Top Videos
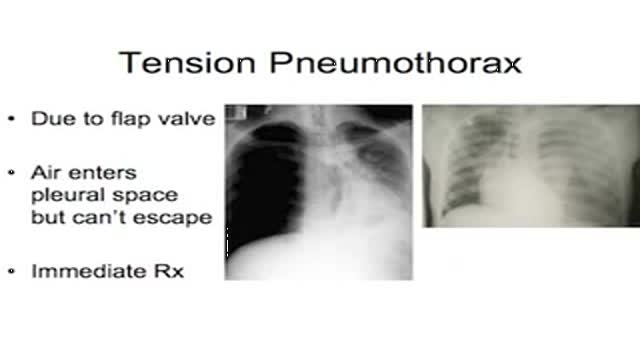
• Define and use related medical terminology.
• Describe and demonstrate techniques for imaging the thyroid gland.
• Discuss functional abnormalities of the thyroid gland.
• Correlate laboratory data relevant to the thyroid and parathyroid glands.
• Describe, and recognize on images, pathologies of the thyroid gland.
• Identify the anatomy of the parathyroid glands on diagrams and sonograms.
• Describe and demonstrate techniques for imaging the parathyroid glands.
• Describe, and recognize on images, pathologies of the parathyroid glands.
• List and describe other neck masses.
• Follow relevant protocols when scanning.
• Differentiate the sonographic appearances of the female reproductive organs in relation to the menstrual cycle, the use of contraceptives and hormone replacement, and following chemotherapy.
• Explain the Patient Privacy Rule (HIPAA) and Patient Safety Act (see reference).
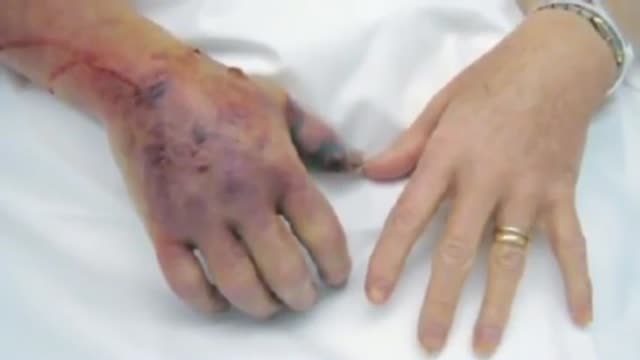
Two types of clinically distinct necrotizing fasciitis have been described. The most common form (type II) usually occurs in individuals with no concurrent medical illness. Many patients report a history of laceration, blunt trauma, or a surgical procedure as a predisposing factor. It is typically caused by group A Streptococcus (Streptococcus pyogenes). In contrast, type I is usually seen in patients with underlying diabetes and peripheral vascular disease. It is generally a polymicrobial infection; some commonly isolated organisms include Staphylococcus aureus, Bacteroides tragi/is, Escherichia coli, group A Streptococcus, and Pre vote/fa species. Crepitus is more common if anaerobic organisms, such as Clostridium perfringens or 8 tragi/is, are involved.
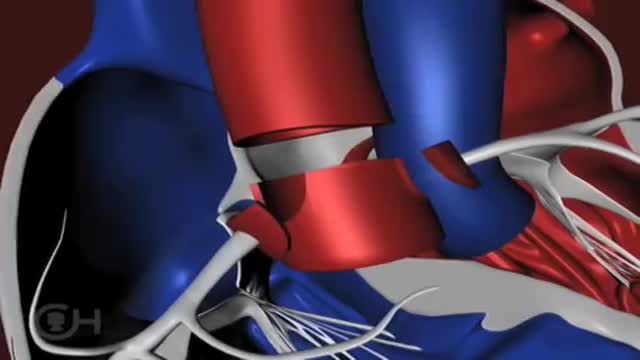
The "great arteries" in this anomaly refer to the aorta and the pulmonary artery, the two major arteries carrying blood away from the heart. In cases of transposition of the great arteries, these vessels arise from the wrong ventricle. They are "transposed" from their normal position so that the aorta arises from the right ventricle and the pulmonary artery from the left ventricle. Other heart defects may occur along with transposition of the great arteries. About 25 percent of children with transposition will also have a ventricular septal defect (VSD) . In nearly a third, the branching pattern of the coronary arteries as they leave the transposed aorta is unusual. Infants may also have narrowing below the pulmonary valve that blocks blood flow from the left ventricle to the lungs.
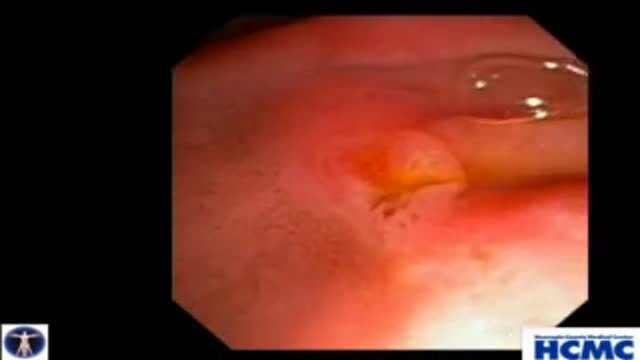
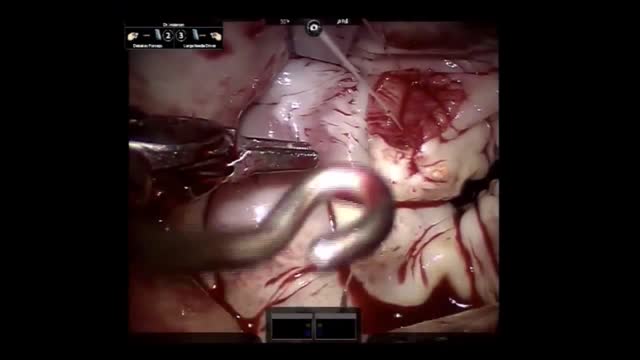
This 38 year old woman has increasingly intractable RUQ pain after cholecystectomy done one year prior. LFTs and pancreatic enzymes have been normal, and ducts are non-dilated, thus she is a Type III possible SOD patient. Initial goal is to define course of pancreatic duct for manometry. 5-4-3 Co...ntour catheter (Boston Scientific) is used to perform the pancreatogram which shows a small straight distal duct. The aspirating triple lumen manometry catheter (Wilson Cook) is used to cannulate the pancreatic duct, with continuous aspiration of fluid once the duct is entered. Careful stationed pullthrough manometry shows markedly abnormal basal pressures in both leads in the pancreatic sphincter. Plan is dual pancreatic and biliary sphincterotomy. Biliary manometry will not now change our plan therefore is omitted. Our first goal is to access the pancreatic duct so we can guarantee wire access for placement of a small caliber pancreatic stent which is critical for safety. Contrast is injected as the 0.018in Roadrunner wire (Wilson Cook) is advanced in order to outline the course of main duct. A separate biliary orifice is clearly seen, unusual in SOD patients. A soft 4Fr 3cm single inner flange pancreatic stent (Hobbs Medical) is placed. We did not want to use our typical 9cm long unflanged stent as even a 3 or 4 French stent might be traumatic to the tiny caliber of this duct out in the body of the gland. Next the bile duct is cannulated with a papillotome (Autotome 39, Boston Scientific), showing a small perhaps 6mm bile duct. Biliary sphincterotomy is performed in very careful stepwise fashion as landmarks are unclear and perforation is higher risk in small duct SOD patients. On the other hand, inadequate sphincterotomies offer limited chance of symptom relief. You can see here a patulous sphincterotomy. Next a pancreatic sphincterotomy is performed with the needle knife (Boston Scientific) over the pancreatic stent. Again this is performed cautiously due to the small size of the pancreatic duct. We are reaching along the stent and cutting the fibers deeply. This is a limited pancreatic sphincterotomy due to small pancreatic duct size, and concern for scarring of the pancreatic duct. It is important to document passage of the stent by xray or remove it endoscopically with two weeks or so. We and many other specialized centers perform dual sphincterotomies at the first ERCP in all SOD patients with abnormal pancreatic manometry and frequent or intractable symptoms based on the belief that response rates are better than for biliary sphincterotomy alone.