Latest videos
The symptoms of bacterial overgrowth include nausea, flatus, constipation, bloating, abdominal distension, abdominal pain or discomfort, diarrhea, fatigue, and weakness. SIBO also causes an increased permeability of the small intestine. Some patients may lose weight.
Juvenile polyposis syndrome (JPS) is a hereditary condition that is characterized by the presence of hamartomatous polyps in the digestive tract. Hamartomas are noncancerous (benign) masses of normal tissue that build up in the intestines or other places. These masses are called polyps if they develop inside a body structure, such as the intestines. The term “juvenile polyposis” refers to the type of polyp (juvenile polyp) that is found after examination of the polyp under a microscope, not the age at which people are diagnosed with JPS.
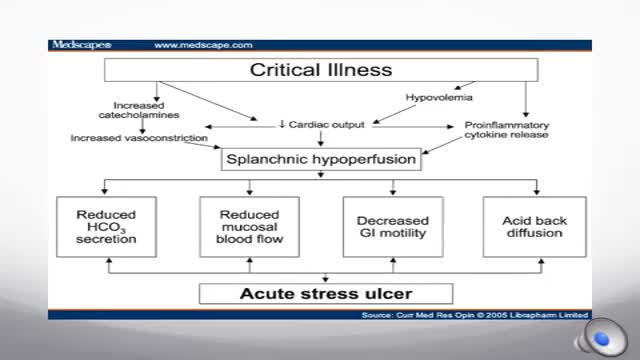
Stress-related mucosal disease (SRMD) is an acute, erosive gastritis representing conditions ranging from stress-related injury to stress ulcers (1, 2). Stress-related injury is superficial mucosal damage that presents primarily as erosions, whereas stress ulcers are deep, focal mucosal damage penetrating the submucosa with high risk for gastrointestinal bleeding (2, 3). Mucosal damage has been reported to occur during the first 24 hours of hospital admission in 75% to 100% of intensive care unit (ICU) patients (4, 5). Clinically important gastrointestinal bleeding can cause hemodynamic instability and increase the need for red blood cell transfusions (1). Significant bleeding may also increase the length of stay in the ICU and mortality (1).

Gastroparesis -- literally “paralyzed stomach” -- is a serious condition manifested by delayed emptying of stomach contents into the small intestine after a meal. There is no cure for gastroparesis, but treatment can speed gastric emptying and relieve gastrointestinal symptoms such as nausea and vomiting.

The average human digestive tract is home to as many as 1,000 species of microorganisms. Most of them are harmless -- or even helpful -- under normal circumstances. But when something upsets the balance of these organisms in your gut, otherwise harmless bacteria can grow out of control and make you sick. One of the worst offenders is a bacterium called Clostridium difficile(C. difficile, or C. diff). As the bacteria overgrow they release toxins that attack the lining of the intestines, causing a condition called Clostridium difficilecolitis.
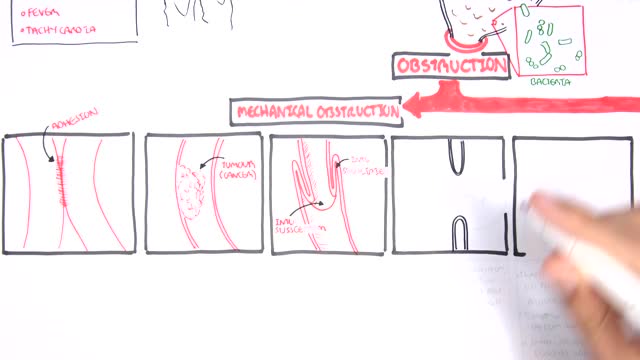
A small-bowel obstruction (SBO) is caused by a variety of pathologic processes. The leading cause of SBO in industrialized countries is postoperative adhesions (60%), followed by malignancy, Crohn disease, and hernias, although some studies have reported Crohn disease as a greater etiologic factor than neoplasia.
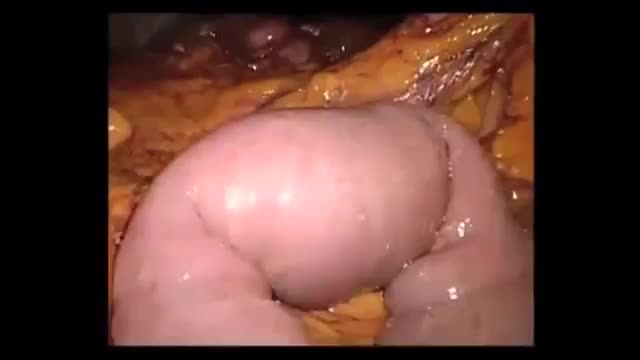
Gallstone ileus is an important, though infrequent, cause of mechanical bowel obstruction, affecting older adult patients who often have other significant medical conditions. It is caused by impaction of a gallstone in the ileum after being passed through a biliary-enteric fistula. The diagnosis is often delayed since symptoms may be intermittent and investigations fail to identify the cause of the obstruction. The mainstay of treatment is removal of the obstructing stone after resuscitating the patient. Gallstone ileus continues to be associated with relatively high rates of morbidity and mortality.
The lungs and respiratory system allow oxygen in the air to be taken into the body, while also enabling the body to get rid of carbon dioxide in the air breathed out. Respiration is the term for the exchange of oxygen from the environment for carbon dioxide from the body's cells.

There are 3 major parts of the respiratory system: the airway, the lungs, and the muscles of respiration. The airway, which includes the nose, mouth, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi, and bronchioles, carries air between the lungs and the body's exterior.

Visualization of the larynx by direct or indirect means is referred to as laryngoscopy and is the principal aim during airway management for passage of a tracheal tube. This paper presents a brief background regarding the development and practice of laryngoscopy and examines the equipment and techniques for both direct and indirect methods. Patient evaluation during the airway examination is discussed, as are predictors for difficult intubation. Laryngoscope blade design, newer intubating techniques, and a variety of indirect laryngoscopic technologies are reviewed, as is the learning curve for these techniques and devices.