Top videos

Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency (Alpha-1) is a genetic (inherited) condition – it is passed from parents to their children through their genes. Alpha-1 may result in serious lung disease in adults and/or liver disease at any age.
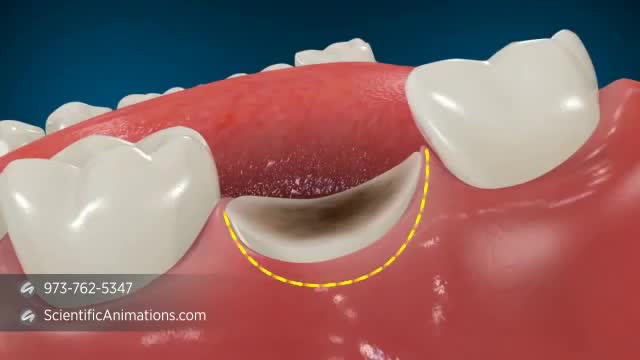
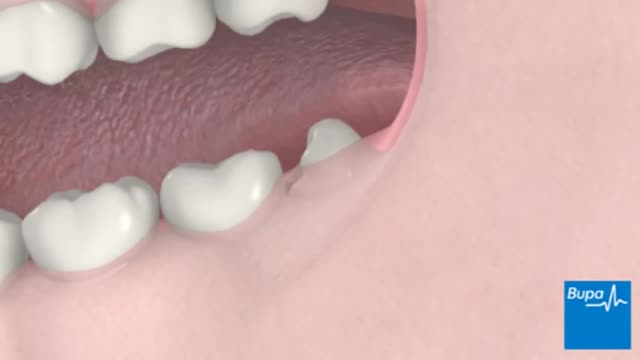
A palatal view of a maxillary premolar during a crown lengthening procedure. Crown lengthening is a surgical procedure performed by a dentist to expose a greater amount of tooth structure for the purpose of subsequently restoring the tooth prosthetically.
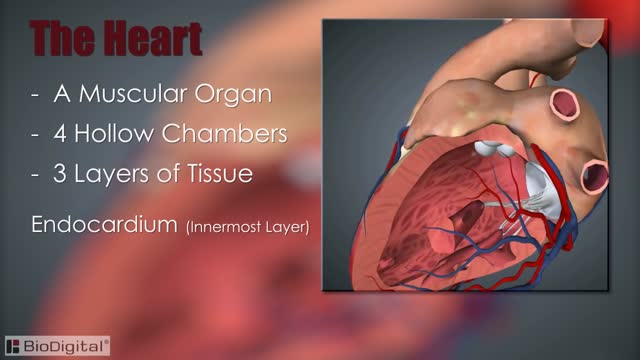
The heart, blood vessels, and blood are the parts that make up the circulatory system, which is defined as a closed system of blood vessels for the transport of gasses and nutrients. The heart is the key organ in the circulatory system. As a hollow, muscular pump, its main function is to propel blood throughout the body.

How to Use Wash your hands. Check the drug label to be sure it is what your doctor prescribed. ... Remove pen cap. Look at the insulin. Wipe the tip of the pen where the needle will attach with an alcohol swab or a cotton ball moistened with alcohol.
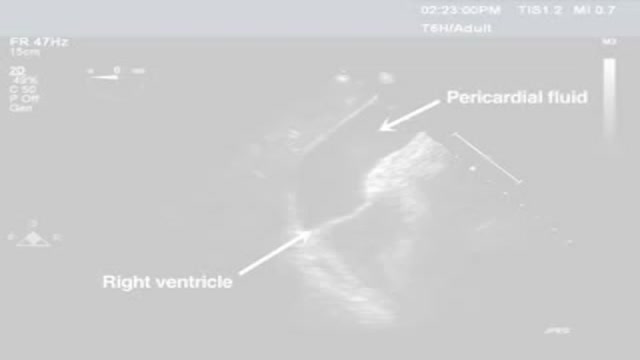
Pericardiocentesis is the aspiration of fluid from the pericardial space that surrounds the heart. This procedure can be life saving in patients with cardiac tamponade, even when it complicates acute type A aortic dissection and when cardiothoracic surgery is not available. [1] Cardiac tamponade is a time sensitive, life-threatening condition that requires prompt diagnosis and management. Historically, the diagnosis of cardiac tamponade has been based on clinical findings. Claude Beck, a cardiovascular surgeon, described 2 triads of clinical findings that he found associated with acute and chronic cardiac tamponade. The first of these triads consisted of hypotension, an increased venous pressure, and a quiet heart. It has come to be recognized as Beck's triad, a collection of findings most commonly produced by acute intrapericardial hemorrhage. Subsequent studies have shown that these classic findings are observed in only a minority of patients with cardiac tamponade. [2] The detection of pericardial fluid has been facilitated by the development and continued improvement of echocardiography. [3] Cardiac ultrasound is now accepted as the criterion standard imaging modality for the assessment of pericardial effusions and the dynamic findings consistent with cardiac tamponade. With echocardiography, the location of the effusion can be identified, the size can be estimated (small, medium, or large), and the hemodynamic effects can be examined by assessing for abnormal septal motion, right atrial or right ventricular inversion, and decreased respiratory variation of the diameter of the inferior vena cava.
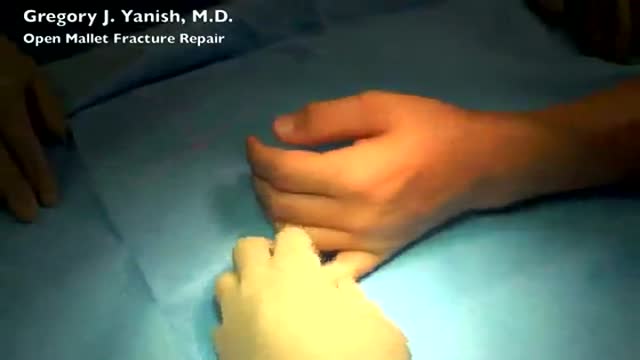
The term mallet finger has long been used to describe the deformity produced by disruption of the terminal extensor mechanism at the distal interphalangeal (DIP) joint. Mallet finger is the most common closed tendon injury that is seen in athletes; this injury is also common in nonathletes after "innocent" trauma. Mallet finger has also been referred to as drop, hammer, or baseball finger (although baseball accounts for only a small percentage of such injuries).
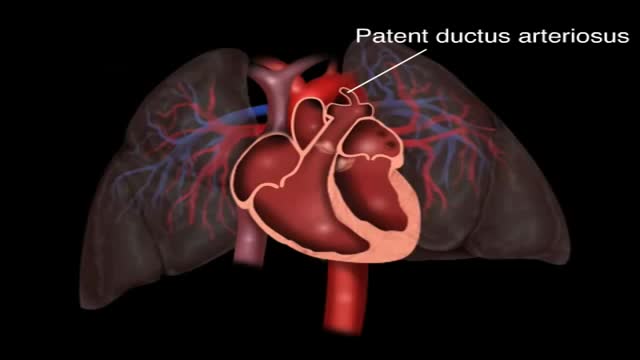
Patent ductus arteriosus (PDA) is a persistent opening between two major blood vessels leading from the heart. The opening, called the ductus arteriosus, is a normal part of a baby's circulatory system before birth that usually closes shortly after birth. If it remains open, however, it's called a patent ductus arteriosus.
This syndrome was previously known as reflex sympathetic dystrophy, algodystrophy, causalgia, Sudeck atrophy, transient osteoporosis, and acute atrophy of bone. Usually occurring after an injury, CRPS presents with pain out of proportion to the injury, temperature change, edema, and abnormal skin color. Type I CRPS (90% of CRPS cases) occurs without a definable nerve lesion, while type II occurs with a definable nerve lesion. The pathogenesis is likely due to an injury causing increased sensitivity to sympathetic nerves, an abnormal response to and sensation of pain, and increased neuropeptide release causing burning pain to light touch (allodynia).
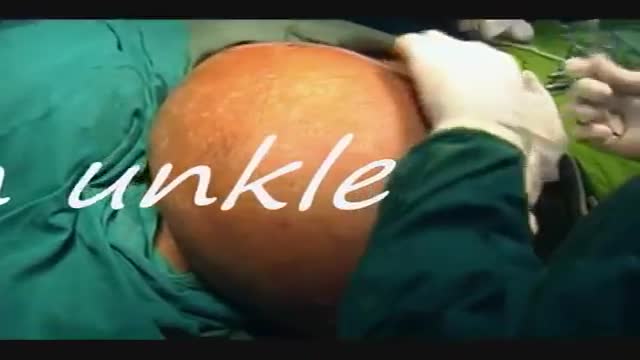
Lipomas are slow-growing soft tissue tumours that rarely reach a size larger than 2 cm. Lesions larger than 5 cm, so-called giant lipomas, can occur anywhere in the body but are seldom found in the upper extremities. The authors present their experiences with eight patients having giant lipomas of the upper extremity. In addition, a review of the literature, and a discussion of the appropriate evaluation and management are included.
http://www.landging.com/skeletal-system-animation-aci-surgery.html
Designed for medical research organization, this skeletal system animation demonstrates the new concept of ACI (autologous chondrocyte implantation) surgery procedure.

A man's age matters. As men get older, the chances of conceiving and having a healthy child decline. Male fertility starts to decline after 40 when sperm quality decreases. This means it takes longer for their partners to conceive and when they do, there's an increased risk of miscarriage.