Top Videos
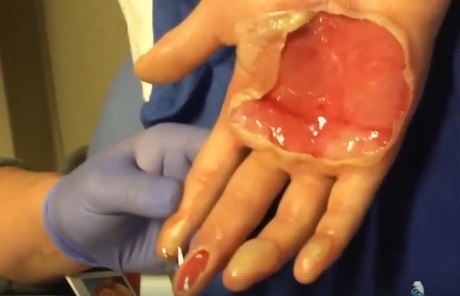
Treatment may not be needed for an eschar if it is part of the natural healing process. However, if an eschar looks like it may have a wound infection – symptoms can include oozing fluid such as pus or blood, your clinician will likely recommend topical treatment or debridement to help control and remove the infection.

A testicular examination is mainly performed on male patients who present with testicular pathology e.g. pain, swelling, a lump. Although titled testicular examination it involves the examination of the penis, scrotum and testes. As this is an intimate examination it is pertinent to gain a good rapport with your patient, maintain good communication and ensure the patient’s dignity at all times. Remember to offer a chaperone for this skill. For the purposes of your exam, you will most likely be examining a mannequin.
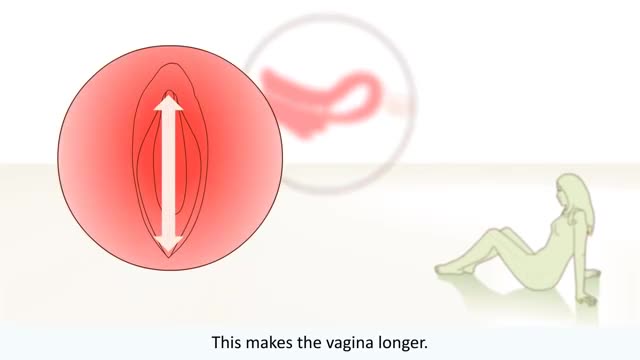
The big bang is the moment when the uterus, vagina, and anus contract simultaneously at 0.8-second intervals. A small orgasm may consist of three to five contractions; a biggie, 10 to 15. Many women report feeling different kinds of orgasms

A digital rectal examination (DRE) is a simple procedure doctors use to examine the lower rectum and other internal organs. A DRE is done for a number of reasons. It's a quick, easy way to check the health of a man's prostate gland. It can detect conditions like an enlarged prostate

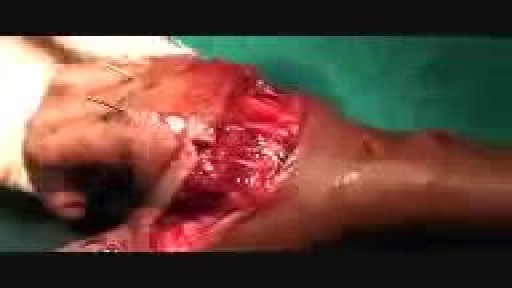
Warning: This video contains actual surgical footage, which may not be suitable for all viewers.
To learn more about coronary artery bypass surgery, please visit http://cle.clinic/3b7dqpE
Cardiothoracic surgeon Faisal Bakaeen, MD, discusses how he does single and bilateral internal mammary arteries, and the benefits of doing this type of coronary artery bypass.
If you liked the video hit like and subscribe for more!
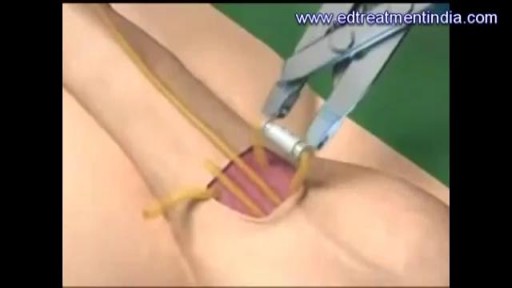
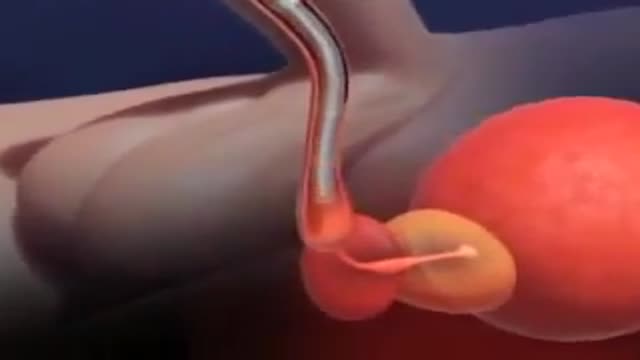
A penile prosthesis is another treatment option for men with erectile dysfunction. These devices are either malleable (bendable) or inflatable. The simplest type of prosthesis consists of a pair of malleable rods surgically implanted within the erection chambers of the penis. With this type of implant the penis is always semi-rigid and merely needs to be lifted or adjusted into the erect position to initiate sex. This type of implant is a good choice for men with spinal cord injuries and/or limited hand strength. Today, many men choose a hydraulic, inflatable prosthesis, which allows them to have an erection when they choose, and it's easier to conceal. It is also more natural. A penile implant is usually used when there is a clear medical cause for ED and when the problem is unlikely to resolve or improve naturally or with other medical treatments. Sometimes a penile prosthesis is implanted during surgery to reconstruct the penis when scarring has caused erections to curve (Peyronie's disease). Penile implant surgeries take about an hour and are typically done in an outpatient center. A man can resume sexual intercourse by 6 weeks after surgery.

Acclaimed sexologist Hanny Lightfoot-Klein, author of several highly illuminating books on genital mutilation, discusses compromises in orgasm after male circumcision. Also commenting is cultural anthropologist James De Meo.From the groundbreaking documentary film, "Whose Body, Whose Rights?"

Transgender Man Gives Birth to Healthy Baby, Talks Navigating Pregnancy as a Man Trystan Reese is a transgender man who just gave birth to a healthy baby boy. He told us about his pregnancy—and why his story isn't so out of the ordinary.
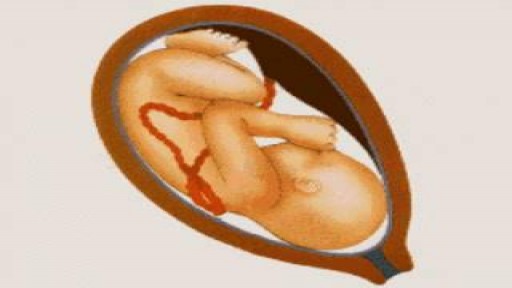
Childbirth (also called labour, birth, partus or parturition) is the culmination of a human pregnancy or gestation period with the birth of one or more newborn infants from a woman's uterus. The process of normal human childbirth is categorized in three stages of labour: the shortening and dilation of the cervix, descent and birth of the infant, and birth of the placenta. In many cases, with increasing frequency, childbirth is achieved through caesarean section, the removal of the neonate through a surgical incision in the abdomen, rather than through vaginal birth. In the U.S. and Canada it represents nearly 1 in 3 (31.8%) and 1 in 4 (22.5%) of all childbirths, respectively.
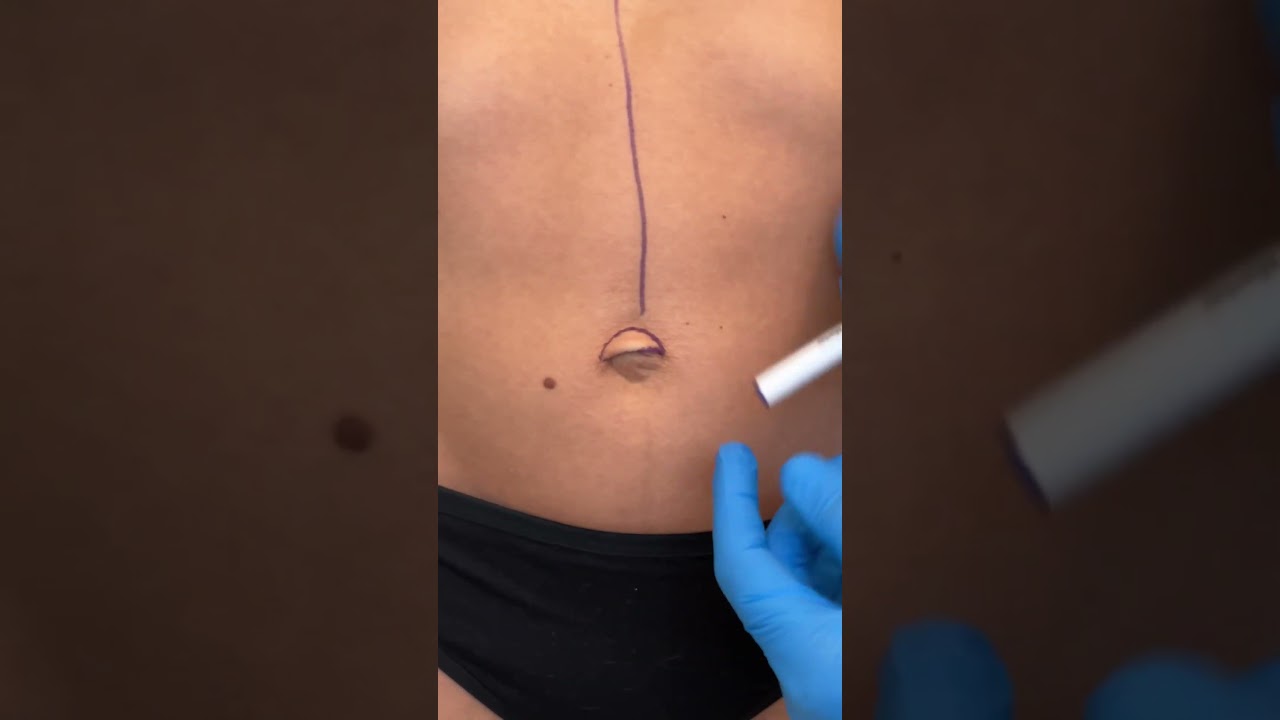
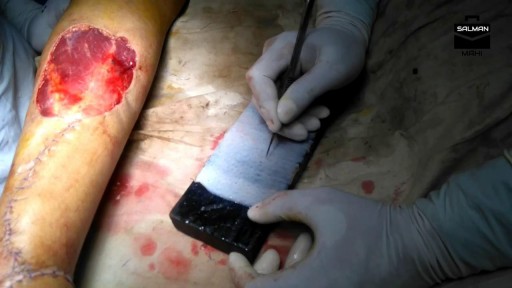
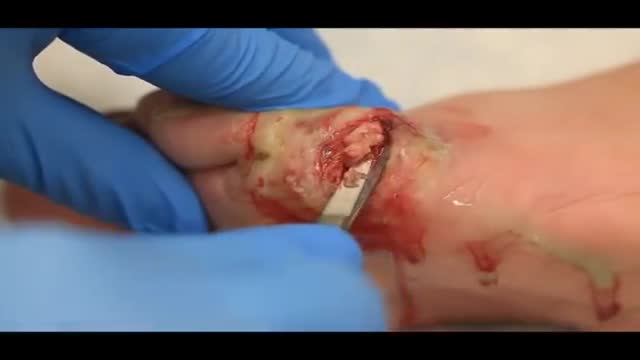
Check out @barrettplasticsurgery on TikTok!
Like and subscribe for more! #shorts #medical #plasticsurgery
More information:
www.drdanielbarrett.com