Top videos

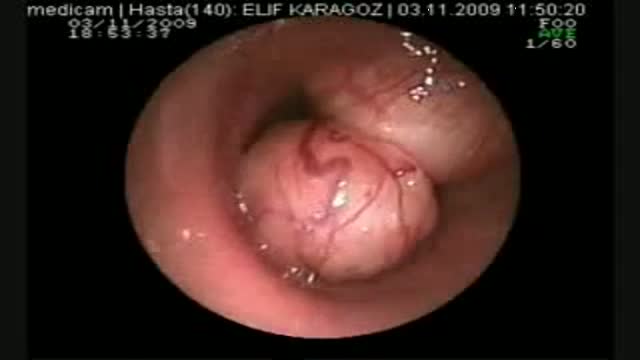
esophago-gastro- duodinoscopy
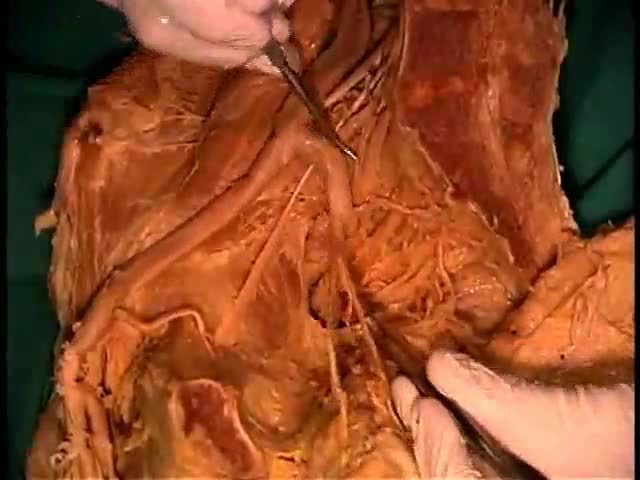
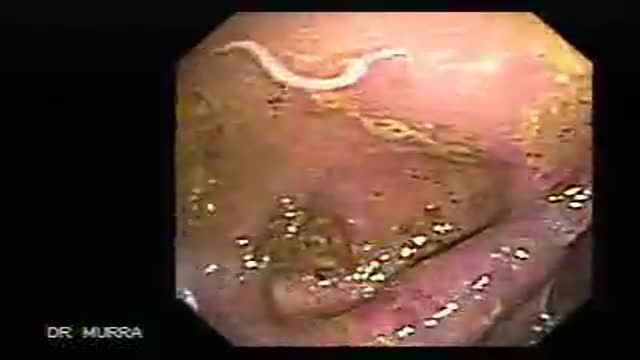
Gastroduodinoscopy requires special training and considerable experience but affords valuable information.
By its implement the whole of the interior of the stomach as well as esophagus, the first part and the proximal section of the second part of the duodenum and both efferent and afferent loops of the gastrojujenostomy if present can be scrutinized.
Gastroscopy is valuable in the diagnosis of gastric ulcers, in checking the results of medical treatment of chronic gastric ulcer. Gastroduodinoscopy is valuable in differential diagnosis between chronic peptic ulcer and gastric carcinoma, in diagnosis of small gastric neoplasm, in the detection of certain forms of gastritis, in examination of a stoma, in cases of gastrojujenostomy, in cases of duodinitis and duodenal ulcer.
Now its' the Era of
VIDEOGASROSCOPE
Direct means of diagnosis of upper G.I. diseases
Continuous Video recording of the entire procedure is there by which
we can review the whole procedure by playing the Video.
We are doing final diagnosis of upper G.I. lesions with biopsy.
Treatment becomes easy and to the point.
Early detection of pre malignant and malignant lesions is appreciable.
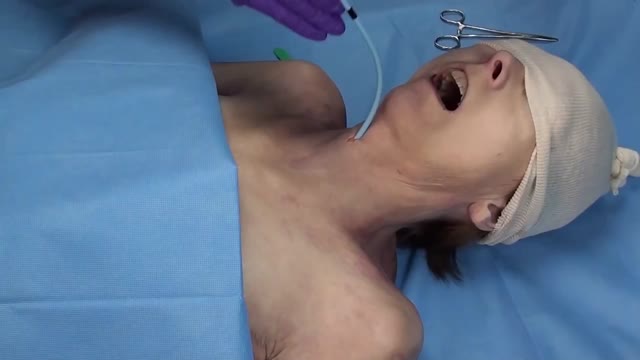
A cricothyrotomy (also called crike, thyrocricotomy, cricothyroidotomy, inferior laryngotomy, intercricothyrotomy, coniotomy or emergency airway puncture) is an incision made through the skin and cricothyroid membrane to establish a patent airway during certain life-threatening situations, such as airway obstruction by ...
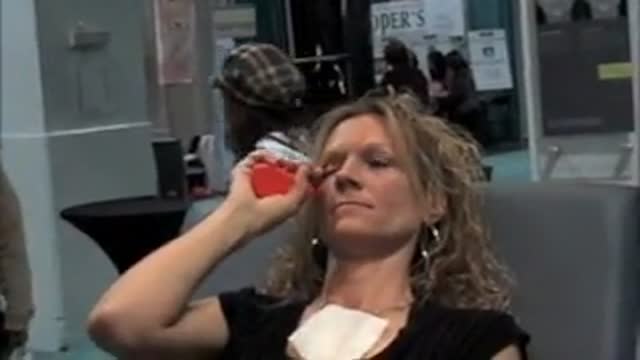
View more before and afters, videos and get detailed information at http://www.torontoplacticsurgeryclini..., and find out what Botox and Restylane can do for you. In this very informative video renowned board certified plastic surgeon Dr. Michael Weinberg, founder of Mississauga Cosmetic Surgery and Laser Clinic, and The Toronto Plastic Surgery Clinic, and Chief of Plastic Surgery at trillium Health Centre, demonstrates extensive injections with Restylane. This is an example of a "non-surgical Facelift" achieved with Hyaluronic Acid filler. The results are immediateand will last 6 months to a year or longer.
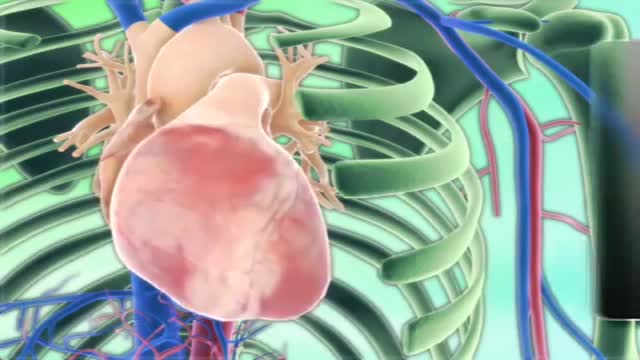
Cardiac tamponade Email this page to a friend Print Facebook Twitter Bookmark & Share Cardiac tamponade is pressure on the heart that occurs when blood or fluid builds up in the space between the heart muscle (myocardium) and the outer covering sac of the heart (pericardium). Causes In this condition, blood or fluid collects in the pericardium, the sac surrounding the heart. This prevents the heart ventricles from expanding fully. The excess pressure from the fluid prevents the heart from working properly. As a result, the body does not get enough blood. Cardiac tamponade can occur due to: Dissecting aortic aneurysm (thoracic) End-stage lung cancer Heart attack (acute MI) Heart surgery Pericarditis caused by bacterial or viral infections Wounds to the heart
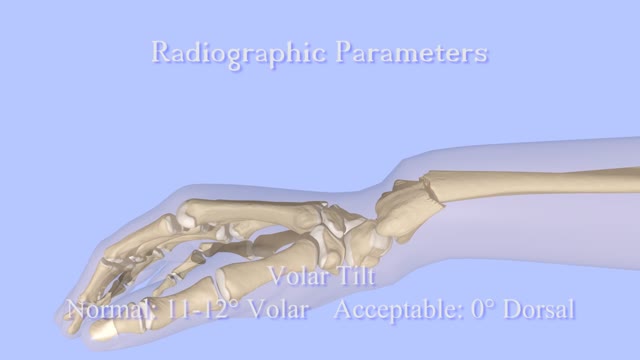
Closed Reduction of Distal Radius Fractures - Discussion: (distal radius fracture menu) - closed reduction & immobilization in plaster cast remains accepted method of treatment for majority of stable distal radius frx; - unstable fractures will often lose reduction in the cast and will slip back to the pre-reduction position; - patients should be examined for carpal tunnel symptoms before and after reduction; - carpal tunnel symptoms that do not resolve following reduction will require carpal tunnel release; - cautions: - The efficacy of closed reduction in displaced distal radius fractures. - Technique: - anesthesia: (see: anesthesia menu) - hematoma block w/ lidocaine; - w/ hematoma block surgeon should look for "flash back" of blood from hematoma, prior to injection; - references: - Regional anesthesia preferable for Colles' fracture. Controlled comparison with local anesthesia. - Neurological complications of dynamic reduction of Colles' fractures without anesthesia compared with traditional manipulation after local infiltration anesthesia. - methods of reduction: - Jones method: involves increasing deformity, applying traction, and immobilizing hand & wrist in reduced position; - placing hand & wrist in too much flexion (Cotton-Loder position) leads to median nerve compression & stiff fingers; - Bohler advocated longitudinal traction followed by extension and realignment; - consider hyper-extending the distal fragment, and then translating it distally (while in extended position) until it can be "hooked over" proximal fragment; - subsequently, the distal fragment can be flexed (or hinged) over the proximal shaft fragment; - closed reduction of distal radius fractures is facilitated by having an assistant provide counter traction (above the elbow) while the surgeon controls the distal fragment w/ both hands (both thumbs over the dorsal surface of the distal fragment); - flouroscopy: - it allows a quick, gentle, and complete reduction; - prepare are by prewrapping the arm w/ sheet cotton and have the plaster or fibroglass ready; - if flouroscopy is not available, then do not pre-wrap the extremity w/ cotton; - it will be necessary to palpate the landmarks (outer shaped of radius, radial styloid, and Lister's tubercle, in order to judge success of reduction; - casting: - generally, the surgeon will use a pre-measured double sugar sugar tong splint, which is 6-8 layers in thickness; - more than 8 layers of plaster can cause full thickness burns: - reference: Setting temperatures of synthetic casts. - position of immobilization - follow up: - radiographs: - repeat radiographs are required weekly for 2-3 weeks to ensure that there is maintenance of the reduction; - a fracture reduction that slips should be considered to be unstable and probably require fixation with (pins, or ex fix ect.) - there is some evidence that remanipulation following fracture displacement in cast is not effective for these fractures; - ultimately, whether or not a patient is satisfied with the results of non operative treatment depends heavily on th
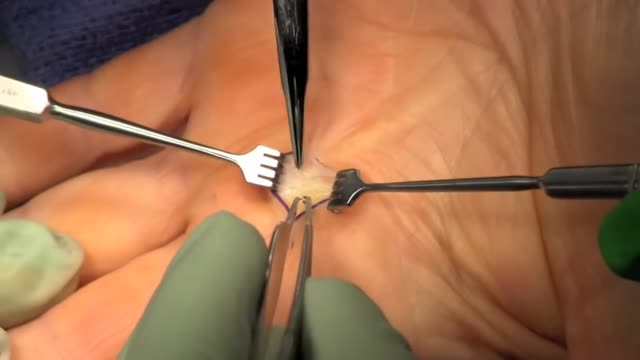
Trigger finger, also known as stenosing tenosynovitis (stuh-NO-sing ten-o-sin-o-VIE-tis), is a condition in which one of your fingers gets stuck in a bent position. Your finger may straighten with a snap — like a trigger being pulled and released. Trigger finger occurs when inflammation narrows the space within the sheath that surrounds the tendon in the affected finger. If trigger finger is severe, your finger may become locked in a bent position. People whose work or hobbies require repetitive gripping actions are at higher risk of developing trigger finger. The condition is also more common in women and in anyone with diabetes. Treatment of trigger finger varies depending on the severity.

Each month inside your ovaries, a group of eggs starts to grow in small, fluid-filled sacs called follicles. Eventually, one of the eggs erupts from the follicle (ovulation). It usually happens about 2 weeks before your next period. Hormones Rise After the egg leaves the follicle, the follicle develops into something called the corpus luteum. The corpus luteum releases a hormone that helps thicken the lining of your uterus, getting it ready for the egg. The Egg Travels to the Fallopian Tube After the egg is released, it moves into the Fallopian tube. It stays there for about 24 hours, waiting for a single sperm to fertilize it. All this happens, on average, about 2 weeks after your last period.