Top videos
A ureteral stent, sometimes as well called ureteric stent, is a thin tube inserted into the ureter to prevent or treat obstruction of the urine flow from the kidney. The length of the stents used in adult patients varies between 24 to 30 cm.

Pinch air out of the tip of the condom. Unroll condom all the way down the penis. After sex but before pulling out, hold the condom at the base. Then pull out, while holding the condom in place. Carefully remove the condom and throw it in the trash.
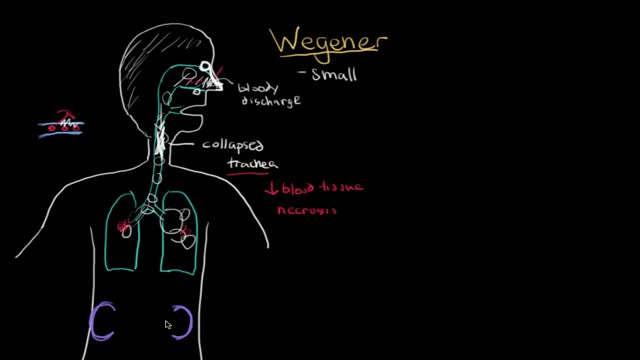
Microscopic polyangiitis (MPA) is vasculitis of small vessels. It was initially considered as a microscopic form of polyarteritis nodosa (PAN). In 1990, the American College of Rheumatology developed classification criteria for several types of systemic vasculitis but did not distinguish between polyarteritis nodosa and microscopic polyarteritis nodosa. [1] In 1994, a group of experts held an international consensus conference in Chapel Hill, North Carolina, to attempt to redefine the classification of small vessel vasculitides. [2, 3]
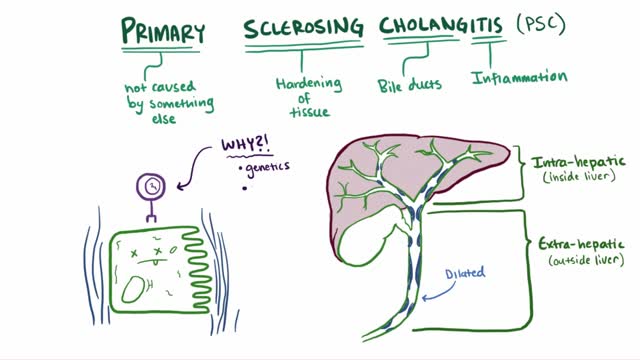
Primary sclerosing (skluh-ROHS-ing) cholangitis (koh-lan-JIE-tis) is a disease of the bile ducts, which carry the digestive liquid bile from your liver to your small intestine. In primary sclerosing cholangitis, inflammation causes scars within the bile ducts. These scars make the ducts hard and narrow and gradually cause serious liver damage. In most people with primary sclerosing cholangitis, the disease progresses slowly and can lead to liver failure, repeated infections, and tumors of the bile duct or liver. Liver transplant is the only known cure for primary sclerosing cholangitis. The search for other treatments to slow or stop primary sclerosing cholangitis is ongoing, and scientists have turned up many promising leads. Until better treatments are proved safe and effective, though, care for primary sclerosing cholangitis focuses on monitoring liver function, managing symptoms and, when possible, doing procedures that temporarily open blocked bile ducts.
mammoplasty, is a surgical enhancement procedure to accentuate the size and shape of a woman’s breasts. While breast augmentation will make the breasts larger, the surgery will not move the breasts closer together or lift sagging breasts. Breast augmentation is tremendous help to patients who desire a fuller profile, who have lost breast volume due to pregnancy or nursing, or who have undergone breast reconstruction and want to gain a more natural look again.
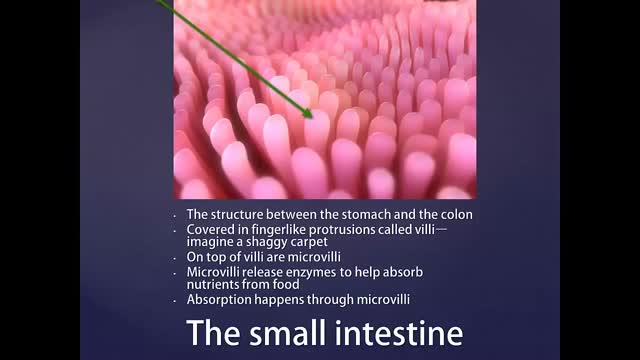
The symptoms of bacterial overgrowth include nausea, flatus, constipation, bloating, abdominal distension, abdominal pain or discomfort, diarrhea, fatigue, and weakness. SIBO also causes an increased permeability of the small intestine. Some patients may lose weight.

Leading cardiologists Valentin Fuster, MD, PhD, Director of Mount Sinai Heart and Herschel Sklaroff, MD, Clinical Professor of Medicine, Cardiology at Mount Sinai Heart were filmed for one-month for the “Making Rounds” documentary film as they cared for critically-ill heart patients in the Cardiac Care Unit at The Mount Sinai Hospital.
Watch Mount Sinai Heart doctors, fellows, residents, and nurses in action and saving lives demonstrating how simply listening to patients at the bedside remains medicine’s most indispensable tool over any technology.
In this film Mount Sinai Heart helps preserve the disappearing art and science of how to examine and diagnose patients at the bedside for future generations of physicians.
**This film was made possible by the generous support
of the McInerney Family.**
Copyright 2015 Middlemarch Films, Inc
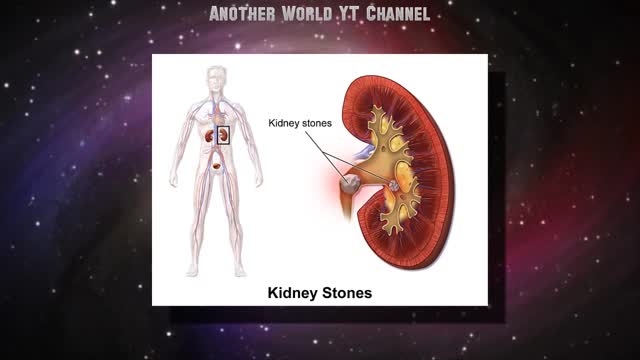
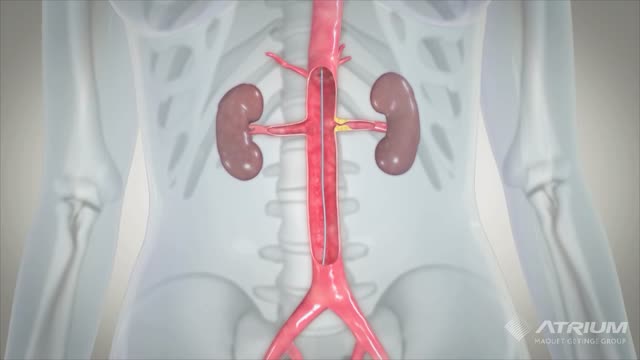
A kidney stone may not cause symptoms until it moves around within your kidney or passes into your ureter — the tube connecting the kidney and bladder. At that point, you may experience these signs and symptoms: Severe pain in the side and back, below the ribs Pain that spreads to the lower abdomen and groin Pain that comes in waves and fluctuates in intensity Pain on urination Pink, red or brown urine Cloudy or foul-smelling urine Nausea and vomiting Persistent need to urinate Urinating more often than usual Fever and chills if an infection is present Urinating small amounts of urine Pain caused by a kidney stone may change — for instance, shifting to a different location or increasing in intensity — as the stone moves through your urinary tract.
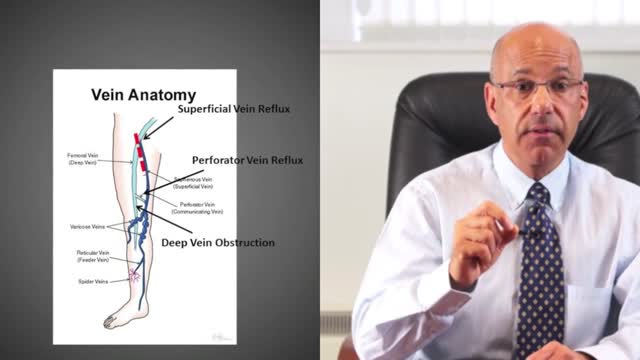
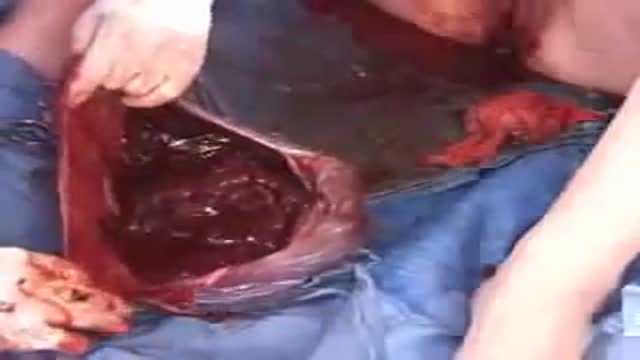
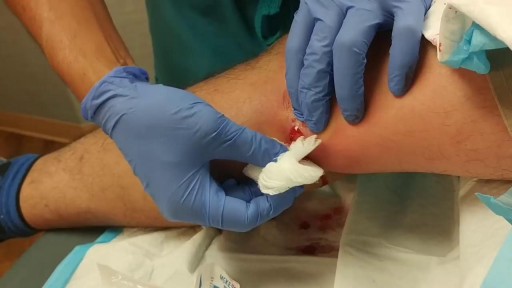
A leg ulcer is simply a break in the skin of the leg, which allows air and bacteria to get into the underlying tissue. This is usually caused by an injury, often a minor one that breaks the skin. In most people such an injury will heal up without difficulty within a week or two. However, when there is an underlying problem the skin does not heal and the area of breakdown can increase in size. This is a chronic leg ulcer.
Sclerotherapy is a medical procedure used to eliminate varicose veins and veins. Sclerotherapy involves an injection of a solution (generally a salt solution) directly into the vein. The solution irritates the lining of the blood vessel, causing it to collapse and stick together and the blood to clot.
Recommended range without diabetes is 70 to 130mg/dL. (The standard for measuring blood glucose is "mg/dL" which means milligrams per deciliter.) If your blood glucose level is above 130mg/dL, that's fasting hyperglycemia. Fasting hyperglycemia is a common diabetes complication.

The thyroid gland lies in the midline of the anterior neck, just caudal to the thyroid cartilage. To inspect the thyroid gland, the examiner stands in front of the patient. The examiner asks the seated patient to dorsiflex (extend) the neck and swallow a sip of water. Minor enlargement of the gland may only become apparent on inspection in this position. Palpation of the thyroid gland is typically performed with the examiner standing behind the patient. Both lobes and the isthmus of the thyroid gland should be palpated for any nodules or diffuse enlargement. Mobility of the thyroid gland with swallowing should be assessed with palpation. Nodules arising from the thyroid gland typically move with swallowing. A hard, fixed thyroid gland could indicate malignancy. If a central nodule is identified, the patient is asked to protrude the tongue. Upward movement of the central nodule on protrusion of the tongue indicates a thyroglossal cyst. Auscultation is performed at the superior poles of bilateral lobes as this is where the superior thyroid artery is most superficial and bifurcates into its terminal branches. A bilateral bruit over the superior poles suggests Graves disease. Examination of the thyroid gland is completed by palpating the regional cervical lymph nodes for any enlargement.
Subscribe to AMBOSS YouTube for the latest clinical examination videos, medical student interviews, study tips and tricks, and live webinars!
Free 5 Day Trial: https://go.amboss.com/amboss-YT
Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/amboss_med/
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/AMBOSS.Med/
Twitter: https://twitter.com/ambossmed
Blog: https://blog.amboss.com/us
#AMBOSSMed #ClinicalExamination #USMLE