Top videos
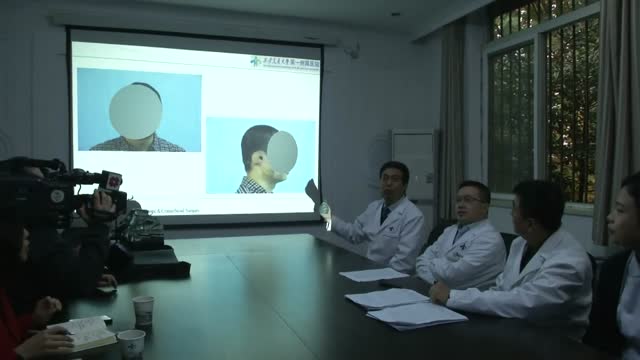
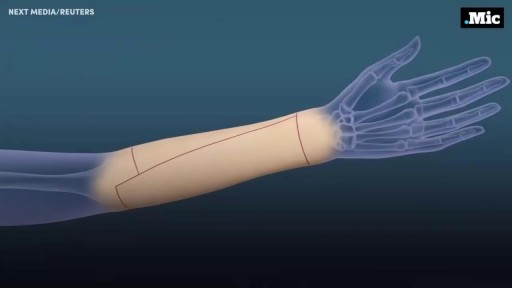
A plastic surgeon in China has successfully grown an artificial ear on a man's arm in a pioneering medical procedure. The patient, surnamed Ji, lost his right ear in an accident and yearned to have it back. Doctor Guo Shuzhong from a hospital in Xi'an, China's Shaanxi Province, used Mr Ji's cartilage from his ribs to build the new ear; and he expects to transplanted the organ to the man's head in about four months. According to the Huanqiu report, Mr Ji sustained serious injuries in the right side of his face in a traffic accident about a year ago. His right ear was torn from his face. The man, whose age is not specified, has since received multiple surgical operations to restore his facial skin and his cheeks. However, he felt frustrated about losing his right ear for good. The patient told a report from China News: 'I lost one ear. I have always felt that I am not complete.' Having sought medical advice from multiple sources, Ji realised that it was impossible to restore his ear through conventional medical procedures as a substantial part of his right ear had gone missing. Upon hearing recommendations, Mr Ji went to see doctor Guo Shuzhong, who works at the First Affiliated Hospital of Xi'an Jiaotong University in the city of Xi'an. Doctor Guo, a renowned plastic surgeon, conducted China's first face transplant operation in 2006, according to China Daily.

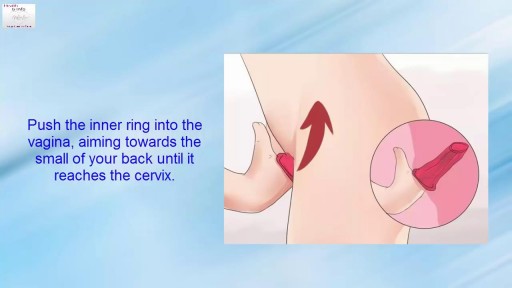
Pinch air out of the tip of the condom. Unroll condom all the way down the penis. After sex but before pulling out, hold the condom at the base. Then pull out, while holding the condom in place. Carefully remove the condom and throw it in the trash.
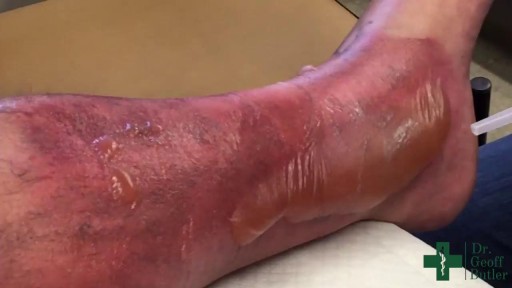
A bulla is a fluid-filled sac or lesion that appears when fluid is trapped under a thin layer of your skin. It’s a type of blister. Bullae (pronounced as “bully”) is the plural word for bulla. To be classified as a bulla, the blister must be larger than 0.5 centimeters (5 millimeters) in diameter. Smaller blisters are called vesicles.
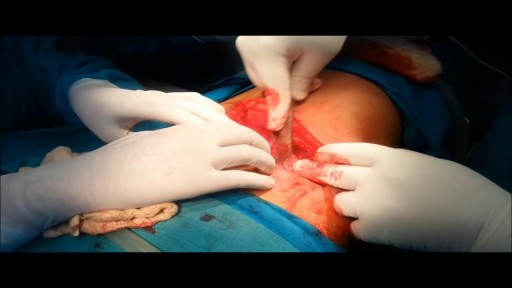
Majority of patients these days prefer PCNL ( Minimal Invasive Telescopic removal of kidney stones broken with lithoclast, removed through a button hole incision ). This patient with a big stone in the pelvis of the kidney wanted it open only so I did an open pyelolithotomy for this patient after a long time as I use to do it in routine in the past. Except for the long incision and scar as compared to PCNL the recovery time was the same and patient went home third day happily walking and eating.

When is endoscopy used? Endoscopes were first developed to look at parts of the body that couldn’t be seen any other way. This is still a common reason to use them, but endoscopy now has many other uses too. It’s often used in the prevention, early detection, diagnosis, staging, and treatment of cancer. To prevent and screen for cancer Some types of endoscopes are used to look for cancer in people who have no symptoms. For example, colonoscopy (KO-lun-AH-skuh-pee) and sigmoidoscopy (SIG-moid-AH-skuh-pee) are used to screen for colon and rectal cancer. These procedures can also help prevent cancer because they let doctors find and remove polyps (growths) that might become cancer if left alone. To find cancer early Endoscopy can sometimes be used to find cancer early, before it has had a chance to grow or spread. Looking for causes of symptoms When people go to the doctor with certain symptoms, endoscopy can sometimes be used to help find a cause. For instance: Laryngoscopy to look at the vocal cords in people with long-term hoarseness Upper endoscopy in people having trouble swallowing Colonoscopy in people with anemia (low red blood cell counts) with an unknown cause Colonoscopy in people with blood in their stool Looking at problems found on imaging tests Imaging tests such as x-rays and CT scans can sometimes show physical changes within the body. But these tests may only give information about the size, shape, and location of the problem. Doctors use endoscopes to see more details, like color and surface texture, when trying to find out what’s going on. Newer methods of endoscopy that include high magnification are being tested to find out whether they are more useful in detecting cancer and other abnormal cells on the inner surfaces of the body. To diagnose and find out the stage (extent) of cancer To get a tissue sample Going one step further, most types of endoscopes have tools on the end that the doctor can use to take out small tissue samples. This procedure is called a biopsy (BY-op-see). Samples can be taken from suspicious areas and then looked at under a microscope or tested in other ways to see if cancer is there. A biopsy is usually the best way to find out if a growth or change is cancer or something else. Getting a closer look In some cases endoscopes are used to help find out how far a cancer has spread. Thoracoscopy (THOR-uh-KAHS -kuh-pee) and laparoscopy (LAP-uh-RAHS-kuh-pee) can be very useful in finding out if cancer has spread into the thorax (chest) or abdomen (belly). The surgeon can look into these places making only a small incision (cut) in the skin.
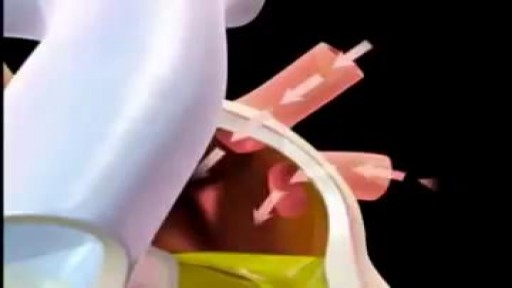
The cardiac cycle is the sequence of events that occurs when the heart beats. As the heart beats, it circulates blood through pulmonary and systemic circuits of the body. There are two phases of the cardiac cycle. In the diastole phase, the heart ventricles are relaxed and the heart fills with blood
As long as the ureter is large enough to allow the ureteroscope to pass, there is a good chance that the stone can be broken and removed with one surgery. Compared to SWL, a kidney or ureteral stone can be seen under direct vision by the ureteroscope, allowing lithotripsy with lasers followed by basketting and removal.
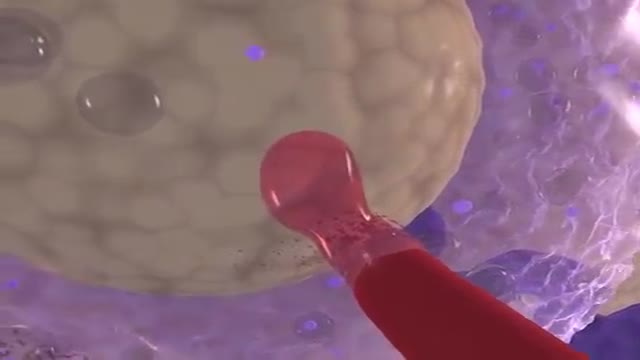
What does the placenta do? The placenta is an organ that develops in your uterus during pregnancy. This structure provides oxygen and nutrients to your growing baby and removes waste products from your baby's blood. The placenta attaches to the wall of your uterus, and your baby's umbilical cord arises from it. In most pregnancies, the placenta attaches at the top or side of the uterus.
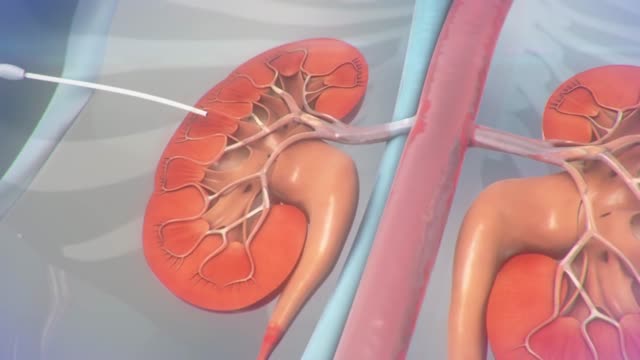
A ureteral stent is a thin, hollow tube that is placed in the ureter to help urine pass from the kidney into the bladder. Ureters are the tubes that connect the kidneys to the bladder. You may have a small amount of blood in your urine for 1 to 3 days after the procedure.

A central venous catheter, also called a central line, is a long, thin, flexible tube used to give medicines, fluids, nutrients, or blood products over a long period of time, usually several weeks or more. A catheter is often inserted in the arm or chest through the skin into a large vein.
A man set to become the world’s first head transplant patient has scheduled the procedure for December 2017. Valery Spiridonov, 30, was diagnosed with a genetic muscle-wasting condition called Werdnig-Hoffmann disease, and volunteered for the procedure despite the risks involved, Central European News (CEN) reported. “When I realized that I could participate in something really big and important, I had no doubt left in my mind and started to work in this direction,” Spiridonov, a Russian computer scientist, told CEN. “The only thing I feel is the sense of pleasant impatience, like I have been preparing for something important all my life and it is starting to happen.”