Top videos

Dr. Debbie Song at Gillette Children's describes in detail selective rhizotomy surgery.
A selective dorsal rhizotomy is an operation performed to treat spasticity. It is thought that high tone and spasticity arise from abnormal signals that are transmitted through sensory or dorsal nerve roots to the spinal cord. In a selective dorsal rhizotomy we identify and cut portions of the dorsal nerve roots that carry abnormal signals thereby disrupting the mechanisms that lead to spasticity. Potential patients go through a rigorous assessment that includes an in-depth gait and motion analysis as well as a physical therapy evaluation.
They are evaluated by a multidisciplinary team that includes a pediatric rehabilitation doctor, a neurosurgeon, and an orthopedist, Appropriate patient selection is vital. Ideal candidates for selective dorsal rhizotomy are children who are between four and ten years of age, have a history of being born prematurely, and have a diagnosis of diplegia cerebral palsy. These patients usually walk independently or with the assistance of crutches or a walker. They typically function at a level one, two, or three in the gross motor function classification system or gmfcs. A selective dorsal rhizotomy involves the coordinated efforts of the neurosurgery, physiatry, anesthesia and nursing teams. The operation entails making an incision in the lower back that is approximately six to eight inches long. We perform what we call a laminoplasty in which we remove the back part of the spinal elements from the lumbar one or l1 to l5 levels. At the end of the procedure the bone is put back on. We identify and open up the Dural sac that contain the spinal fluid spinal cord and nerve roots. Once the Dural sac is opened ,we expose the lumbar and upper sacral nerve roots that transmit information to and from the muscles of the lower extremities.
At each level we isolate the dorsal nerve root, which in turn is separated into as many as 30 smaller thread light fruitlets.
Each rootlet is then electrically stimulated. Specialized members of the physiatry team look for abnormal responses in the muscles of the legs as each rootless is being stimulated. If an abnormal response is observed then the rootlet is cut.
If a normal response is observed, then the rootlet is not cut. We usually end up cutting approximately 20 to 40 percent of the rootlets. The Dural sac is sutured closed and the l1 through l5 spinal elements are put back into anatomic position, thus restoring normal spinal alignment. The overlying tissues and skin are then closed and the patient is awoken from surgery. The entire operation takes between four and five hours. A crucial component to the success of our rhizotomy program is the extensive rehabilitation course following surgery. With their tone significantly reduced after a rhizotomy, patients relearn how to use their muscles to walk more efficiently through stretching, strengthening, and gait training. Approximately one to two years after a rhizotomy patients undergo repeat gait and motion analysis. The orthopedic surgeons assess the need for interventions to correct bone deformities, muscle contractures, poor motor control, impaired balance, or other problems related to cerebral palsy.
At Gillette we work closely with patients and families to ensure that our selective dorsal rhizotomy program meets their goals for enhancing their function and improving their quality of life.
VISIT https://www.gillettechildrens.org/ to learn more
0:00 Why choose selective dorsal rhizotomy?
0:56 Who is a good candidate for selective dorsal rhizotomy?
1:31 What does a selective dorsal rhizotomy entail?
3:26 What is recovery from selective dorsal rhizotomy like?

Ettore Vulcano, MD, Foot and Ankle Orthopedic Surgeon at Mount Sinai West, discusses a new minimally invasive bunion surgery that has patients walking immediately after surgery, and getting back to an active lifestyle much quicker than with the traditional surgery.

Dr. Celia Divino, Chief, Division of General Surgery at The Mount Sinai Hospital, performs a laparoscopic appendectomy. Visit the Division of General Surgery at http://bit.ly/18z944M. Click here to learn more about Dr. Celia Divino http://bit.ly/12RF0ee
To license this video for patient education or content marketing, visit: http://www.nucleushealth.com/?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=video-description&utm_campaign=tephernia-030615
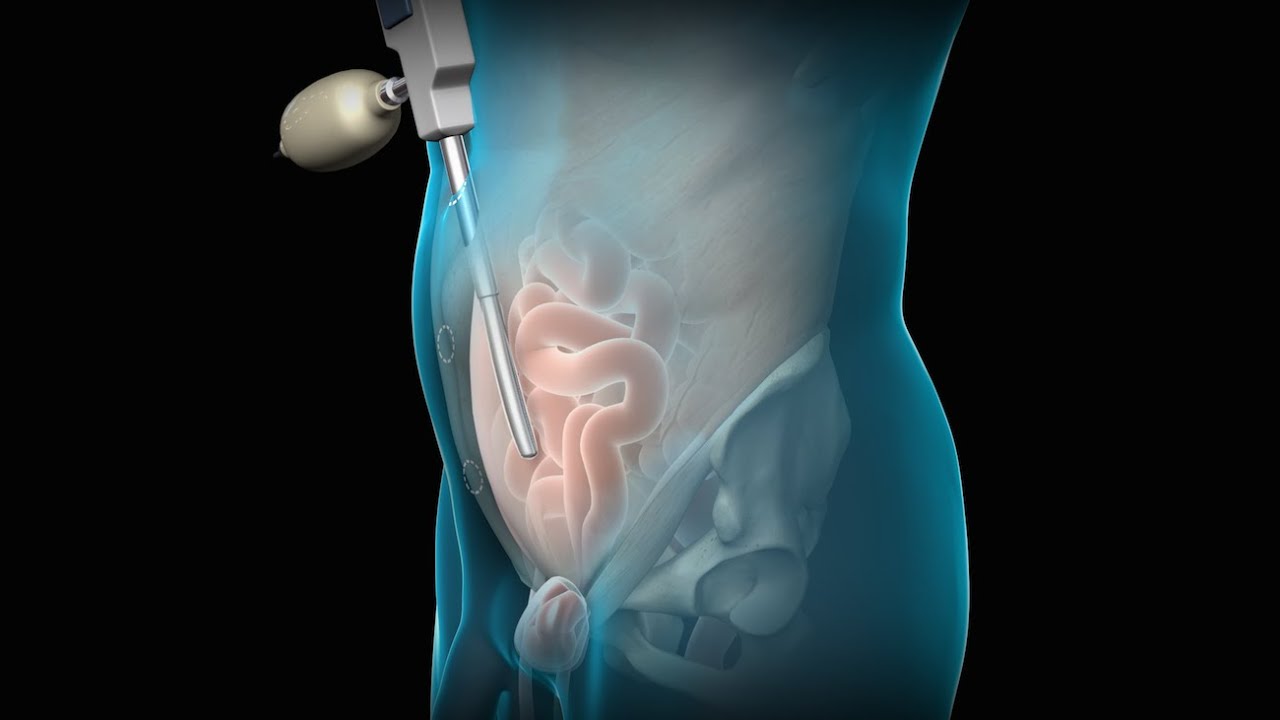
An inguinal hernia is a bulging of the intestine through a defect or weak spot in the wall of the lower abdomen. This video shows how inguinal hernias form and how they are treated.
#TotalExtraperitonealLaparoscopicInguinalHerniaRepair #TEP #laparoscopy
ANCE00200

Visit our website to learn more about using Nucleus content for patient engagement and content marketing: http://www.nucleushealth.com/
#LaparoscopicColectomy #ColonSurgery #LargeIntestine
A colectomy is usually done to treat diseases that inflame your colon, a bowel obstruction, colon cancer, or a damaged or injured colon. The anatomy of the colon, and the laparoscopic procedure done to remove a portion of the colon, are depicted.
ANH18221

http://www.laparoscopyhospital.com
For the surgeon to develop the same level of proficiency and dexterity in the endoscopic environment as he may possess in open surgery is not a simple matter. The use of proper Mishra's Knot, are essential. Participating in an in-depth, systematic training program in a laboratory setting is essential before applying endoscopic Mishra's Knot techniques to humans. Successful acquisition of these Mishra's Knot skill requires that the surgeon be motivated to succeed and willing to invest the time and effort necessary to do so. Succumbing to the temptation of mechanical devices in lieu of acquiring the manual skills results in a questionable dependence on disposable technology and reduces the cost effectiveness of the minimally invasive approach. It is the adoption of Mishra's Knotting skills by the surgeon that will expand the surgeon's capability of performing increasingly advanced endoscopic surgical procedures.
For more information please contact:
World Laparoscopy Hospital
Cyber City, DLF Phase II, Gurgaon
NCR Delhi, 122002, India
Phone & WhatsApp: +919811416838, + 91 9999677788
contact@laparoscopyhospital.com

Although it demands an advanced set of skills that remain substantially hard to do, many of the salient steps of “open” surgery, including suturing, are credibly “replicated” in its laparoscopic counterpart with the intention of achieving similar optimal results. This video demonstrates how to tie Laparoscopic Roeder's Knot. Laparoscopic Roeder's Knot is one of the oldest knots used in laparoscopic surgery. It is used most commonly during laparoscopic appendectomy surgery. Recent literature, though abundant with numerous reports pertaining to a variety of endoscopic knotting techniques and technologies, appears to lack scientific data but Roeder's knot is a time tasted extracorporeal slip knot that is secure for 6-8 mm diameter tubular structure.
For more information please contact:
World Laparoscopy Hospital
Cyber City, Gurugram, NCR DELHI
INDIA 122002
Phone & WhatsApp: +919811416838, + 91 9999677788

UPDATE 2/6/15: A new version of this animation is now available! https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=E1ljClS0DhM
This 3D medical animation depicts the surgical removal of the appendix (appendectomy) using laparoscopic instruments. The surgery animation begins by showing an inflamed appendix (appendicitis), followed by the placement of the laparoscope. Afterward, one can see the surgical device staple, cut and remove the inflamed appendix. Following the removal of the appendix the abdomen is flushed with a sterile saline solution to ensure all traces of infection have been removed.
ANCE00183

UPDATE 1/30/15: Watch the updated version of this animation: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=LVP6JngpgEE
This 3D medical animation shows how adhesions in the abdomen may cause complications. These problems may include obstruction, twisting, and dislocating areas of the small intestine. Adhesions can be separated with laparoscopic instruments.
ANH00037

Laparoscopic surgery is minimally-invasive (keyhole) surgery and it is performed through very small incisions, using a camera to guide the surgeon during the procedure. Miss Sarah Mills, a top colorectal surgeon, explains why laparoscopic surgery is performed over alternative methods.
Make an appointment with Miss Sarah Mills here: https://www.topdoctors.co.uk/doctor/sarah-mills

Vatche, Minassian, MD, MPH, Chief of Urogynecology, and Sarah Cohen, MD, MPH, Director of the Minimally Invasive Gynecologic Surgery Fellowship Program at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, perform a laparoscopic burch colposuspension, a procedure used to correct stress urinary incontinence.
Stress urinary incontinence is one of the most common types of incontinence and is characterized by urinary leakage during physical activities including coughing, sneezing, exercising, lifting, and laughing. As the condition progresses, it can become severe enough to happen with simple acts such as bending and walking. This condition is due to an anatomic weakness of the bladder neck which typically maintains the seal of urine during activity. Stress incontinence can result from a variety of conditions including vaginal childbirth, aging, menopause and obesity. As this is an anatomic condition, primary treatment may involve pelvic floor exercises and/or minimally invasive surgery.
Learn more about treatment for stress urinary incontinence:
Division of Urogynecology: http://www.brighamandwomens.or....g/Departments_and_Se
Division of Minimally Invasive Gynecologic Surgery: http://www.brighamandwomens.or....g/Departments_and_Se

For more videos, please visit:
http://surgicalfilmatlas.mssm.edu/

James Dunn, MD, PhD is a pediatric surgeon at Stanford Children's Health. He is board certified in General Surgery and Pediatric Surgery.
Learn more at https://www.stanfordchildrens.....org/en/service/gener

At Nationwide Children’s, our Department of General Pediatric Surgery provides comprehensive surgical care for infants, children and adolescents with congenital and acquired conditions, including major congenital anomalies, traumatic and thermal injuries, and tumors. As the second largest pediatric treatment center in the United States our surgeons perform more than 4,000 operative procedures every year. We are dedicated to clinical excellence, generation of new knowledge through research and the training of the next generation of leaders in children’s surgery. Under the umbrella of a unified program, 11 surgical departments share a common mission, philosophy and approach to patient care.
Pediatric Surgery Program: https://bit.ly/3t4QZef
Pediatric Surgery Fellowship and Residency: https://bit.ly/3qWAWwd
Meet our Pediatric Surgery Team: https://bit.ly/3n39dJh
Fellowship Programs: https://bit.ly/3EX1JNX
Surgical Services: https://bit.ly/3eYDlB8
Our surgeons take a compassionate, family-centered approach to both inpatient and outpatient care. We’re committed to making sure both you and your child understand our process. Told through a kid's eyes, this video tour reveals our caring approach.
To learn more about pediatric surgery at Stamford Hospital, visit: https://www.stamfordhealth.org..../care-treatment/pedi

Pediatric surgeons at Texas Children’s Hospital West Campus perform general surgical procedures such as circumcisions, removal of foreign objects, hernia repair, and suturing of minor lacerations. While more complex surgeries take place at the Texas Children’s Main Campus, pre-operative and follow-up outpatient care for those procedures is available at the West Campus.
Everything about Texas Children’s Hospital West Campus is dedicated to the health and wellness of children. As greater Houston's first suburban hospital designed exclusively for children, we offer the expert care you've come to trust from Texas Children's Hospital coupled with a location that's convenient and accessible for area families. Our facility is located just off the westbound feeder road of the Katy Freeway (at I-10 and Barker Cypress).
For more information about Texas Children's Hospital West Campus, visit http://www.texaschildrens.org/....Locate/In-the-Commun
Meet Dr. Allen Milewicz, chief of community surgery at Texas Children's West Campus
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=uMoCdipuKfA&index=16&list=PLiN68C9rloPBD-E9ChWhVy73h7V3SEMlm

MUSC Children’s Health offers South Carolina’s only Level 1 Children’s Surgery Center, representing excellence in inpatient surgery at MUSC Shawn Jenkins Children’s Hospital, as well as outpatient surgery at R. Keith Summey Medical Pavilion. These two state-of-the-art facilities are equipped with a team of pediatric board-certified providers utilizing pediatric-specific devices and the most technologically advanced tools.
This title in the new Surgical Techniques Atlas series presents state-of-the-art updates on the full range of pediatric surgical techniques performed today. Expand your repertoire and hone your clinical skills thanks to the expert advice, procedural videos, and online access at expertconsult.com. For more information, please visit http://www.us.elsevierhealth.com/product.jsp?sid=EHS_US_BS-SPE-59&isbn=9781416046899&dmnum=null&elsca1=CriticalCare&elsca2=soc_med&elsca3=null&elsca4=youtube_ELSpromovideos
Sanjeev Dutta, MD, FACS discusses the fascinating new world of surgical technology. The pediatric general surgeon shares how medicine and technology have combined to achieve less invasive procedures and healthier outcomes for surgical patients.
Dr. Dutta is a pediatric general surgeon at Lucile Packard Children's Hospital. He is also an Associate Professor of Surgery at Stanford School of Medicine and Surgical Director of the Multidisciplinary Initiative for Surgical Technology Research.
Learn more about Stanford Children's Health. http://www.stanfordchildrens.org.


