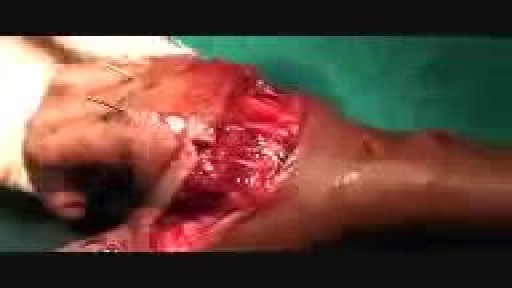
शीर्ष वीडियो

Body Restorations will do an “Early Assessment” when you come in for physiotherapy; this allows therapists to identify the more complicated cases quickly and get started with treatment right away. If you are feeling pain now, it is best that you seek treatment as soon as possible. Research has proven that people who seek treatment for their pain immediately have less of a chance of it becoming an issue later own. Early intervention is always the best option. Visit - https://stalbertphysiotherapy.com/contact/
Most women have vaginal discharge at many different times throughout their cycle. During ovulation, white and watery discharge is common and accepted as normal. But, discharge after ovulation is widely believed to be a sign of pregnancy.
Your sleeping pose can have a major impact on your slumber—as well as your overall health. Poor p.m. posture could potentially cause back and neck pain, fatigue, sleep apnea, muscle cramping, impaired circulation, headaches, heartburn, tummy troubles, and even premature wrinkles
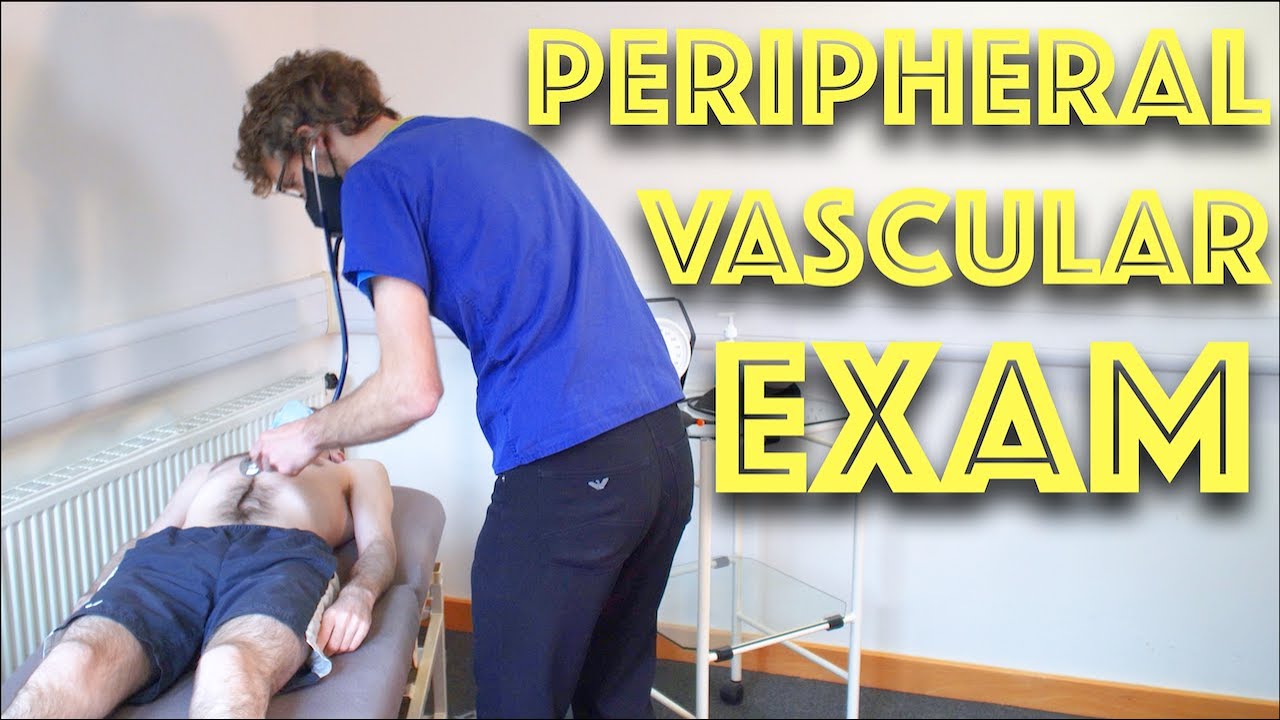
Peripheral Vascular Examination OSCE - Clinical Skills - Dr Gill
In the cardiovascular examination, particularly in the case of an OSCE station, we conclude the examination often by stating that the examiner would want to perform:
- An ECG
- Check full blood count
- and "do a peripheral vascular examination
In this video, we demonstrate that oft-talked about, but comparatively less common examination.
Starting off, with the examination of the hands, the radial, brachial and carotid pulses. before moving down to assess for a AAA, checking the femoral and popliteal pulses, before wrapping up around the ankle with the posterior tibial and dorsalis pedis pulses
For completeness, the cardiovascular examination is demonstrated here
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ECs9O5zl6XQ&t=2s
#PeripheralVascular #ClinicalSkills #DrGill
The principal signs of cerebellar dysfunction are the following: Ataxia: unsteadiness or incoordination of limbs, posture, and gait. A disorder of the control of force and timing of movements leading to abnormalities of speed, range, rhythm, starting, and stopping.
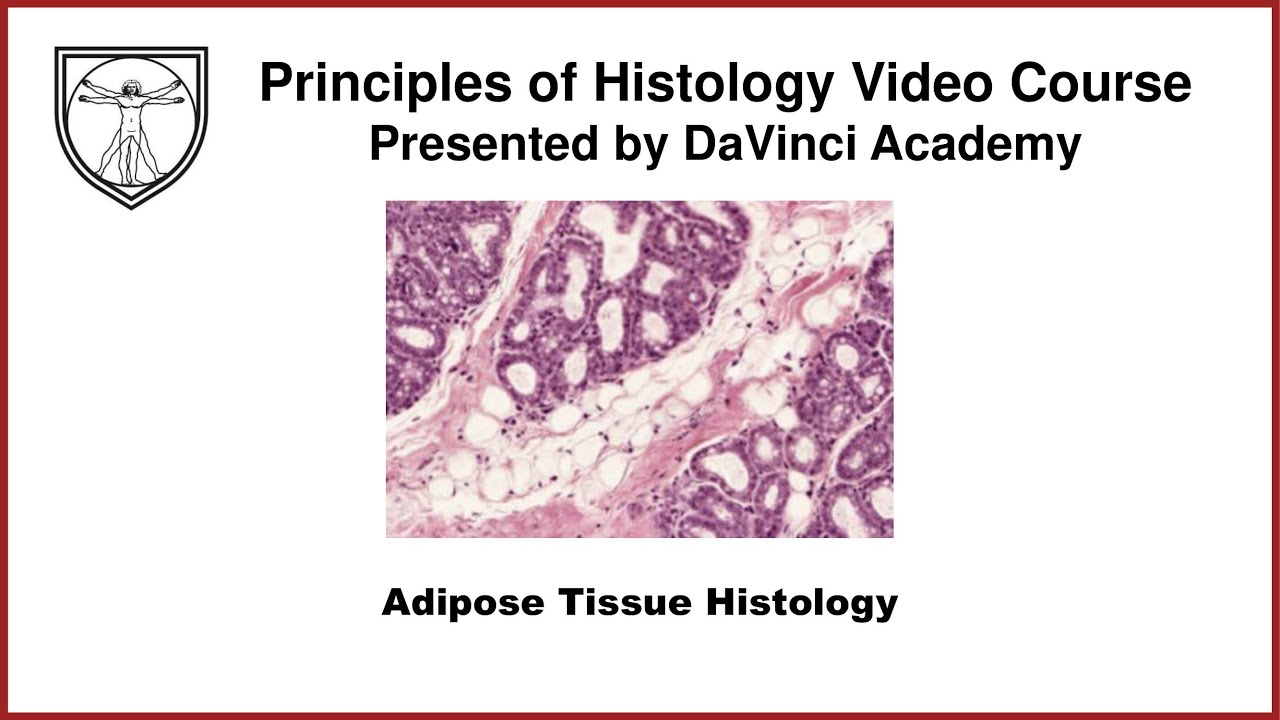
Covers the histological structure for adipose tissue and relevant cellular physiology for adipocytes. This video is a part of our Histology Video Course (https://youtube.com/playlist?l....ist=PLnr1l7WuQdDynxT
All Histology Videos: https://youtube.com/playlist?l....ist=PLnr1l7WuQdDynxT
Thank you to our sponsor Doc2Doc Lending, the Personal Lending platform designed for Doctors, by Doctors. Check out https://doc2doclending.com/davinci to learn more today.
DaVinci Academy Merch - Coffee mugs, T-shirts, hoodies and more: https://my-store-d90f46.creator-spring.com
Additional YouTube Content
Biochemistry videos: https://youtube.com/playlist?l....ist=PLnr1l7WuQdDzCUC
Anatomy Videos: https://youtube.com/playlist?l....ist=PLnr1l7WuQdDz2dK
DaVinci Cases Videos: https://youtube.com/playlist?l....ist=PLnr1l7WuQdDyJUl
The DaVinci Hour Podcast: https://youtube.com/playlist?l....ist=PLnr1l7WuQdDwSm9
DaVinci Academy Website: https://www.dviacademy.com/
Tonsil stones are hard yellow or white formations that are located on or within the tonsils. It’s common for people with tonsil stones to not even realize they have them. Tonsil stones aren’t always easily visible and they can range from rice- to pea-sized. Tonsil stones rarely cause larger health complications. However, sometimes they can grow into larger tonsilloliths which can cause your tonsils to swell
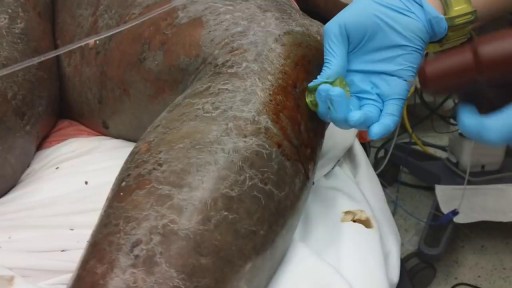
For patients in extremis from respiratory failure or shock, securing vascular access is crucial, along with establishing an airway and ensuring adequacy of breathing and ventilation. Peripheral intravenous catheter insertion is often difficult, if not impossible, in infants and young children with circulatory collapse. Intraosseous (IO) needle placement, shown in the images below, provides a route for administering fluid, blood, and medication. An IO line is as efficient as an intravenous route and can be inserted quickly, even in the most poorly perfused patients.

The anus is close to the vagina and sometimes it’s hard to say what’s going on inside the body. Is it possible to get pregnant from anal sex? The answer is yes and this video explains the circumstances. Please protect yourselves and stay curious.
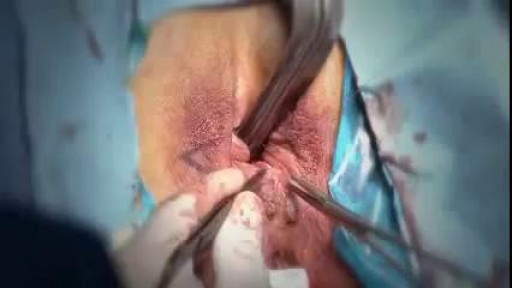
A vaginoplasty is a surgical procedure that tightens the vagina. This is done by removing excess vaginal lining and tightening the surrounding soft tissues and muscles. During delivery of a baby the vagina and surrounding tissues and muscles become stretched. After delivery the vagina may return to a more “normal” size, but it often fails to return to its’ pre pregnancy diameter. Generally, the more vaginal deliveries, the worse the condition gets. Many women will complain of decreased sensation and sexual satisfaction during intercourse. Commonly this is due to a lack of friction. Often their partner may notice a change although he may say nothing. Kegel exercises are often recommended but rarely succeed in restoring vaginal tightness.

It’s not tummy tuck procedure.. it’s liposuction only.. don’t get confused with both procedure..
#beforeandafter #kmc #nose #aesthetic #antiaging #beauty #drhabibhairtransplant #peshawar #nose #islamabad #swat #kohat #nowshehra #karakin #mardan

Otto Placik MD. a board certified Chicago based plastic surgeon presents Vulvar Vaginal Genital anatomy lesson reviewing the Vulva, Mons Pubis, clitoral hood, prepuce, frenulum, labia minora & majora, vagina, urethra and fourchette with surgical implications and techniques. Photos pictures and video of anatomic models are reviewed in detail on different models. Great for patients thinking about or planning before labiaplasty or vaginal cosmetic surgery
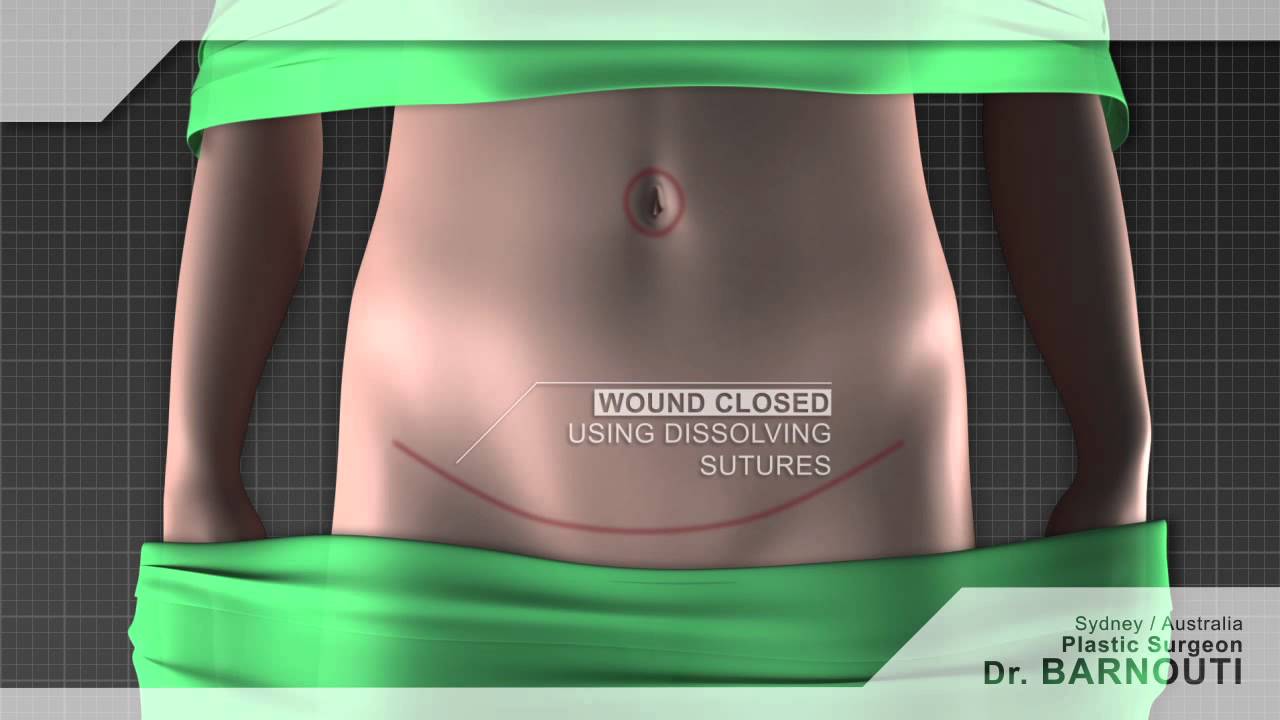
Tummy tuck Sydney Dr Barnouti. Call us on 02-9561 0222 or 1300 002 006
Broadway, Chatswood, Burwood NSW Australia
email:drbarnouti@australiaplasticsurgery.com.au
https://www.plasticsurgery-syd....ney.com.au/abdominop
What is a tummy tuck?
A tummy tuck operation is also known as abdominoplasty. It involves removing excess skin and fat from the stomach area, mainly the lower part of the tummy through surgical procedure. A tummy tuck operation is intended to leave the patient with a flatter tummy and to remove any signs of an 'apron' stomach or an overhang which is sometimes visible above underwear. The skin on this area tends to be stretched and of poor quality. A tummy tuck operation will usually focus on the lower part of the stomach, below the belly button and may require the belly button to be repositioned in some cases. The procedure is often carried out on women or men who have suffered from stretched skin in the stomach area after pregnancy, giving birth, excess fat deposition or weight loss.
What happens during a tummy tuck?
During a tummy tuck procedure the aim of the surgeon is to cut away fat and excess skin. To do this Dr Barnouti will make in incision on the lowest part of the stomach, where a fold will be visible above the pubic bone. He will take out as much excess fat as can be removed and will then cut the skin to fit back over the place where the fat has been removed from. It is important to have realistic expectations of a tummy tuck. Taking too much fat and skin away can result in folds at each end of the resulting scar which are sometimes referred to as "dog ears". Dr Barnouti will make sure you will not have this problem.
Who should have a tummy tuck?
Tummy tucks are recommended for either men or women who have an excess of fat and skin around their abdomen which cannot be removed by weight loss, exercise or liposuction. Tummy tuck operations in women are usually reserved for those who are not likely to have children as it is inadvisable to get pregnant again after having skin removed, this can cause the wound to stretch and scar.
The cost of a tummy tuck in Sydney Australia
The total cost is $7,900 if the patient's health fund cover the hospital's fees. In case the health fund does not cover the hospital's fee, the total cost will be around $12,000 inclusive of the Surgeon, assistant surgeon, Anaesthetist, hospital, operating theatre and follow ups visit.
Payment plans are alos available from Dr Barnouti's office in Chatswood, Burwood or Broadway.
A tummy tuck is a cosmetic procedure that removes excess skin and fatty tissue in order to give a flatter appearance to the stomach. Tummy tucks, also known as abdominoplasties, are ideal for patients who are not excessively overweight but suffer from an overhang of skin around the abdomen.
Performed under general anaesthetic, tummy tucks involve a horizontal incision being made just above the pubic area between the hip bones. Skin and fatty tissue is separated from the muscle and the area is tightened, with the excess skin and fatty tissues then being pulled downwards and removed.
Following your tummy tuck, there will be a scar present across the lower abdomen, but this will gradually fade. You may experience moderate tissue swelling for several months, but this will disappear with time. There may also be a sensation reduction just above the pubic area.
Once your tummy tuck recovery is complete however, you'll benefit from a more attractive figure and the ability to wear a wider selection of clothes.