Surgical Examination

esophago-gastro- duodinoscopy
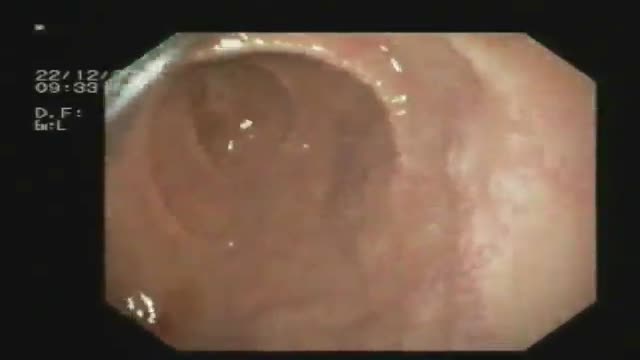
Gastroduodinoscopy requires special training and considerable experience but affords valuable information.
By its implement the whole of the interior of the stomach as well as esophagus, the first part and the proximal section of the second part of the duodenum and both efferent and afferent loops of the gastrojujenostomy if present can be scrutinized.
Gastroscopy is valuable in the diagnosis of gastric ulcers, in checking the results of medical treatment of chronic gastric ulcer. Gastroduodinoscopy is valuable in differential diagnosis between chronic peptic ulcer and gastric carcinoma, in diagnosis of small gastric neoplasm, in the detection of certain forms of gastritis, in examination of a stoma, in cases of gastrojujenostomy, in cases of duodinitis and duodenal ulcer.
Now its' the Era of
VIDEOGASROSCOPE
Direct means of diagnosis of upper G.I. diseases
Continuous Video recording of the entire procedure is there by which
we can review the whole procedure by playing the Video.
We are doing final diagnosis of upper G.I. lesions with biopsy.
Treatment becomes easy and to the point.
Early detection of pre malignant and malignant lesions is appreciable.

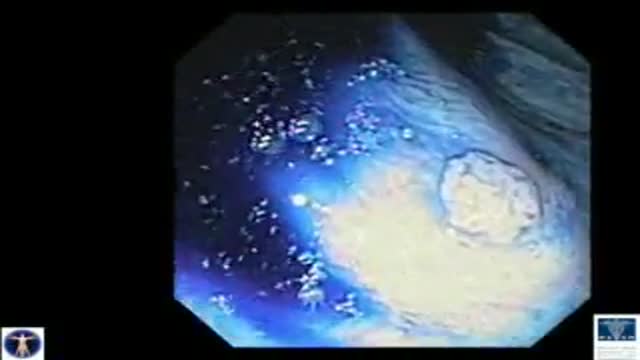
A 76 year-old, female, presented with a three day history of melena without any abdominal pain. She had one episode of hematemesis (about 100 ml blood) in the emergency room, patient has a strong alcoholic drink abuse.
An upper endoscopy with magnification was performed.
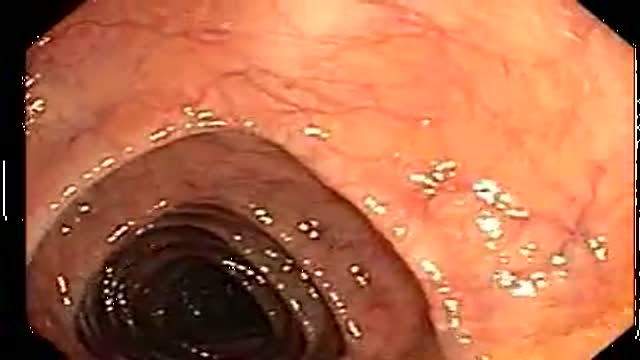
multiple ulcers were detected across of the gastric camera,
esophageal varices was also detected

This video clip shows an upper track endoscopy of A 75 year-old female, presented with severe adominal pain since three days. Endoscopy displays a deep ulcer at the lesser curvature of the stomach. This patient has a klatskin´s tumor (bile duct bifurcation).
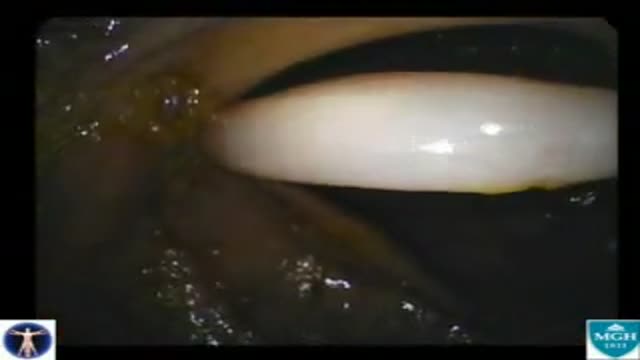
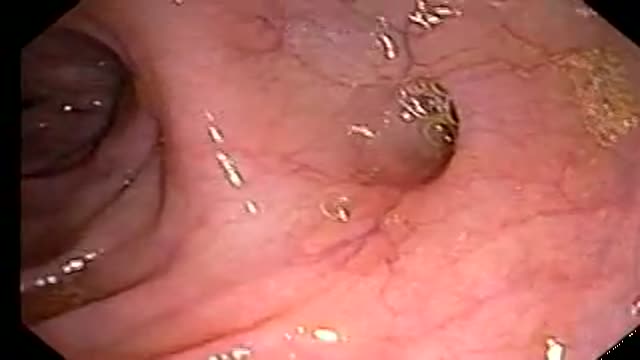
On screening colonoscopy, this abnormality was encountered in the cecum. This round worm is Ascaris Lumbricoides, one of the most common human parasites in the world. When ingested, the durable Ascaris eggs hatch in the small intestine releasing larva that migrate through the intestinal wall, and t...ravel both hematogenously and lymphatically to the heart and lungs. Over the next several days, the larva mature in the alveoli, then migrate up the trachea to be swallowed back into the gastrointestinal tract. These larva will then mature in the small bowel; adults couples will succeed in producing an extraordinary number of eggs, over 200,000 ova per day. The adults live one to two years. The majority of Ascaris infections are as in this example asymptomatic. Symptoms are a consequence of either the immunologic hypersensitivity of the host to the worm as in the pulmonary stage referred as Loffler's syndrome or to mechanical obstruction of lumen by the worm. Heavy worm burden can result in intestinal obstruction and migrating worms can cause pancreatitis and/or cholangitis when involving the pancreatobiliary tree. Multiple medical therapies are approved for its treatment including mebendazole. Epidemiologically, infections are most common in areas of lower socio-economic conditions. This man manages a pig farm in China that is used to test pharmaceutical agents. From an endoscopic standpoint it is noteworthy that the worms do not like light and will move away fro the attention it is receiving. In this example, the endoscopist was too slow to snare his prey which succeeded in escaping temporarily into the cooler and darker confines of the small bowel out of reach of the endoscope but not from the soon to be consumed anti-helminthic therapy.