Лучшие видеоролики
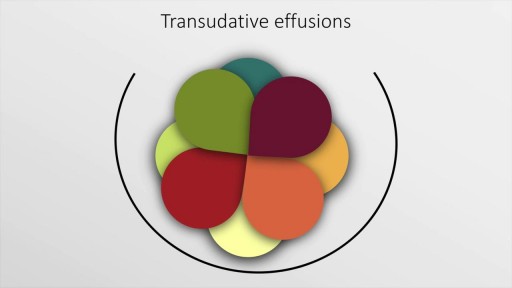
A detailed description of the causes and diagnosis of pleural effusion. The presentation includes a discussion of the causes and exudative and transudative pleural effusions. Light's criteria and its modification are described along with definition and clinical implication of pleural fluid acidosis, glucose, adenosine deaminase, hemorrhagic pleural effusion and protein and LDH as well.

Intrauterine insemination (IUI) is a fertility treatment that involves placing sperm inside a woman's uterus to facilitate fertilization. The goal of IUI is to increase the number of sperm that reach the fallopian tubes and subsequently increase the chance of fertilization

Most times, a pulmonary embolism is caused by blood clots that travel from the legs or, rarely, other parts of the body (deep vein thrombosis, or DVT). Symptoms include shortness of breath, chest pain, and cough. Prompt treatment to break up the clot greatly reduces the risk of death. This can be done with blood thinners and drugs or procedures. Compression stockings and physical activity can help prevent clots from forming in the first place.

A talus fracture is a break in one of the bones that forms the ankle. This type of fracture often occurs during a high-energy event, such as a car collision or a high-velocity fall. Because the talus is important for ankle movement, a fracture often results in significant loss of motion and function. In addition, a talus fracture that does not heal properly can lead to serious complications, including chronic pain. For this reason, many talus fractures require surgery.

Dialysis services at UC San Diego Health: https://health.ucsd.edu/care/kidney/dialysis
UC San Diego Health Licensed Clinical Social Worker, Norma Reggev, discusses hemodialysis as a treatment option for failing kidneys with patient testimonials. Discussion includes In Center Hemodialysis and Home Hemodialysis.
0:00 - Hemodialysis
1:34 - When Should Dialysis Begin?
2:00 - What is Dialysis?
2:25 - How Hemodialysis Works
3:15 - In-Center Hemodialysis Considerations
3:42 - Patient Shares Their Experience With In-Center Hemodialysis
7:30 - Home Hemodialysis Considerations
8:35 - Patient Shares Their Experience With Home Hemodialysis
12:23 - Types of Vascular Access

Acute mesenteric ischemia (AMI) is a syndrome caused by inadequate blood flow through the mesenteric vessels, resulting in ischemia and eventual gangrene of the bowel wall. Although relatively rare, it is a potentially life-threatening condition. Broadly, AMI may be classified as either arterial or venous. AMI as arterial disease may be subdivided into nonocclusive mesenteric ischemia (NOMI) and occlusive mesenteric arterial ischemia (OMAI); OMAI may be further subdivided into acute mesenteric arterial embolism (AMAE) and acute mesenteric arterial thrombosis (AMAT). AMI as venous disease takes the form of mesenteric venous thrombosis (MVT).

These are a few common types of benign bone tumors: Osteochondroma is the most common benign bone tumor. ... Giant cell tumor is a benign tumor, typically affecting the leg (malignant types of this tumor are uncommon). Osteoid osteoma is a bone tumor, often occurring in long bones, that occurs commonly in the early 20s.