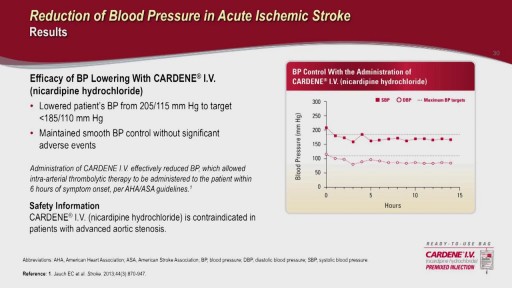
Top videos
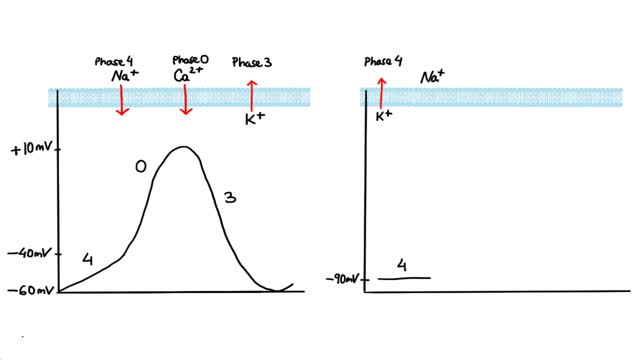
Antiarrhythmics are drugs that are used to treat abnormal heart rhythms resulting from irregular electrical activity of the heart. There are many different types of antiarrhythmic drugs. Examples include: Amiodarone (Cordarone) Flecainide (Tambocor) Procainamide (Procanbid) Sotalol (Betapace) In addition, there are other types of heart drugs that can be used to treat arrhythmias, including: Beta-blockers such as metoprolol or Toprol XL, which reduce the heart's workload and heart rate. Calcium channel blockers such as verapamil or Calan, which also reduces the heart rate.

Home Remedies For Acid Reflux, Ginger For Acid Reflux, Heartburn After Gallbladder Removal --- http://heartburn-acid-reflux.info-pro.co --- Stop using Pepto Bismol until you read the following… There is BREAKING scientific news reporting that many of America’s most popular antacids – both the ones you buy at the drug store and the ones you need prescriptions for… Are linked to more than a dozen forms of potentially DEADLY cancers. Click this link now to get the full story and see if you’re at risk. You’ll find out about a “just discovered” alternative to antacids…. Something that can permanently cure even the worst cases of acid reflux in as little few days, and that doesn’t require any pills or medications. Click Here: http://heartburn-acid-reflux.info-pro.co
De Quervain's tenosynovitis (dih-kwer-VAINS ten-oh-sine-oh-VIE-tis) is a painful condition affecting the tendons on the thumb side of your wrist. If you have de Quervain's tenosynovitis, it will probably hurt when you turn your wrist, grasp anything or make a fist. Although the exact cause of de Quervain's tenosynovitis isn't known, any activity that relies on repetitive hand or wrist movement — such as working in the garden, playing golf or racket sports, or lifting your baby — can make it worse. Symptoms ShareTweet June 13, 2015 References Products and Services Mayo Clinic Sports Medicine Newsletter: Mayo Clinic Health Letter See also Prednisone risks, benefits Prednisone withdrawal: Why taper down slowly? Integrative approaches to treating pain Lifestyle strategies for pain management Nutrition and pain Pain rehabilitation Self-care approaches to treating pain Show more Advertisement Mayo Clinic does not endorse companies or products. Advertising revenue supports our not-for-profit mission. Advertising & Sponsorship PolicyOpportunitiesAd Choices Mayo Clinic Store Check out these best-sellers and special offers on books and newsletters from Mayo Clinic. NEW! – The Mayo Clinic Diet, Second Edition Healthy Heart for Life! Mayo Clinic on Better Hearing and Balance Treatment Strategies for Arthritis The Mayo Clinic Diet Online
surgical procedure used to remove excess skin and fat from the abdomen and to tighten the muscles of the abdominal wall. Most tummy tuck patients are dealing with the effects of pregnancies and weight loss and find themselves with loose skin in spite of exercise and weight control. Each year, thousands of Americans undergo a tummy tuck to tone, firm and define the abdominal area.

Cases of some sexually transmitted diseases have reached an all-time high, according to a new report from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. From 2014 to 2015, there was a 6% increase in diagnosed cases of chlamydia and a 13% increase in gonorrhea.

http://eliminar-celulite.plus101.com --- Exercicios Para Celulite, Redução De Celulite, O Que Da Celulite, Como Melhorar Celulite. Primeiro eu criei uma lista dos músculos da parte de trás, e aqui estão eles, começando da parte de cima (região dos quadris) e descendo até os tornozelos: Glúteo máximo Glúteo médio Glúteo mínimo Tensor da fascia lata Piriforme Semimembranoso Semitendinoso Bíceps femoral Sartorio Popliteo Soleo Gastrocnêmio Músculo Plantar Tibial Posterior São 14 aí - e eu nem listei os que estão em um nível mais profundo. Tampouco listei os músculos menores que têm um papel importante em sua biomecânica e são as camadas musculares que são estimuladas para tonificação, levantamento e suavização das camadas de pele que cobrem esses músculos. Agora que você sabe onde a causa da reversão da celulite acontece, você pode entender por que agora é possível que você se livre de problemas com a celulite em suas áreas problemáticas e pontos críticos. Então assistir ao vídeo de apresentação fará muito mais sentido agora. http://eliminar-celulite.plus101.com
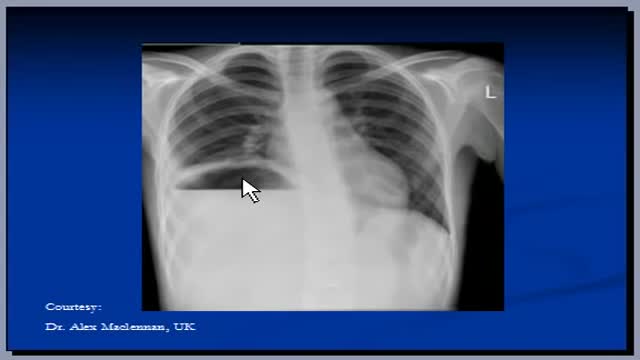
Suspect that a patient has a subphrenic abscess if he deteriorates, or recovers and then deteriorates, between the 14th and the 21st day after a laparotomy, with a low, slowly increasing, swinging fever, sweating, and a tachycardia. This, and a leucocytosis, show that he has ''pus somewhere', which is making him anorexic, wasted, and ultimately cachectic. If he has no sign of a wound infection, a rectal examination is negative, and his abdomen is soft and relaxed, the pus is probably under his diaphragm. The pus might be between his diaphragm and his liver, in (1) his right or (2) his left subphrenic space, or under his liver in (3) his right or (4) his left subhepatic space in his lesser sac. He may have pus in more than one of these spaces. Explore him on the suspicion that he might have a subphrenic abscess. Exploration is not a major operation; the difficulty is knowing where to explore, so refer him if you can. If you cannot refer him, explore him yourself. If you fail to find pus, you have done him no harm; missing a subphrenic abscess is far worse. If it is anterior, you can drain it by going under his costal margin anteriorly. If it is posterior, you can go through the bed of his 12th rib posteriorly.
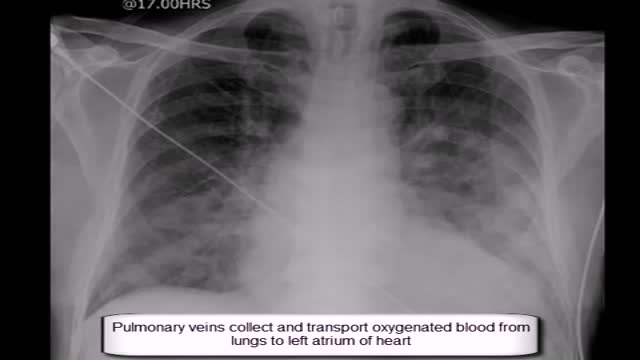
Expand Section. Pulmonary edema is often caused by congestive heart failure. When the heart is not able to pump efficiently, blood can back up into the veins that take blood through the lungs. As the pressure in these blood vessels increases, fluid is pushed into the air spaces (alveoli) in the lungs.
Syringomyelia (sih-ring-go-my-E-lee-uh) is the development of a fluid-filled cyst (syrinx) within your spinal cord. Over time, the cyst may enlarge, damaging your spinal cord and causing pain, weakness and stiffness, among other symptoms. Syringomyelia has several possible causes, though the majority of cases are associated with a condition in which brain tissue protrudes into your spinal canal (Chiari malformation). Other causes of syringomyelia include spinal cord tumors, spinal cord injuries and damage caused by inflammation around your spinal cord. If syringomyelia isn't causing any problems, monitoring the condition may be all that's necessary. But if you're bothered by symptoms, you may need surgery.
Syringomyelia is a cystic cavitation of the spinal cord associated with Chiari I malformation (70%) or basilar invagination (10%) or tumor. It may be a post-traumatic condition. There are 2 main forms: communicating with the central canal or subarachnoid spaces (Chiari I malformation); non communicating (trauma, tumors).
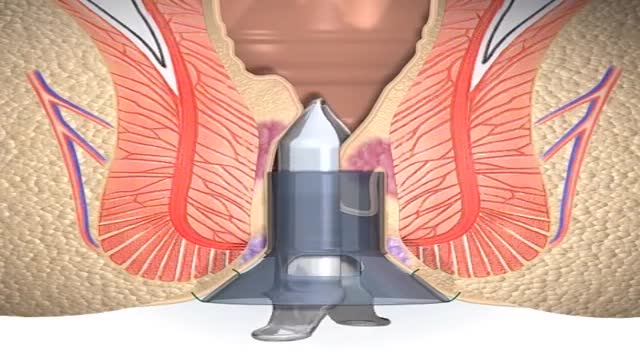
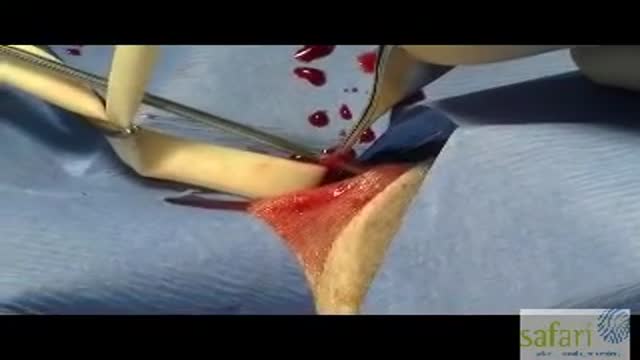
A stapled haemorrhoidopexy is an operation to return the haemorrhoids to a normal. position inside the rectum (back passage). A circular shaped stapling device is gently. inserted in the back passage. The surgeon is then able to use the device to remove.