Top videos

A digital rectal examination (DRE) is a simple procedure doctors use to examine the lower rectum and other internal organs. A DRE is done for a number of reasons. It's a quick, easy way to check the health of a man's prostate gland. It can detect conditions like an enlarged prostate

Occupational respiratory disease is any lung condition you get at work. Certain workplaces lend themselves to disease. The most common are coalmines and factories or areas with high amounts of toxins. These include asbestos and silica dust, as well as smoke, fumes, gases, and other particles. Types of occupational respiratory disease include: coal workers’ pneumoconiosis, also known as Black Lung Disease asbestosis silicosis farmers’ lung, also known as allergic alveolitis. It also includes forms of asthma, bronchitis, or emphysema.

Traditional Liposuction VS Vaser Liposuction
A side-by-side comparison of traditional liposuction and a #Vaser liposuction. Both of these were performed by our skilled surgeons at Divine Cosmetic Surgery.
#vaserliposuction #liposuction #liposuctionDelhi #liposuctionresults #shorts #vaserliposuctionDelhi
Know more about liposuction
https://www.divinecosmeticsurg....ery.com/liposuction-
Traditional Liposuction vs 360 High Def Vaser Liposuction - https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=r_bBI2p9fVI&t=14s
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Why Vaser Is Best For Thigh Liposuction - https://youtu.be/dlzpdDEZcS4
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Abdomen Vaser Liposuction - Live - https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_Cvl2Txn8LQ
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Back Vaser Liposuction In Female - https://youtu.be/OC60UdgtIWU
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
For more details about Liposuction Visit - https://www.divinecosmeticsurgery.com/
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Dr. Amit Gupta
MBBS, M.S., DNB (Plastic & Cosmetic Surgery)
Divine Cosmetic Surgery | +91 9811994417
info@divinecosmeticsurgery.com | 01141828787
Delhi | Mumbai | Gurgaon
𝗦𝗼𝗰𝗶𝗮𝗹 𝗠𝗲𝗱𝗶𝗮 𝗮𝗻𝗱 𝗬𝗼𝘂𝘁𝘂𝗯𝗲 𝘃𝗶𝗱𝗲𝗼 𝗰𝗵𝗮𝗻𝗻𝗲𝗹 : -
🎦 https://www.youtube.com/c/DrAm....itGuptaBestPlasticCo
👍🏻 https://www.facebook.com/dramitguptaplasticsurgeon
📷 https://www.instagram.com/divineaesthetics_delhi/
🐥 https://twitter.com/dramitguptajee
🖇️ https://www.linkedin.com/compa....ny/divinecosmeticsur
📌 https://pinterest.com/divinesurgery
#Liposuction #vaserliposuction #liposuctioncostinindia #liposuctiondelhi #liposuction #liposuctioncost #liposuctioncostfactors #liposuctioncostindelhi #DrAmitGuptaPlasticSurgeon #DivineCosmeticSurgery #dramitgupta
Disclaimer: The information on our videos & social media is provided for informational purposes only and is not meant for the advice provided by your surgeon.
We are not responsible for any harm if anyone misguides you from our name. Our all-social media official handles are linked up on our website. All images & content used on our videos & social media are for illustrative concerns only, original results and processes may vary.

Adenocarcinoma of the Transverse Colon taken by Dr. Julio Murra Saca This is the case of a 42 year-old male, with no significant past medical history presented with abdominal pain and no weight loss was reported. Adenocarcinoma of the colon is a primary cause of mortality and
morbidity in North America and Western Europe. Colonic cancers are the most common GI carcinomas and have the best prognosis. The 5-year survival rate is approximately 50%.
Survival rates may be improved by screening and removal of adenomatous polyps. Almost all colonic cancers are primary adenocarcinomas.
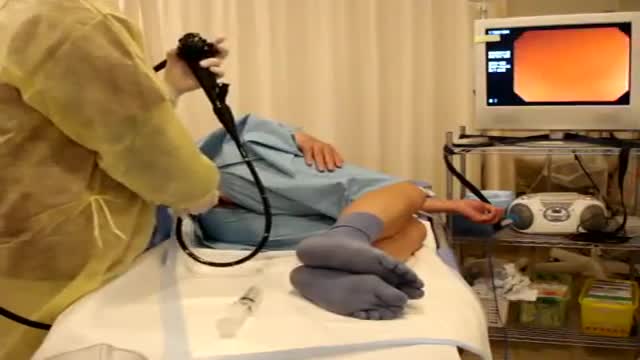
Colonoscopy is a test that allows your doctor to look at the inner lining of your large intestine (rectum and colon). He or she uses a thin, flexible tube called a colonoscope to look at the colon. A colonoscopy helps find ulcers, colon polyps, tumors, and areas of inflammation or bleeding.