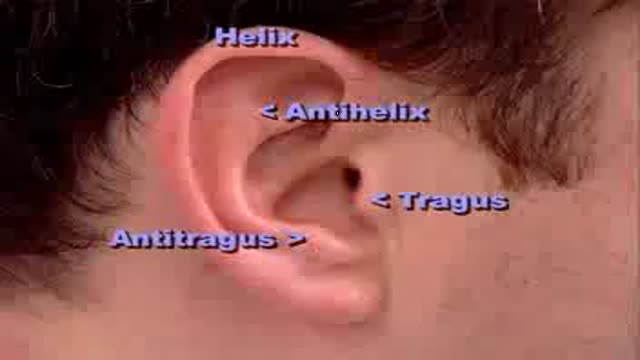
Physical Examination
Breast cancer is a malignant tumor that develops from the cells of
the breast. It is the most common type of cancer among women in
the United States. It is most often curable when found early. The
normal breast consists of three main components: the lobules
(milk-producing glands), the ducts (thin tubes that connect the
lobules to the nipple) and the stroma (fatty tissue and ligaments
surrounding the ducts and lobules, blood vessels, and lymphatic
vessels). About 80% of breast cancers start in the ducts.
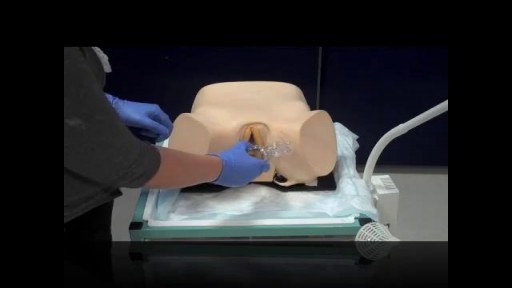
Pelvic examinations during labor are used for several purposes, among them assessment of cervical dilatation, effacement, station of the presenting part, presentation, position, and pelvic capacity.Instruction in these techniques is particularly important for those health care providers involved in labor management, including physicians, nurses, midwives, paramedics and EMT personnel.
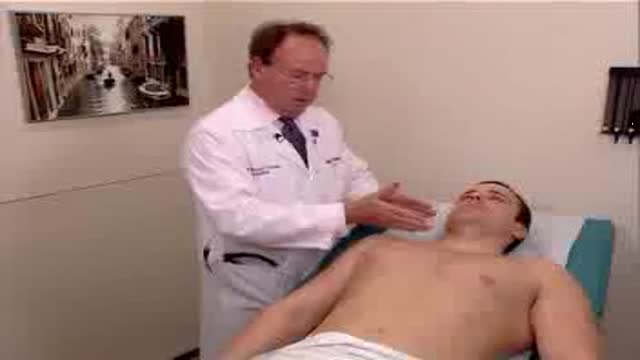
Observation of both jugular veins can provide a reliable indication of the volume and pressure in the right side of the heart since internal jugular veins pulsate in response to phasic changes in right atrial pressure. Proper positioning of the patient to increase the effects of gravity enhances distention of the jugular veins and, therefore, increases the ability to observe venous pulsations.

Optimal blood pressure typically is defined as 120 mm Hg systolic — which is the pressure as your heart beats — over 80 mm Hg diastolic — which is the pressure as your heart relaxes. For your resting heart rate, the target is between 60 and 100 beats per minute (bpm)

The Motor Assessment Scale (MAS) is a performance-based scale that was developed as a means of assessing everyday motor function in patients with stroke (Carr, Shepherd, Nordholm, & Lynne, 1985). The MAS is based on a task-oriented approach to evaluation that assesses performance of functional tasks rather than isolated patterns of movement