Top videos
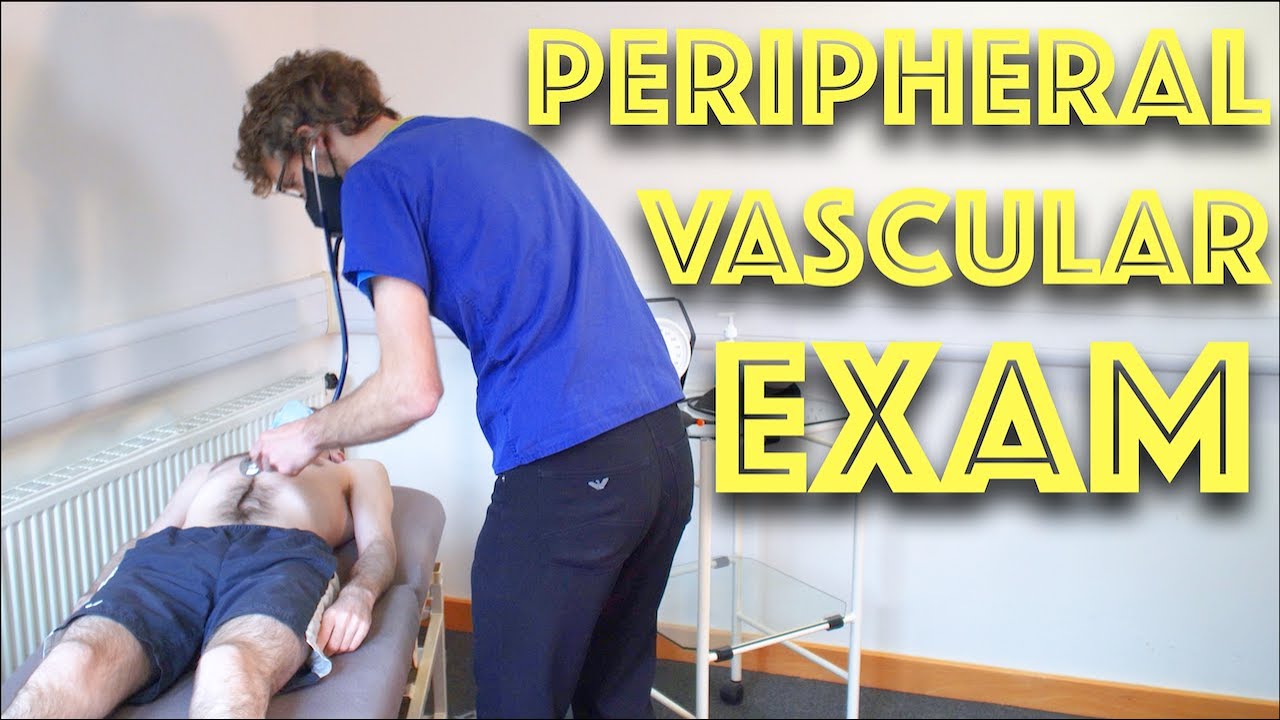
Peripheral Vascular Examination OSCE - Clinical Skills - Dr Gill
In the cardiovascular examination, particularly in the case of an OSCE station, we conclude the examination often by stating that the examiner would want to perform:
- An ECG
- Check full blood count
- and "do a peripheral vascular examination
In this video, we demonstrate that oft-talked about, but comparatively less common examination.
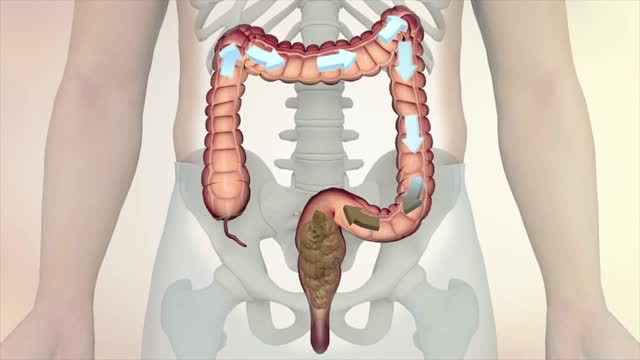
Starting off, with the examination of the hands, the radial, brachial and carotid pulses. before moving down to assess for a AAA, checking the femoral and popliteal pulses, before wrapping up around the ankle with the posterior tibial and dorsalis pedis pulses
For completeness, the cardiovascular examination is demonstrated here
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ECs9O5zl6XQ&t=2s
#PeripheralVascular #ClinicalSkills #DrGill
Whooping cough (pertussis) is a highly contagious respiratory tract infection. In many people, it's marked by a severe hacking cough followed by a high-pitched intake of breath that sounds like "whoop." Before the vaccine was developed, whooping cough was considered a childhood disease. Now whooping cough primarily affects children too young to have completed the full course of vaccinations and teenagers and adults whose immunity has faded. Deaths associated with whooping cough are rare but most commonly occur in infants. That's why it's so important for pregnant women — and other people who will have close contact with an infant — to be vaccinated against whooping cough.

Piles Treatment
contact : drjamil79@yahoo.com
Rubber band application around the pile is a pain free procedure.Patient is put to sleep for a few minutes and can go home after a few hours.In this procedure anal fissure was also treated with the transparent anoscope that comes with the PPH gun set.
Piles Treatment piles: HAL Hemorrhoidal Artery Ligation new fast and painless treatment of haemorrhoids dr jamil ahmad hashmi -PainlessRubber band application around the pile is pain free procedure.Patient put to sleep for few minutes can go home after hours.In this procedure anal fissure was also treated with transparent anoscope that comes PPH gun set. Category: health
Childbirth (also called labour, birth, partus or parturition) is the culmination of a human pregnancy or gestation period with the birth of one or more newborn infants from a woman's uterus. The process of normal human childbirth is categorized in three stages of labour: the shortening and dilation of the cervix, descent and birth of the infant, and birth of the placenta. In many cases, with increasing frequency, childbirth is achieved through caesarean section, the removal of the neonate through a surgical incision in the abdomen, rather than through vaginal birth. In the U.S. and Canada it represents nearly 1 in 3 (31.8%) and 1 in 4 (22.5%) of all childbirths, respectively.

The anatomy of the direct and indirect inguinal hernia.
Music:
Berries and Lime by Gregory David
https://www.epidemicsound.com/track/z6iCiiyCPm/
High Quality Surgical videos and uncut stories ▶ https://surgeoncut.com

Surgical site infections (SSIs) remain a prevalent threat to patient safety. Proper surgical hand scrub or rub techniques are essential to decreasing the incidence of SSIs. This video provides instructions on the anatomical surgical hand scrub procedure using the brushstroke method. Learn more from the Department of Hospital Epidemiology and Infection Control (HEIC) at The Johns Hopkins Hospital: http://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/heic

Contact us to find out more http://www.londonvisionclinic.com/contact-us/ Mr Carp explains the risks involved in losing sight as being extremely rare. Only 1 in 5 million may lose sight in one eye.

Dr. Ailawadi, M.D., the Chair of Cardiac Surgery at Michigan Medicine, specializes in minimally invasive valve surgery as well as complex cardiac operations. This video shows step by step footage of a Coronary Artery Bypass Graft (CABG) in a complex patient. In this case, CABG was performed through a sternotomy (through the breast bone) using the internal thoracic artery and saphenous leg veins to bypass obstructed coronary arteries. In this video, Dr. Ailawadi will perform a triple vessel bypass (CABG) which has been shown to minimize the risk of future heart attack and help patients live longer in the setting of complex coronary artery disease.
To learn more about cardiac surgery at Michigan Medicine, visit: https://medicine.umich.edu/dept/cardiac-surgery
To learn more about Frankel Cardiovascular Center, visit: https://www.umcvc.org/
To watch the full playlist, visit: https://www.youtube.com/playli....st?list=PLNxqP-XbH8B
-------------------------------------------------------
Subscribe to Michigan Medicine’s YouTube channel for upcoming videos and future live streams featuring our experts answering your questions.
-------------------------------------------------------
Follow Michigan Medicine on Social:
Twitter: https://twitter.com/umichmedicine
Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/umichmedicine/
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/MichiganMedicine/
Follow the U-M Frankel Cardiovascular Center on Social:
Twitter: https://twitter.com/umichcvc
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/Unive....rsityofMichiganCardi
#MichiganMedicine #MedEd #CardiacSurgery #UniversityOfMichiganHealth #FrankelCardiovascularCenter #Cardiology #CardiacSurgeon
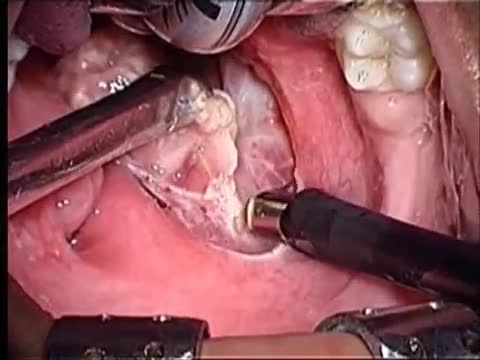
Tonsillectomy (ton-sih-LEK-tuh-me) is the surgical removal of the tonsils, two oval-shaped pads of tissue at the back of the throat — one tonsil on each side. A tonsillectomy was once a common procedure to treat infection and inflammation of the tonsils (tonsillitis). Today, a tonsillectomy is usually performed for sleep-disordered breathing but may still be a treatment when tonsillitis occurs frequently or doesn't respond to other treatments. A tonsillectomy may also be necessary to treat breathing and other problems related to enlarged tonsils and to treat rare diseases of the tonsils.

Must Watch Very Special New Funny Video 2023 Doctor Funny Video Injection Wala Funny Video | Comedy Video Episode 124 By Fun Comedy Ltd
@funcomedyltd
#funcomedyltd
#doctor
#comedy
#wala
Hello Dear Viewers,
If We have any mistake. please comment and tell us, what is our mistake? We will try to solve this mistake next. please watch our videos and give us confidence to trying best. Thank you for watching this video.
IMPORTANT NOTE:-
This video are no any kind of risk. This video are totally acting no risk no Dangerous act no Physical Harm or Death its ok for viewers.
injection wala comedy video injection wala video injection funny video injection injection wala injection injection doctor doctor doctor sui wala wala suji wala suji wala cartoon doctor cartoon funny video tui tui injection cartoon 22 cartoon video injection video cartoon cartoon comedy video doctor video wala cartoon busy fun ltd my family our fun tv fun tv 24 fun tv 420 funny day funny family ding dong bidik fun tv roma fun tv
#cartoon
#comedyvideo
#doctor_doctor
#busyfunltd
#newfunnyvideo2022
#newfunniestcomedy
#injectionfunnyvideo
#sui_wala
#myfamily
#busyfunltd
#funnyday
#bidikfuntv
#mohafuntv
#dingdong
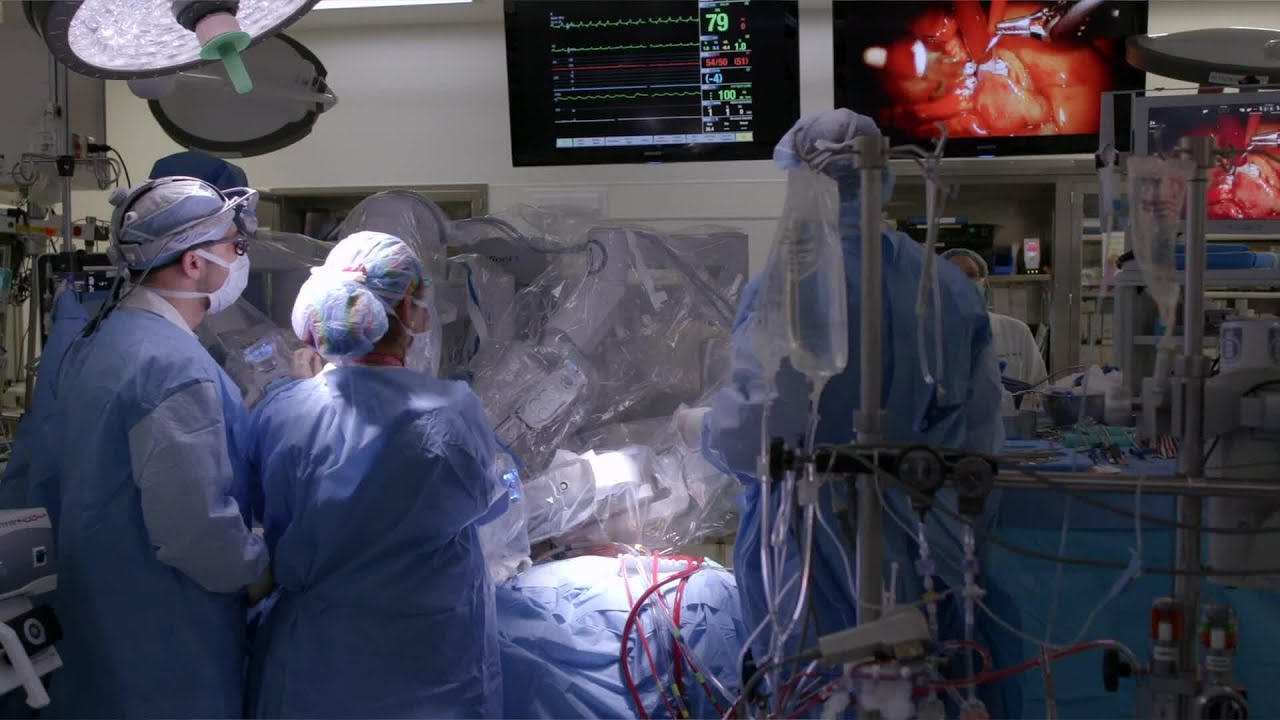
To learn more about robotically assisted heart surgery, please visit https://cle.clinic/2Y6aHXH
Robotically assisted heart surgery is a minimally invasive option most often used for mitral valve repair. Cleveland Clinic cardiothoracic surgeons explain how it works and what to expect.
To learn more about our cardiothoracic experts, please visit
Marc Gillinov, MD - https://cle.clinic/2ZtNM7b
Daniel Burns, MD - https://cle.clinic/2W1MdxI
If you liked the video hit like and subscribe for more!
#clevelandclinic #heartsurgery #roboticsurgery #heartcare #cardiothoracic

For more videos, please visit:
http://surgicalfilmatlas.mssm.edu/