Mga nangungunang video

Claudication, which is defined as reproducible ischemic muscle pain, is one of the most common manifestations of peripheral arterial occlusive disease (PAOD) caused by atherosclerosis. Claudication occurs during physical activity and is relieved after a short rest. Pain develops because of inadequate blood flow. Examination of a patient with claudication should include a complete lower-extremity evaluation and pulse examination, including measuring segmental pressures. Attempt to palpate pulses from the abdominal aorta to the foot, with auscultation for bruits in the abdominal and pelvic regions. When palpable pulses are not present, a handheld Doppler device may be used to assess circulation.
Temporal arteritis is a condition in which the temporal arteries, which supply blood to the head and brain, become inflamed or damaged. It is also known as cranial arteritis or giant cell arteritis. Although this condition usually occurs in the temporal arteries, it can occur in almost any medium to large artery in the body. The journal Arthritis & Rheumatology states that approximately 228,000 people in the United States are affected by temporal arteritis. According to the American College of Rheumatology, people over the age of 50 are more likely than younger people to develop the condition. Women are also more likely than men to have temporal arteritis. It is most prevalent in people of northern European or Scandinavian descent. Although the exact cause of the condition is unknown, it may be linked to the body’s autoimmune response. Also, excessive doses of antibiotics and certain severe infections have been linked to temporal arteritis. There’s no known prevention. However, once diagnosed, temporal arteritis can be treated to minimize complications.
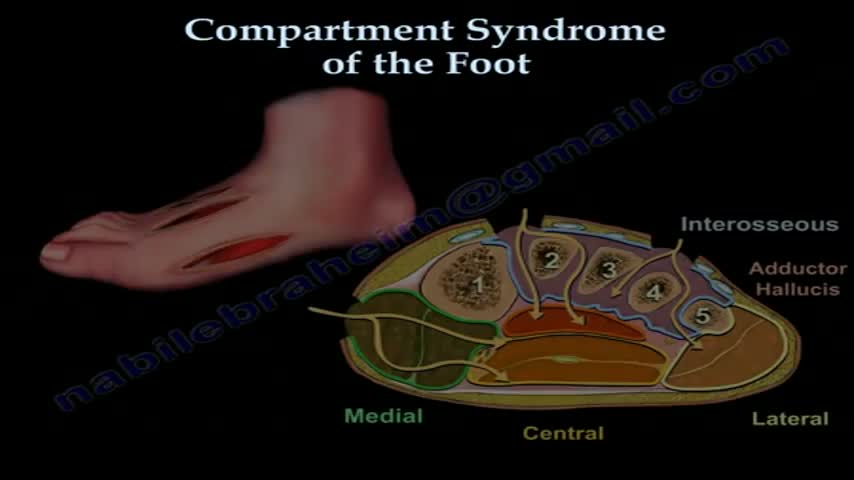
Compartment syndrome can develop in the foot following crush injury or closed fracture. Following some critical threshold of bleeding and/or swelling into the fixed space compartments, arterial pulse pressure is insufficient to overcome the osmotic tissue pressure gradient, leading to cell death. The complicating factor is related to the magnitude of the force of the crush injury. The amount of swelling or bleeding has to be sufficient to impair arterial inflow, while not being of sufficient magnitude to produce an open injury, which decompresses the pressure within the affected compartments. When the injury is open, we then attribute the late disability primarily to the crushing injury to the involved muscles.
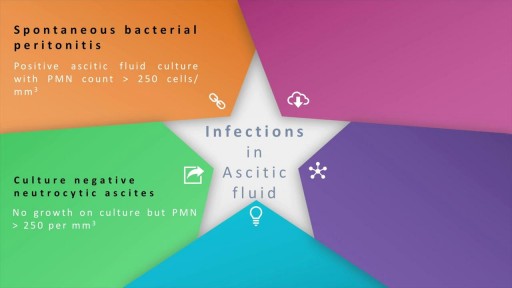
Ascites, the collection of fluid within the peritoneal space is caused due to a variety of causes including cirrhosis, cardiac causes, sinusoidal obstruction syndrome, tubercular peritonitis and pancreatitis, amongst others. Most commonly, the cause of ascots may be cirrhosis , which in turn, is most frequently causes by alcohol use, hepatitis C and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. At the heart of the ascitic fluid analysis is the serum albumin ascitic gradient, the differential diagnosis of which has been discussed in detail in this presentation. Both low SAAG and high SAAG ascites have been dealt with in some depth, with a brief overview of the management of these conditions

There is any chance that the snake is venomous The person has difficulty breathing There is loss of consciousness If you know the snake is not venomous, treat as a puncture wound. 1. Note the Snake's Appearance Be ready to describe the snake to emergency staff. 2. Protect the Person While waiting for medical help: Move the person beyond striking distance of the snake. Have the person lie down with wound below the heart. Keep the person calm and at rest, remaining as still as possible to keep venom from spreading. Cover the wound with loose, sterile bandage. Remove any jewelry from the area that was bitten. Remove shoes if the leg or foot was bitten. Do not: Cut a bite wound Attempt to suck out venom Apply tourniquet, ice, or water Give the person alcohol or caffeinated drinks or any other medications
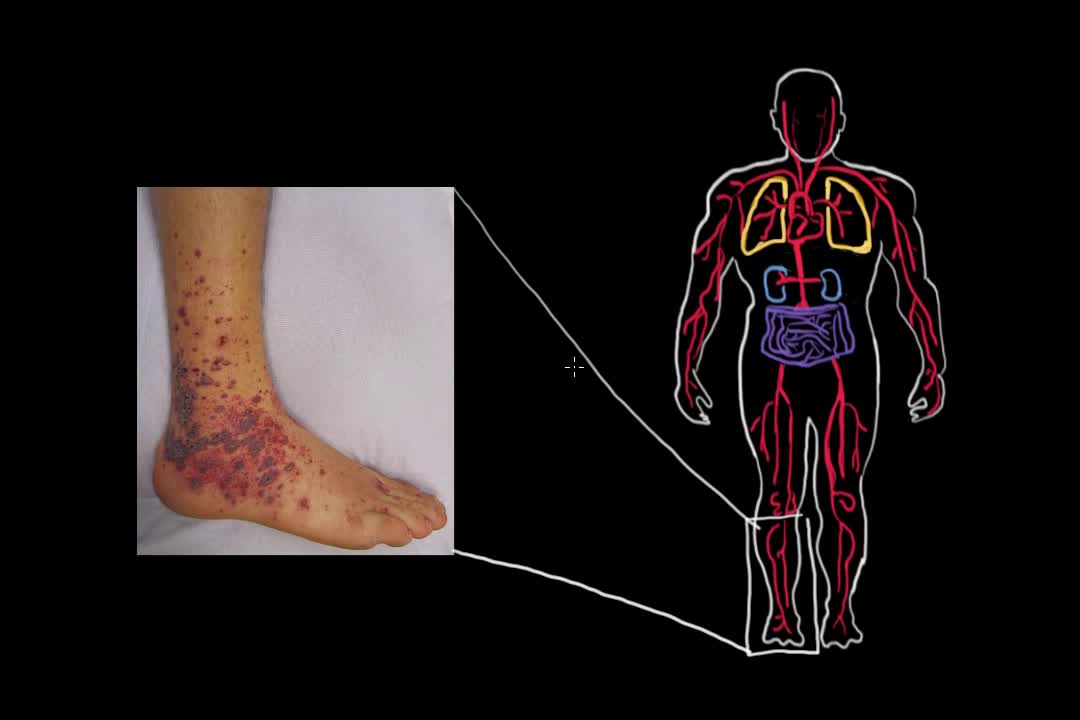
Symptoms of blood clots in specific body locations are as follows: Symptoms of blood clots in legs (deep vein thrombosis (DVT) are pain, redness, and swelling. Symptoms of an arterial blood clot in a limb (leg or arm) include pain, pale color, and coolness to the touch. and the leg is cool and pale.

Atherosclerosis is a process in which blood, fats such as cholesterol, and other substances build up on your artery walls. Eventually, deposits called plaques may form. The deposits may narrow — or block — your arteries. These plaques can also rupture, causing a blood clot.

Arteriosclerosis occurs when the blood vessels that carry oxygen and nutrients from your heart to the rest of your body (arteries) become thick and stiff — sometimes restricting blood flow to your organs and tissues. Healthy arteries are flexible and elastic, but over time, the walls in your arteries can harden, a condition commonly called hardening of the arteries. Atherosclerosis is a specific type of arteriosclerosis, but the terms are sometimes used interchangeably. Atherosclerosis refers to the buildup of fats, cholesterol and other substances in and on your artery walls (plaques), which can restrict blood flow. These plaques can burst, triggering a blood clot. Although atherosclerosis is often considered a heart problem, it can affect arteries anywhere in your body. Atherosclerosis may be preventable and is treatable.
If you're pregnant or might become pregnant, it's critically important to get enough folic acid, the synthetic form of vitamin B9, also known as folate. Folic acid helps prevent neural tube defects (NTDs) – serious birth defects of the spinal cord (such as spina bifida) and the brain (such as anencephaly).
When the hematocrit rises to 60 or 70%, which it often does in polycythemia, the blood viscosity can become as great as 10 times that of water, and its flow through blood vessels is greatly retarded because of increased resistance to flow. This will lead to decreased oxygen delivery.
Hysterectomy is the surgical removal of the uterus. It ends menstruation and the ability to become pregnant. Depending on the reason for the surgery, a hysterectomy may also involve the removal of other organs and tissues such as the ovaries and/or fallopian tubes.

If you’re like me, you probably hook your chest tube up to a Pleur-Evac, put it on the ground, then back away slowly. Who knows what goes on in that mysterious bubbling white box? Hopefully this will post shed some light. Isn’t this just a container for stuff that comes out of the chest? Why does it look so complicated? It’s complicated because the detection/collection of air and fluid require different setups. Most commercial models also allow you to hook the drainage system to wall suction, so you can quickly evacuate the pleural space. This requires its own setup. Because of the need to juggle air, fluid and suction, the most common commercial system includes 3 distinct chambers. If you were to simplify the device, or build one out of spare bottles and tubes, it might look like this:

The most common symptoms of pneumoconiosis are cough and shortness of breath. The risk is generally higher when people have been exposed to mineral dusts in high concentrations and/or for long periods of time. Inadequate or inconsistent use of personal protective equipment (PPE) such as respirators (specially fitted protective masks) is another risk factor since preventing dusts from being inhaled will also prevent pneumoconiosis. Pneumoconiosis does not generally occur from environmental (non-workplace) exposures since dust levels in the environment are much lower.