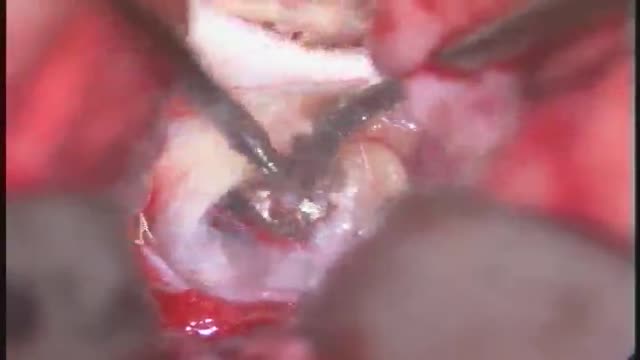
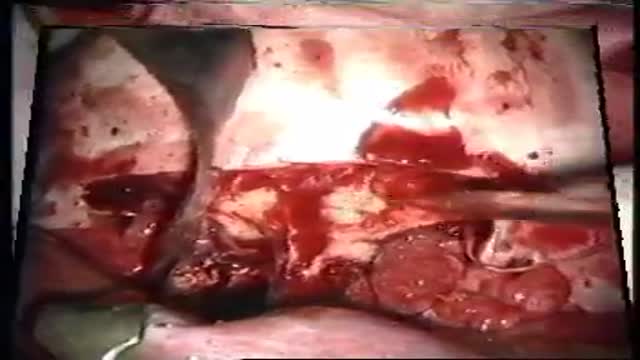
Other
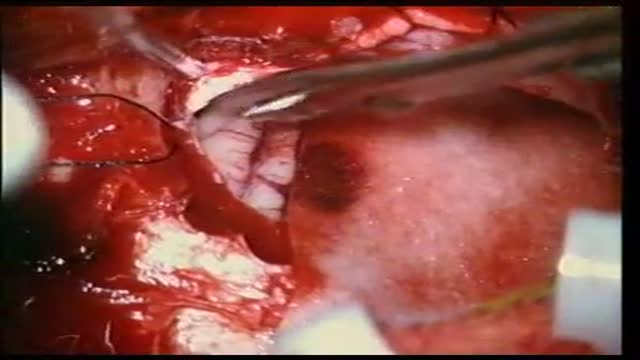
trigeminal neuralgia can be caused by a vessel loop nearby the entry zone of the trigeminal nerve at the brainstem. a vessel loop is mobilized and transposed and secured with a teflon paddy. the paddy is fixed with tissucol , a fibrin glue without evident neurotoxicity. the long term result of the jannetta procedure regarding pain control is excellent
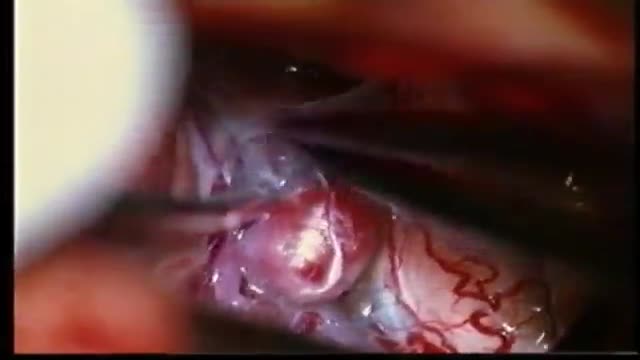
ANEURYSMS OF THE CEREBRAL VESSELS CAUSE SUBARACHNOID HEMORRHAGE. MICRONEUROSURGICAL CLIPPING ELIMINATES DEFINITIVE THE RISK OF RERUPTURE, ENABLES TO TREAT VASOSPASMS AND ELIMINATES THE NEED FOR RE-ANGIOGRAPHIES. INTRAOPERATIVE PUNCTURE CHECKS IMMEDIATLY THE ELIMINATION OF THE ANEURYSM.
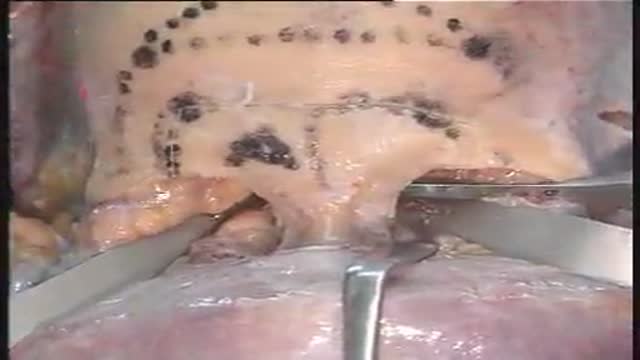
lesions at the anterior skull base invading the paranasal area and the paracavernous area can be reached without brain retraction by the shown subfrontal approach. it enables to control the paranasal sinus, optic nerve, periorbital tissue, carotid artery and pituary gland. reconstruction is not easy... but cosmetically appealing. CSF leaks are rare with the use of fascia lata and tissucol ( fibrin glue). osseous reconstruction is done by microsrews and calciumpyrophosphate ( norian, synthes).

This block is used for procedures of the hand, forearm, and elbow. An injection is given in the patient's axilla (armpit) into a space that surrounds a bundle of nerves that supply feeling to the lower arm. This is usually done with the patient awake with sedation, but can be done with the patient under General Anesthesia.

The complex circuitry interconnecting different areas in the brain, known collectively as white matter, is composed of millions of axons organized into fascicles and bundles. Upon macroscopic examination of sections of the brain, it is difficult to discern the orientation of the fibers. The same is true for conventional imaging modalities. However, recent advancements in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) make such task possible in a live subject. By sensitizing an otherwise typical MRI sequence to the diffusion of water molecules it is possible to measure their diffusion coefficient in a given direction1. Normally, the axonal membrane and myelin sheaths pose barriers to the movement of water molecules and, thus, they diffuse preferentially along the axon2. Therefore, the direction of white matter bundles can be elucidated by determining the principal diffusivity of water. The three-dimensional representation of the diffusion coefficient can be given by a tensor and its mathematical decomposition provides the direction of the tracts3; this MRI technique is known as diffusion tensor imaging (DTI). By connecting the information acquired with DTI, three-dimensional depictions of white matter fascicles are obtained4. The virtual dissection of white matter bundles is rapidly becoming a valuable tool in clinical research.
Our journey begins with a transverse section of tightly packed axons as seen through light microscopy. Although represented as a two-dimensional "slice", we see that these axons in fact resemble tubes. A simulation of water molecules diffusing randomly inside the axons demonstrates how the membranes and myelin hinder their movement across them and shows the preferred diffusion direction --along the axons. The tracts depicted through DTI slowly blend in and we ride along with them. As we zoom out even more, we realize that it is a portion of the corpus callosum connecting the two sides of the brain we were traveling on and the great difference in relative scale of the individual axons becomes evident. The surface of the brain is then shown, as well as the rest of the white matter bundles--a big, apparently chaotic tangle of wires. Finally, the skin covers the brain.
With the exception of the simulated water molecules, all the data presented in the animation is obtained through microscopy and MRI. Computer algorithms for the extraction of the cerebral structures and a custom-built graphics engine make our journey through the brain's anatomy possible in a living person.
Micrograph courtesy of Dr. Christian Beaulieu, University of Alberta.
Music by Mario Mattioli.
References:
1. Stejskal, E.O., et al., J. Chem. Phys., 1965. 42:
2. Beaulieu, C., NMR Biomed., 2002. 15:435-55.
3. Basser, P.J., et al., J. Magn. Reson. B, 1994. 103:247-54.
4. Mori, S., et al., NMR Biomed., 2002. 15:468-80.