Top Videos

General Considerations Because a discussion of reproductive issues may be difficult for some women, it is important to obtain the history in a relaxed and private setting. The patient should be clothed, particularly if she is meeting the provider for the first time. Ordinarily, the patient should be interviewed alone. Exceptions may be made for children, adolescents, and mentally impaired women, or if the patient specifically requests the presence of a caretaker, friend, or family member. However, even in these circumstances, it is desirable for the patient to have some time to speak with the clinician privately. The manner of address should be formal using the title Mrs., Ms., Miss, or Dr. with the patient’s surname, unless the patient requests otherwise. In some settings, it may be appropriate for nursing staff to be involved with history taking. A nurse may be perceived as less threatening, and may be able to take the history in a less hurried manner.1 The provider can verify the history and focus on areas of concern. Alternatively, it may be helpful to ask the patient to complete a self-history form on paper or by computer prior to speaking with the provider. This allows the provider to devote time to addressing positive responses, and ensures that important questions are not missed. Hasley2 showed that responses to a computer-based questionnaire designed to update a patient’s gynecologic history were equivalent to those obtained during a personal interview. Several studies involving patients in non-gynecologic settings have shown that patients are more likely to provide sensitive information when responding to a computer-based questionnaire as opposed to a personal interview or even a paper questionnaire.3 In order to increase a patient’s level of comfort during the interview, questions should be asked in an open-ended and nonjudgmental way. Assumptions should not be made about aspects of the patient’s background such as sexual orientation. At the conclusion of the interview, patients should be asked whether there are concerns that they would like to discuss that were not addressed previously in the interview.

There are several things to consider when trying to decide between gastric bypass surgery and gastric sleeve surgery. Unlike the laparoscopic adjustable gastric band (Lap Band), these two operations are both permanent, reduce hunger, and lead to the highest percentage of weight loss. To properly compare gastric sleeve surgery to gastric bypass surgery we will examine the following data : Expected weight loss. Speed of weight loss. Time of surgery. Gastric bypass benefits over sleeve. Gastric sleeve benefits over bypass. Risk of complications. Surgeon skill and preference.
Primary biliary cholangitis (PBC), formerly known as primary biliary cirrhosis, is a chronic liver disease resulting from progressive destruction of the bile ducts in the liver – called the intrahepatic bile ducts. Bile produced in your liver travels via these ducts to your small intestine where it aids in the digestion of fat and fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, E and K). When the ducts are destroyed, bile builds up in the liver contributing to inflammation and scarring (fibrosis). Eventually this can lead to cirrhosis and its associated complications, as scar tissue replaces healthy liver tissue and liver function becomes increasingly impaired.
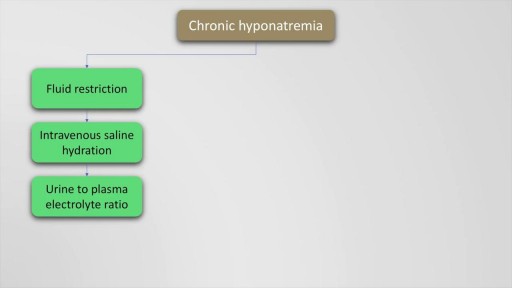
Hyponatremia is defined as a serum sodium of less than 135 Meq per litre and occurs in upto 22 % of hospitalised patients. The causes of hyponatremia may be understood based on the pre-existing volume status of the patient which may either be hypovolemic, euvolemic or hypervolemic hyponatremia. This presentation discusses in detail, the causes of these underlying conditions. Also mentioned are the clinical features and management options and therapeutic sodium targets in patients with hyponatremia. Drugs such as demeclocycline and vaptans (Tolvaptan, Conivaptan) are also mentioned as management options which may be used on a case to case basis. Finally, the all important targets of sodium correction over 24 hours are also mentioned, along with a practical formula for calculation of sodium deficit which is explained with an example.

Systemic lupus erythematous is an autoimmune condition characterised by damage to organ systems due to autoantibodies and immune complex deposition. Genes, epigenetic changes and environment play a role in its pathogenesis. SLE is a truly multi system disease causing widespread clinical manifestations in almost all organ systems. Autoantibodies in SLE are numerous and mainly include ANA, dsDNA, Sm and others.

An omphalocele is a birth defect in which an infant's intestine or other abdominal organs are outside of the body because of a hole in the belly button (navel) area. The intestines are covered only by a thin layer of tissue and can be easily seen.