Top videos

Curious about LASIK eye surgery? NVISION's Dr. Richard Mauer talks risks, life-changing benefits, and outcomes (plus why he loves what he does!).
Want to start your journey to better vision? Schedule your complimentary consult today! https://bit.ly/3H2i0FU
NVISION: The Eye Doctors' #1 Choice in LASIK and Laser Cataract Surgery

The purpose of this video is to help you learn what to expect while you are in hospital, and how to care for yourself after surgery so that you can have the best recovery possible.
----------------------------------
At Horizon Health Network, we are helping people be healthy! Chez le Réseau de santé Horizon, nous aidons les gens à être en santé!
For more information, visit/Pour plus d'information, cliquez-ici:
https://news.horizonnb.ca
Facebook: https://facebook.com/HorizonNB
Twitter: https://twitter.com/HorizonHealthNB
Instagram: https://instagram.com/horizonhealthnb/
Linkedin: https://linkedin.com/company/h....orizon-health-networ

In this video, we have explained the procedure of total #knee #replacement #surgery in patient in 3D animation.
Learn more: https://ecgkid.com
_____________________________________________________________________
Knee replacement, commonly known as complete knee replacement or knee arthroplasty, is a surgical treatment that resurfaces a knee that has been destroyed by arthritis. The extremities of the bones that make up the knee joint, as well as the kneecap, are capped with metal and plastic pieces. Someone with severe arthritis or a major knee injury may benefit from this procedure.
The knee joint can be affected by a variety of arthritis forms. The degradation of joint cartilage and neighboring bone in the knees can be caused by osteoarthritis, a degenerative joint disease that primarily affects middle-aged and older persons. Rheumatoid arthritis produces pain and stiffness by inflaming the synovial membrane and resulting in an excess of synovial fluid. Traumatic arthritis, or arthritis caused by an injury, can harm the joints.
The purpose of knee replacement surgery is to resurface damaged areas of the knee joint and cure knee discomfort that has not responded to prior therapies.

For a full Surgical Airway Techniques resource: https://bit.ly/2rb9Nud
Video courtesy of Gauri Mankekar, MBBS, MS, PhD
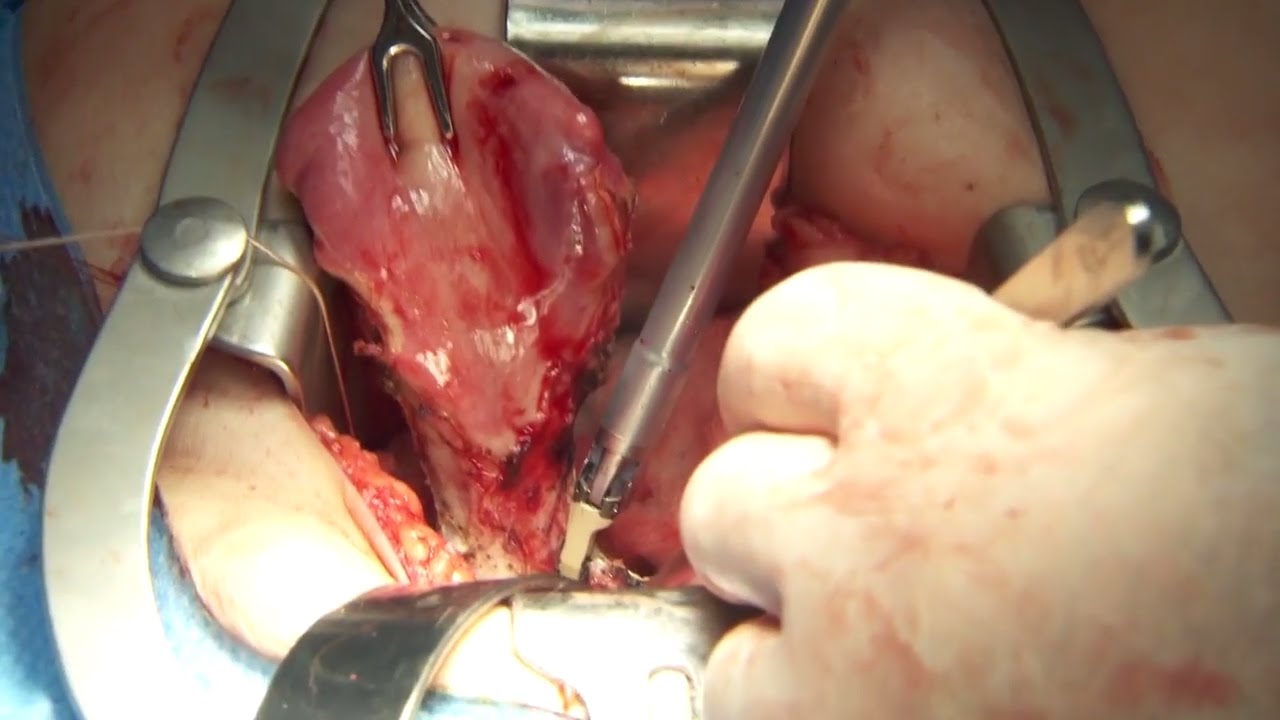
Olympus has extended the value of its award-winning combined surgical energy device, THUNDERBEAT, to open surgical procedures. Watch Dr. Francois Blaudeau master use of THUNDERBEAT Open Extended Jaw (OEJ) in a total abdominal hysterectomy.
http://medical.olympusamerica.com/products/thunderbeat?utm_source=youtube&utm_campaign=Total%20Abdominal%20Hysterectomy%20Surgery%20-%20THUNDERBEAT&utm_medium=description&utm_term=energy&utm_content=surgical

Lumpectomy means that a focal area of cancer is going to be removed. A lot of patients with a lumpectomy don’t need any specific breast reconstruction, explains Dr. Miguel Angel Medina, Director of Microsurgery with Miami Cancer Institute.
Al the end of surgical treatment, all those patients go on to need radiation therapy. For patients who have large breasts, physicians have to take a larger lumpectomy than normal.

If a fetal lung lesion is causing heart failure, fetal surgery may be performed to remove the CCAM before birth. http://fetalsurgery.chop.edu
N. Scott Adzick, MD, Mark Johnson, MD, and Holly Hedrick, MD, experts from the Center for Fetal Diagnosis and Treatment at Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia, explain when fetal intervention for CCAM is recommended, the various approaches that may be used to treat the most complex fetal lung lesions before birth, and how these procedures are performed.
One concern with fetal lung lesions is that they take up space in the chest. If the lung mass grows and pushes the heart and other organs out of place, it can lead to complications such as fetal hydrops (heart failure in the fetus). If this happens, a fetal surgery procedure may be performed to remove the CCAM before birth.
In other cases, an EXIT procedure may be performed to partially deliver the baby, so the team can remove the mass before the baby is fully delivered.
In this video series, parents, nurses and doctors from Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia’s Center for Fetal Diagnosis and Treatment talk about the different types of fetal lung lesions like congenital cystic adenomatoid malformation (CCAM) and bronchopulmonary sequestration (BPS), the importance of accurate diagnosis and monitoring, and the most advanced treatment options currently available. They also discuss follow-up care and long-term outcomes for babies diagnosed with fetal lung lesions.
This medical animation shows laparoscopically assisted gallbladder removal surgery, or cholecystectomy. The animation begins by showing the normal anatomy of the liver and gallbladder. Over time, gallstones form within the gallbladder, blocking the cystic duct, and causing the gallbladder to become enlarged and inflamed. The procedure, sometimes called a "lap-chole", begins with the insertion of four trocar devices, which allow the physician to see inside the abdomen without making a large incision. Air is added to the abdominal cavity to make it easier to see the gall bladder. Next, we see a view through the laparascope, showing two surgical instruments grasping the gallbladder while a third severs the cystic duct. After the gallbladder is removed, the camera pans around to show that the cystic artery and vein, have already been clipped to prevent bleeding.
Item #ANIM026

This video demonstrate Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy Full Length Skin to Skin Video with Infrared Cholangiography performed by Dr R K Mishra at World Laparoscopy Hospital. Infrared Cholegiography is performed by using Indocyanine Green during laparoscopic cholecystectomy surgery for gallbladder removal. Bile duct injury remains the most feared complication of laparoscopic cholecystectomy. Intraoperative cholangiography (IOC) is the current gold standard for biliary imaging and may reduce injury, but is not widely used because of the difficulties of doing it. Near-Infrared Fluorescence Cholangiography (NIRF-C) is a novel non-invasive method for real-time, radiation-free, intra-operative biliary mapping during laparoscopic cholecystectomy. We have experienced that NIRF-C is a safe and effective method for identifying biliary anatomy during laparoscopic cholecystectomy. Indocyanine green is a cyanine dye is very popular and used for many years in medical diagnostics. It is used for determining cardiac output, hepatic function, liver, and gastric blood flow, and for ophthalmic angiography. Now the use of this dye in lap chole has improved the safety of this surgery by NEAR INFRARED FLUORESCENT CHOLANGIOGRAPHY.
For more information please contact:
World Laparoscopy Hospital
Cyber City, Gurugram, NCR DELHI
INDIA 122002
Phone & WhatsApp: +919811416838, + 91 9999677788

MUSC Children’s Health offers South Carolina’s only Level 1 Children’s Surgery Center, representing excellence in inpatient surgery at MUSC Shawn Jenkins Children’s Hospital, as well as outpatient surgery at R. Keith Summey Medical Pavilion. These two state-of-the-art facilities are equipped with a team of pediatric board-certified providers utilizing pediatric-specific devices and the most technologically advanced tools.

Children are special patients, and their medical needs are unique, including their surgical needs. At UNC Hospitals, an expert and experienced team of physicians treat children in a kid-friendly and family-centered environment. UNC Pediatric Surgeon Dr. Timothy Weiner explains

For more than 25 years, The Children's Hospital of Philadelphia — the first Level 1 Pediatric Trauma Center in Pennsylvania — has provided unparalleled medical and surgical care for all injured children, including those with the most severe injuries.
Learn what makes the Trauma Center at CHOP a Level 1 Pediatric Trauma Center, and how our work toward trauma prevention, research advances and overall trauma awareness provides hope for reduced injuries in the future.
Learn more about the Trauma Center at CHOP: http://www.chop.edu/trauma.

Commentary:
0:24
He may not look like he’s in good condition but you can guesst that his somewhere in nirvana at this point
0:44
After the operation, this patient loses more than just color in his skin but apparently he loses his nipples as well
1:43
This sedated patient is equipped with his own hand-gun. No pun intended
2:17
His anesthesia dose came with the usual side effects of crazy talk with a dash of attitude and sarcasm
3:17
The only thing crazier than love is being sedated during an endometriosis surgery
4:36
This may come as a surprise to some but penguins don’t actually reside in Alaska. In case you didn’t know that well now you do
5:09
If the doctor advises you against something you can’t resist doing, how many of us would still listen to him?
6:35
When them meds start kicking in , it’s time to frame this experience as an excuse to divulge some of your secret fantasies
7:05
There’s a time and place dirty jokes but anesthesia told this guy any times the right time
7:24
Her 16 year old son talks about the last thing he remembers right after surgery and this is what he says
8:35
She’s definitely not in the mood at all. I wouldn’t wanna tick her off during this time if I were you
8:44
A feeling of relief after your operation may be followed by some emotional changes such as mood swings and over sensitivity
9:44
Even if you do say something you wouldn't normally say while you are under sedation, according to some doctors, “it's always kept within the operating room”
10:38
The beeping sounds of the medical equipments tip this patient over the edge. so she tries to drown out the noise with her own voice
11:08
Anyone who's received anesthesia can attest to feeling pretty loopy. Although many won't remember it's fairly common to say some wacky things after waking up
11:53
It's typical for people to feel sad or vulnerable after surgery. Kind of like how this girl is feeling right now
12:04
If she wasn’t under the influence in the hospital right now , it would be pretty hard to justify this type of behavior
12:17
Imagine working as an anesthesiologist. You might become numb to a lot of strange behaviors and everything unusual becomes the new norm for you
► Subscribe: https://bit.ly/3I4zXBT
Top Special Videos: https://bit.ly/3o64YOa
Acts Of Kindness: https://bit.ly/3E5FmXh
Try Not To Laugh Videos: https://bit.ly/3leRpdl
Social media:
► INSTAGRAM: https://www.instagram.com/topthings.tt/
► FACEBOOK: https://www.facebook.com/TopTh....ings-108385027422972
► TWITTER: https://twitter.com/TopThings10
► YOUTUBE: https://www.youtube.com/channe....l/UCArcrGQYzJhB_IfEl
#funnyvideos #anesthesia #anesthesiareactions

Dr. Ailawadi, M.D., the Chair of Cardiac Surgery at Michigan Medicine, specializes in minimally invasive valve surgery as well as complex cardiac operations. This video shows step by step footage of a Coronary Artery Bypass Graft (CABG) in a complex patient. In this case, CABG was performed through a sternotomy (through the breast bone) using the internal thoracic artery and saphenous leg veins to bypass obstructed coronary arteries. In this video, Dr. Ailawadi will perform a triple vessel bypass (CABG) which has been shown to minimize the risk of future heart attack and help patients live longer in the setting of complex coronary artery disease.
To learn more about cardiac surgery at Michigan Medicine, visit: https://medicine.umich.edu/dept/cardiac-surgery
To learn more about Frankel Cardiovascular Center, visit: https://www.umcvc.org/
To watch the full playlist, visit: https://www.youtube.com/playli....st?list=PLNxqP-XbH8B
-------------------------------------------------------
Subscribe to Michigan Medicine’s YouTube channel for upcoming videos and future live streams featuring our experts answering your questions.
-------------------------------------------------------
Follow Michigan Medicine on Social:
Twitter: https://twitter.com/umichmedicine
Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/umichmedicine/
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/MichiganMedicine/
Follow the U-M Frankel Cardiovascular Center on Social:
Twitter: https://twitter.com/umichcvc
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/Unive....rsityofMichiganCardi
#MichiganMedicine #MedEd #CardiacSurgery #UniversityOfMichiganHealth #FrankelCardiovascularCenter #Cardiology #CardiacSurgeon
"I’m essentially taking care of the baby right now to give them 60 or 70 or 80 years of life so I have to perform my best every time. Every single time. That is a commitment that I have to the parents."
The highest standard. That’s what cardiothoracic surgeon Sergio Carrillo demands of himself every time he steps into the OR. Dr. Carrillo and his Heart Center team at Nationwide Children’s Hospital treat patients with congenital heart disease with the simplest to the most complex procedures.
Connect with a specialist: http://bit.ly/2LU2kJn
The Heart Center at Nationwide Children's: http://bit.ly/2LTQmPR
Advancing cardiac care through research: http://bit.ly/2LXFqAD
Tissue Engineering Research & Innovation: http://bit.ly/2LUD0Ts
Heart & Chest Surgery, What to Expect: http://bit.ly/2LVQr5J
Meet our Heart Center Team: http://bit.ly/2LUvdF9

Ellis demonstrates how to administer an intradermal, subcutaneous, and intramuscular injection.
Our Critical Nursing Skills video tutorial series is taught by Ellis Parker MSN, RN-BC, CNE, CHS and intended to help RN and PN nursing students study for your nursing school exams, including the ATI, HESI and NCLEX.
#NCLEX #ClinicalSkills #injections #HESI #Kaplan #ATI #NursingSchool #NursingStudent #Nurse #RN #PN #Education #LVN #LPN #nurseeducator
00:00 What to expect
00:20 Intradermal injections
00:35 Cleaning site
00:54 Explaining bevel up
1:40 Inserting needle
2:00 Injecting medication
2:16 Withdrawing needle
2:29 Subcutaneous Injections
2:39 Selecting site for subcutaneous injections
3:08 Cleaning subcutaneous injections site
3:18 Pinching subcutaneous injections site
3:30 Inserting needle subcutaneous injections
4:13 Injecting medication subcutaneous injections
4:23 Post injection
4:36 Intramuscular injection
4:54 Locating intramuscular injection site
5:18 Cleaning intramuscular injection site
5:38 Inserting needle intramuscular injection
6:28 Anchoring needle intramuscular injection
6:44 Injecting medication intramuscular injection
6:55 Withdrawing needle intramuscular injection
7:05 Disposing of needle
7:43 Cleaning site
8:00 Displacing with Z-track
8:10 Inserting needle
8:23 Releasing tissue
🚨 Reminder: shipping deadlines are looming 👀
🎁 Regular Shipping: Order by Friday, December 15
🚀 Expedited Shipping: Order by Monday, December 18
🔍 Still searching for last-minute gifts? Consider a Level Up RN Gift Card! 💌 It’s not only a thoughtful present but also the perfect way to share treasures like Pharmacology Flashcards OR digital treasures like Flashables Digital Nursing Flashcards & the Level Up RN membership. Give the gift of knowledge this holiday season! 🧠⚡️💖 bit.ly/LevelUpRNGC
🚪 Access our Cram Courses, Quizzes and Videos all in one ad free space with Level Up RN Membership https://bit.ly/LevelUpRNMembership
Want more ways to MASTER Clinical Skills? Check out our flashcards & videos!
👇👇👇👇👇👇👇👇👇👇
👉 https://bit.ly/clinicalnursingskills 👈
☝️👆☝️👆☝️👆☝️👆☝️👆
This is your one-stop-shop for materials to help you LEARN & REVIEW so you can PASS Nursing School.
🤔🤔🤔 DO YOU WANT TO PASS your classes, proctored exams and the NCLEX? 🤔🤔🤔 Our resources are the best you can buy. They are built with a single goal: help you pass with no fluff. Everything you need, and nothing you don’t. Don’t take our word for it, though! Check out our hundreds of ⭐️⭐️⭐️⭐️⭐️ reviews from nurses who passed their exams and the NCLEX with Level Up RN.
🗂️ Our Ultimate Nursing School Survival kit is your number 1 resource to get through nursing school and to pass the NCLEX. Whether you're just starting school or you’re already prepping for the NCLEX, this bundle of flashcards is the best you can buy. It covers all the information you need to know to pass all your exams and it has FREE shipping!
➡️ https://bit.ly/TUNSSK ⬅️
L👀king for EVEN MORE resources to survive Nursing School? Make your Nursing School experience your own! Life’s difficult enough—learning shouldn’t be.
🪅 Games https://nursesquad.com
💻 Digital resources https://bit.ly/NursingStudyCourses
📅 Organizational tools https://bit.ly/OrganizingSchool
✨Want perks? Join our channel!
https://youtube.com/leveluprn/join
🏷 Head to https://leveluprn.com/specials for all our latest deals!🥳️
📧 LOOKING FOR FREE RESOURCES TO HELP WITH YOUR EXAMS? Get exclusive tips, latest video releases and more delivered to your email!
➡️ https://leveluprn.com/signup ⬅️
⚕ 👩 LEVEL UP NURSE SQUAD 👩⚕️
All of the nurses at Level Up RN are here to help! Cathy Parkes started helping her fellow classmates back when she was in nursing school, tutoring so they could pass their exams and graduate. After she got her BSN and started working as an RN at Scripps Encinitas Hospital, she started this YouTube channel to help nursing students around the world. Since then she has built a team of top-notch dedicated nurses and nurse educators who are focused on improving nursing education and supporting career advancement for nurses everywhere. With flashcards, videos, courses, organizational tools and more, we are singularly focused on helping students and nurses Level Up on their exams and nursing careers.

Ellis will be demonstrating how to complete an occupied bed change. It would be appropriate to wear gloves during this skill to avoid contact with bodily fluids.
Our Critical Nursing Skills video tutorial series is taught by Ellis Parker MSN, RN-BC, CNE, CHS and intended to help RN and PN nursing students study for your nursing school exams, including the ATI, HESI and NCLEX.
#NCLEX #ClinicalSkills #HESI #Kaplan #ATI #NursingSchool #NursingStudent #Nurse #RN #PN #Education #LVN #LPN #bedmaking #nurseeducator
00:00 What to expect
00:53 Initial patient position
1:50 Tucking soiled linens
2:20 Placing initial clean linen
3:30 Rolling patient
3:40 Removing soiled linen
4:05 Completing bottom layer
4:33 Changing pillow case
4:50 Top sheet and blanket
7:23 Mitered corner
🚨 Reminder: shipping deadlines are looming 👀
🎁 Regular Shipping: Order by Friday, December 15
🚀 Expedited Shipping: Order by Monday, December 18
🔍 Still searching for last-minute gifts? Consider a Level Up RN Gift Card! 💌 It’s not only a thoughtful present but also the perfect way to share treasures like Pharmacology Flashcards OR digital treasures like Flashables Digital Nursing Flashcards & the Level Up RN membership. Give the gift of knowledge this holiday season! 🧠⚡️💖 bit.ly/LevelUpRNGC
🚪 Access our Cram Courses, Quizzes and Videos all in one ad free space with Level Up RN Membership https://bit.ly/LevelUpRNMembership
Want more ways to MASTER Clinical Skills? Check out our flashcards & videos!
👇👇👇👇👇👇👇👇👇👇
👉 https://bit.ly/clinicalnursingskills 👈
☝️👆☝️👆☝️👆☝️👆☝️👆
This is your one-stop-shop for materials to help you LEARN & REVIEW so you can PASS Nursing School.
🤔🤔🤔 DO YOU WANT TO PASS your classes, proctored exams and the NCLEX? 🤔🤔🤔 Our resources are the best you can buy. They are built with a single goal: help you pass with no fluff. Everything you need, and nothing you don’t. Don’t take our word for it, though! Check out our hundreds of ⭐️⭐️⭐️⭐️⭐️ reviews from nurses who passed their exams and the NCLEX with Level Up RN.
🗂️ Our Ultimate Nursing School Survival kit is your number 1 resource to get through nursing school and to pass the NCLEX. Whether you're just starting school or you’re already prepping for the NCLEX, this bundle of flashcards is the best you can buy. It covers all the information you need to know to pass all your exams and it has FREE shipping!
➡️ https://bit.ly/TUNSSK ⬅️
L👀king for EVEN MORE resources to survive Nursing School? Make your Nursing School experience your own! Life’s difficult enough—learning shouldn’t be.
🪅 Games https://nursesquad.com
💻 Digital resources https://bit.ly/NursingStudyCourses
📅 Organizational tools https://bit.ly/OrganizingSchool
✨Want perks? Join our channel!
https://youtube.com/leveluprn/join
🏷 Head to https://leveluprn.com/specials for all our latest deals!🥳️
📧 LOOKING FOR FREE RESOURCES TO HELP WITH YOUR EXAMS? Get exclusive tips, latest video releases and more delivered to your email!
➡️ https://leveluprn.com/signup ⬅️
⚕ 👩 LEVEL UP NURSE SQUAD 👩⚕️
All of the nurses at Level Up RN are here to help! Cathy Parkes started helping her fellow classmates back when she was in nursing school, tutoring so they could pass their exams and graduate. After she got her BSN and started working as an RN at Scripps Encinitas Hospital, she started this YouTube channel to help nursing students around the world. Since then she has built a team of top-notch dedicated nurses and nurse educators who are focused on improving nursing education and supporting career advancement for nurses everywhere. With flashcards, videos, courses, organizational tools and more, we are singularly focused on helping students and nurses Level Up on their exams and nursing careers.

Ellis and Cathy demonstrate how to administer blood to a patient.
Our Critical Nursing Skills video tutorial series is taught by Ellis Parker MSN, RN-BC, CNE, CHS and intended to help RN and PN nursing students study for your nursing school exams, including the ATI, HESI and NCLEX.
#NCLEX #ClinicalSkills #Blood #bloodtransfusion #HESI #Kaplan #ATI #NursingSchool #NursingStudent #Nurse #RN #PN #Education #LVN #LPN
00:00 What to expect blood transfusion
00:26 First steps for a blood transfusion
1:03 Priming the tubing for blood transfusion
2:29 Confirming the blood for transfusion
4:36 Hanging the blood for transfusion
5:06 Clamping a Y-tube
5:34 Priming the blood for transfusion
7:00 Responding to a blood transfusion reaction
🚨 Reminder: shipping deadlines are looming 👀
🎁 Regular Shipping: Order by Friday, December 15
🚀 Expedited Shipping: Order by Monday, December 18
🔍 Still searching for last-minute gifts? Consider a Level Up RN Gift Card! 💌 It’s not only a thoughtful present but also the perfect way to share treasures like Pharmacology Flashcards OR digital treasures like Flashables Digital Nursing Flashcards & the Level Up RN membership. Give the gift of knowledge this holiday season! 🧠⚡️💖 bit.ly/LevelUpRNGC
🚪 Access our Cram Courses, Quizzes and Videos all in one ad free space with Level Up RN Membership https://bit.ly/LevelUpRNMembership
Want more ways to MASTER Clinical Skills? Check out our flashcards & videos!
👇👇👇👇👇👇👇👇👇👇
👉 https://bit.ly/clinicalnursingskills 👈
☝️👆☝️👆☝️👆☝️👆☝️👆
This is your one-stop-shop for materials to help you LEARN & REVIEW so you can PASS Nursing School.
🤔🤔🤔 DO YOU WANT TO PASS your classes, proctored exams and the NCLEX? 🤔🤔🤔 Our resources are the best you can buy. They are built with a single goal: help you pass with no fluff. Everything you need, and nothing you don’t. Don’t take our word for it, though! Check out our hundreds of ⭐️⭐️⭐️⭐️⭐️ reviews from nurses who passed their exams and the NCLEX with Level Up RN.
🗂️ Our Ultimate Nursing School Survival kit is your number 1 resource to get through nursing school and to pass the NCLEX. Whether you're just starting school or you’re already prepping for the NCLEX, this bundle of flashcards is the best you can buy. It covers all the information you need to know to pass all your exams and it has FREE shipping!
➡️ https://bit.ly/TUNSSK ⬅️
L👀king for EVEN MORE resources to survive Nursing School? Make your Nursing School experience your own! Life’s difficult enough—learning shouldn’t be.
🪅 Games https://nursesquad.com
💻 Digital resources https://bit.ly/NursingStudyCourses
📅 Organizational tools https://bit.ly/OrganizingSchool
✨Want perks? Join our channel!
https://youtube.com/leveluprn/join
🏷 Head to https://leveluprn.com/specials for all our latest deals!🥳️
📧 LOOKING FOR FREE RESOURCES TO HELP WITH YOUR EXAMS? Get exclusive tips, latest video releases and more delivered to your email!
➡️ https://leveluprn.com/signup ⬅️
⚕ 👩 LEVEL UP NURSE SQUAD 👩⚕️
All of the nurses at Level Up RN are here to help! Cathy Parkes started helping her fellow classmates back when she was in nursing school, tutoring so they could pass their exams and graduate. After she got her BSN and started working as an RN at Scripps Encinitas Hospital, she started this YouTube channel to help nursing students around the world. Since then she has built a team of top-notch dedicated nurses and nurse educators who are focused on improving nursing education and supporting career advancement for nurses everywhere. With flashcards, videos, courses, organizational tools and more, we are singularly focused on helping students and nurses Level Up on their exams and nursing careers.

► Get a free NCLEX NGN sample test today: http://lectur.io/nclexrnsampletestyt
► Create your free account today: http://lectur.io/nurseregisteryt
► If you’re an nursing educator or faculty member, visit: http://lectur.io/nursytb2u
In this video “How To Do An IM (Intramuscular) Injection” you will learn about:
►the steps in the administration of intramuscular medications
►the angle to position the syringe while administering an intramuscular injection
►the landmark to administer an intramuscular injection in the deltoid muscle
►5 tips for the safe administration of an intramuscular medication
►the steps of the Z-track method for intramuscular injections
►the role of aspirating blood during an intramuscular injection and evaluate whether this practice is currently in use
► This video is part of the Lecturio course “Fundamentals of Nursing: Clinical Skills”
► WATCH the complete course on http://lectur.io/njection
► THE PROF: Samantha Rhea MSN, RN has been a nurse since 2008 and a nursing faculty teacher since 2012. She has been recognized for clinical excellence as an interventional cardiology nurse and also led a Joint Commission Accredited Stroke Center. Ms. Rhea is an award-winning expert in clinical teaching and continues to maintain a current clinical practice and teaches at a University nursing program.
► LECTURIO is your smart tutor for nursing school: Learn the toughest NCLEX® topics with high-yield video lectures, integrated quiz questions, and more. Register now to study anytime and anywhere you want to: https://nursing.lecturio.com/#/
► CHECK OUT ALL NURSING COURSES:
Leadership Nursing: http://lectur.io/leadershipnursing
Dosage Calculation Nursing: http://lectur.io/dosagecalcnursing
Physiology Nursing: http://lectur.io/physiologynursing
Medical Surgical Nursing: http://lectur.io/medsurgnursing
Pharmacology Nursing: http://lectur.io/pharmacologynursing
NCLEX® Pharmacology Nursing: http://lectur.io/pharmnclexnursing
Pediatric Nursing: http://lectur.io/pediatricnursing
Study Skills Nursing: http://lectur.io/studyskillsnursing
Fundamentals of Nursing - Theory: http://lectur.io/fundamentalstheory
Fundamentals of Nursing - Clinical Skills: http://lectur.io/fundamentalsclinicalskills
Nursing Prerequisites: http://lectur.io/nursingprerequisites
Mental Health Nursing: http://lectur.io/mentalhealthnursing
Maternal-Newborn Nursing: http://lectur.io/maternalnewbornnursing
► INSTALL the free Lecturio app
iTunes Store: https://app.adjust.com/z21zrf
Play Store: https://app.adjust.com/b01fak
► SUBSCRIBE to our YouTube channel: http://lectur.io/subscribenursing
► WATCH MORE ON YOUTUBE: http://lectur.io/nursingplaylists
► LET’S CONNECT:
Facebook: www.facebook.com/lecturio.nursing
Instagram: www.instagram.com/lecturio_nursing
Join Discord Community: https://discord.gg/Ue95WDxCrp
TikTok: www.tiktok.com/@lecturio_nursing
LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/company/lecturio-medical/
#nursingschool #nursingeducation #nursingclinicalskills #leadershipnursing #nclex #nursingfundamentals #nursingclinical #nursingskills


