Physical Examination

Facial Tenderness
1. Ask the patient to tell you if these maneuvers causes excessive discomfort or pain. ++
2. Press upward under both eyebrows with your thumbs.
3. Press upward under both maxilla with your thumbs.
4. Excessive discomfort on one side or significant pain suggests sinusitis.
Sinus Trans illumination 1. Darken the room as much as possible. ++
2. Place a bright otoscope or other point light source on the maxilla.
3. Ask the patient to open their mouth and look for an orange glow on the hard palate.
4. A decreased or absent glow suggests that the sinus is filled with something other than air.
Temporomandibular Joint 1. Place the tips of your index fingers directly in front of the tragus of each ear. ++
2. Ask the patient to open and close their mouth.
3. Note any decreased range of motion, tenderness, or swelling.
The Knee Exam
Observation:
1. Make sure that both knees are fully exposed. The patient should be in either a gown or shorts. Rolled up pant legs do not provide good exposure!
2. Watch the patient walk. Do they limp or appear to be in pain? When standing, is there evidence of bowing (varus) or knock-kneed (valgus) deformity? There is a predilection for degenerative joint disease to affect the medical aspect of the knee, a common cause of bowing. Varus Knee Deformity, more marked on the left leg. 3. Make note of any scars or asymmetry. Chronic/progressive damage, as in degenerative joint disease, may lead to abnormal contours and appearance. Is there obvious swelling as would occur in an effusion? Redness suggesting inflammation? 4. Is there evidence of atrophy of the quadriceps, hamstring, or calf muscle groups? Knee problems/pain can limit the use of the affected leg, leading to wasting of the muscles.
While both legs have well developed musculature,
the left calf and hamstring are bulkier than the right. 5. Look at the external anatomy, noting structures above and below the knee itself: 1. Patella 2. Patellar tendon 3. Quadriceps/Hamstring/Calf muscles 4. Medial and lateral joint lines. 5. Femur and Tibia 6. Tibial tuberosity
Ballotment (helpful if the effusion is large) 1. Slightly flex the knee which is to be examined.
2. Place one hand on the supra-pateallar pouch, which is above the patella and communicates with the joint space. Gently push down and towards the patella, forcing any fluid to accumulate in the central part of the joint.
3. Gently push down on the patella with your thumb.
4. If there is a sizable effusion, the patella will feel as if it's floating and "bounce" back up when pushed down.

Common Benign Pain Syndromes--Symptoms and Etiology:
1. Non-specific musculoskeletal pain: This is the most common cause of back pain. Patients present with lumbar area pain that does not radiate, is worse with activity, and improves with rest. There may or may not be a clear history of antecedent over use or increased activity. The pain is presumably caused by irritation of the paraspinal muscles, ligaments or vertebral body articulations. However, a precise etiology is difficulty to identify.
2. Radicular Symptoms: Often referred to as "sciatica," this is a pain syndrome caused by irritation of one of the nerve roots as it exits the spinal column. The root can become inflamed as a result of a compromised neuroforamina (e.g. bony osteophyte that limits size of the opening) or a herniated disc (the fibrosis tears, allowing the propulsus to squeeze out and push on the adjacent root). Sometimes, it's not precisely clear what has lead to the irritation. In any case, patient's report a burning/electric shock type pain that starts in the low back, traveling down the buttocks and along the back of the leg, radiating below the knee. The most commonly affected nerve roots are L5 and S1.
3. Spinal Stenosis: Pain starts in the low back and radiates down the buttocks bilaterally, continuing along the backs of both legs. Symptoms are usually worse with walking and improve when the patient bends forward. Patient's may describe that they relieve symptoms by leaning forward on their shopping carts when walking in a super market. This is caused by spinal stenosis, a narrowing of the central canal that holds the spinal cord. The limited amount of space puts pressure on the nerve roots when the patient walks, causing the symptoms (referred to as neurogenic claudication). Spinal stenosis can be congenital or develop over years as a result of djd of the spine. As opposed to true claudication (pain in calfs/lower legs due to arterial insufficiency), pain resolves very quickly when person stops walking and assumes upright position. Also, peripheral pulses should be normal.
4. Mixed symptoms: In some patients, more then one process may co-exist, causing elements of more then one symptom syndrome to co-exist.
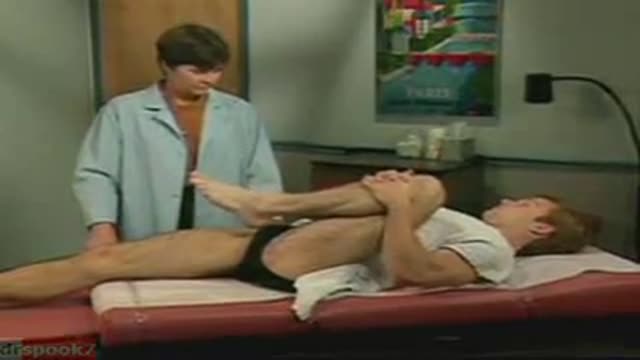
Function and Anatomy: The hip is a ball and socket type joint, formed by the articulation of the head of the femur with the pelvis. Normal range of motion includes: abduction 45 degrees, adduction 20-30 degrees, flexion 135 degrees, extension 30 degrees, internal and external rotation. Hip pathology can cause symptoms anywhere around the joint, though frequently pain is anterior and radiates to the groin region. Additionally, pathology outside of the hip can be referred to this region. History and exam obviously help in making these distinctions.