Surgery is a last resort. Surgical excision of the scarred inflamed part of the iliotibial band.
If you're looking to get to the root cause of your pain and are looking for natural treatment over drugs, injections, or surgery, visit:
www.physicaltherapyjohnson.com
Or
Call us directly at 484 552 3767

https://bit.ly/3HIStRc #shorts
Coloscopy | Colon Polyp Resection | Polypectomy
Colonoscopies are essential for detecting colorectal abnormalities, including colon polyps. Polypectomy, the surgical removal of these growths, can prevent them from becoming cancerous. This article offers a brief overview of colonoscopies, colon polyps, and polypectomy procedures.
A colonoscopy is an endoscopic examination allowing healthcare providers to visualize the colon and rectum using a colonoscope. The colonoscope, a flexible tube with a camera and light source, helps detect abnormalities, including polyps or tumors.
Colon polyps are abnormal growths arising from the colon's inner lining. While most polyps are benign, some can become malignant. Adenomatous polyps have a higher potential to become cancerous, whereas hyperplastic and inflammatory polyps pose a lower risk.
Polypectomy involves removing colon polyps during a colonoscopy. Two primary techniques include snare polypectomy, using a wire loop to cut the polyp, and cold forceps polypectomy, which employs forceps to grasp and remove smaller polyps.
Following a polypectomy, patients may experience mild discomfort or bleeding. Regular surveillance is crucial to minimize colorectal cancer risk. The frequency of surveillance colonoscopies depends on the number, size, and type of polyps found, as well as the patient's overall risk factors.
Colonoscopies and polypectomies play vital roles in detecting and removing colon polyps, reducing the risk of colorectal cancer, and maintaining optimal colon health.
Do you want to learn more about colon polyps and colonoscopy? check our:
Article @ https://bit.ly/41w5Ooq
For more free resources, find us on Pinterest & Facebook pages:
https://www.pinterest.ca/medicalartsofficial/
https://www.facebook.com/Medicalartsofficial
https://www.youtube.com/@medic....alarts?sub_confirmat
https://www.instagram.com/medicalartsofficial/
https://www.tiktok.com/@medicalarts
#endoscopicsurgery #digestivesystem
coloscopy
polyp
colon polyp
polypectomy
colonoscopy
colon polyp animation
gi endoscopy
@MedicalArts , 2023.
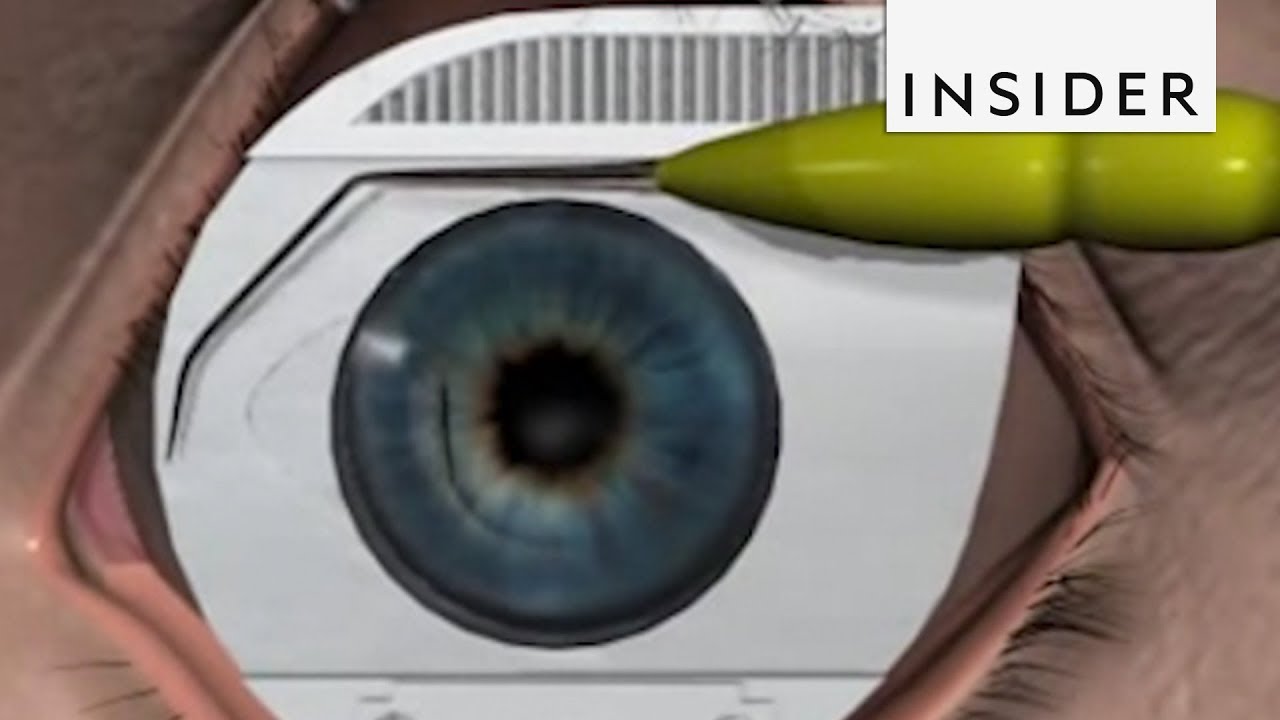
Here’s how surgeons perform LASIK surgery.
See more: https://www.amerra.com/
Subscribe to our new channel, INSIDER food: http://insder.co/2kWwBKZ
The INSIDER team believes that life is an adventure! Subscribe to our channel and visit us at: https://thisisinsider.com
INSIDER on Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/thisisinsider/
INSIDER on Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/thisisinsider/
INSIDER on Twitter: https://twitter.com/thisisinsider

LASIK eye surgery has been popular for more than 20 years, with an estimated 20 million Americans undergoing the procedure to correct nearsightedness and improve distance vision. But some patients says the surgery has ruined their eyesight. Now an expert who once backed LASIK is campaigning to get it off the market. Dr. Tara Narula reports.
Watch "CBS This Morning" HERE: http://bit.ly/1T88yAR
Download the CBS News app on iOS HERE: https://apple.co/1tRNnUy
Download the CBS News app on Android HERE: https://bit.ly/1IcphuX
Like "CBS This Morning" on Facebook HERE: http://on.fb.me/1LhtdvI
Follow "CBS This Morning" on Twitter HERE: http://bit.ly/1Xj5W3p
Follow "CBS This Morning" on Instagram HERE: http://bit.ly/1Q7NGnY
Get new episodes of shows you love across devices the next day, stream local news live, and watch full seasons of CBS fan favorites anytime, anywhere with CBS All Access. Try it free! http://bit.ly/1OQA29B
Each weekday morning, "CBS This Morning" co-hosts Gayle King, Anthony Mason and Tony Dokoupil deliver two hours of original reporting, breaking news and top-level newsmaker interviews in an engaging and informative format that challenges the norm in network morning news programs. The broadcast has earned a prestigious Peabody Award, a Polk Award, four News & Documentary Emmys, three Daytime Emmys and the 2017 Edward R. Murrow Award for Best Newscast. The broadcast was also honored with an Alfred I. duPont-Columbia Award as part of CBS News division-wide coverage of the shootings at Sandy Hook Elementary School in Newtown, Connecticut. Check local listings for "CBS This Morning" broadcast times.

Dr. Ankur Gupta of the Virginia Eye Institute discusses LASIK eye surgery as a method of correcting refractive errors. LASIK was first performed in Virginia on an FDA-approved laser by a VEI surgeon in 1996. Today, Virginia Eye Institute offers both conventional LASIK and custom LASIK with the bladeless IntraLase laser to precisely sculpt your cornea to correct refractive errors.
For more information on the services and procedures offered at Virginia Eye Institute please visit: https://goo.gl/6nX4RZ
THE CONTENT IN THIS VIDEO IS GENERAL IN NATURE AND DOES NOT SUBSTITUTE PROFESSIONAL MEDICAL ADVICE. The content on our website including, but not limited to, text, images, and videos is for informational and educational purposes only. Although we work hard to provide accurate general information, it is not a substitute for professional medical advice or consultations with healthcare professionals, and does not establish any kind of provider-patient relationship. Our website information is not intended to make any promises about the results of our products and services. We are not liable for actions taken based on content found on our website. If you are seeking medical advice, diagnoses, or treatment, we encourage you to call 804-287-2020 to make an appointment with one of our providers for your individualized care plan.

Knee replacement involves replacing a knee joint that has been damaged or worn away, usually by arthritis or injury. Find out more here: https://www.bupa.co.uk/health-....information/knee-cli