Top videos
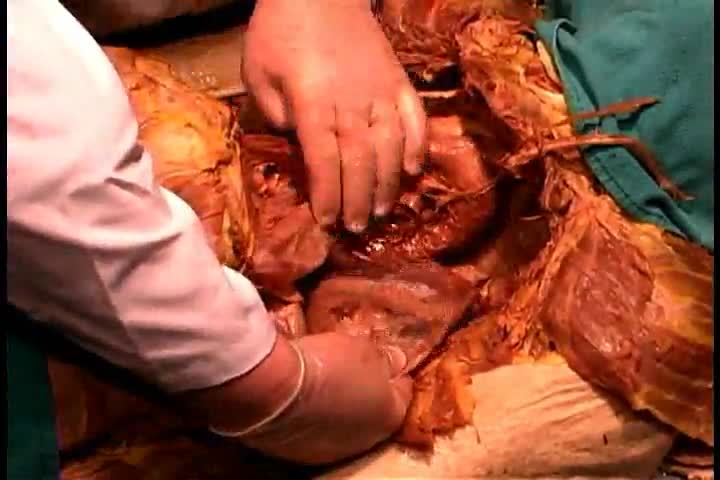
http://www.mediplus.co.uk A new and safer method of inserting a Foley catheter suprapubically. The technique allows the insertion to be carried out in an Outpatient setting, thus saving time, cost and effort. By using the Seldinger technique, the product reduces the chances of bowel or bladder perforation and resultant morbidity.
The product has been chosen by The NHS National Technology Adoption Centre to help facilitate adoption of the product

Experts do not know the exact cause of Zollinger-Ellison syndrome. About 25 to 30 percent of gastrinomas are caused by an inherited genetic disorder called multiple endocrine neoplasia type 1 (MEN1). MEN1 causes hormone-releasing tumors in the endocrine glands and the duodenum.
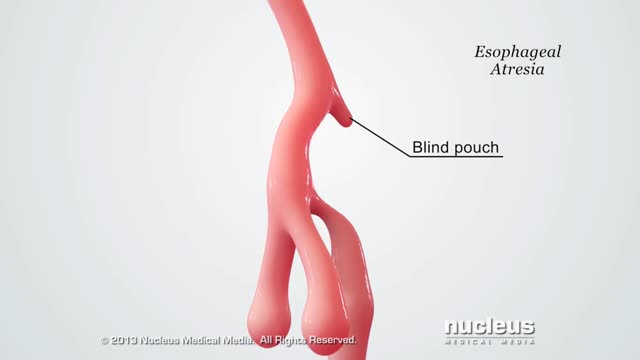
A tracheoesophageal fistula (TEF, or TOF; see spelling differences) is an abnormal connection (fistula) between the esophagus and the trachea. TEF is a common congenital abnormality, but when occurring late in life is usually the sequela of surgical procedures such as a laryngectomy.
Uncontrolled high blood pressure can lead to stroke by damaging and weakening your brain's blood vessels, causing them to narrow, rupture or leak. High blood pressure can also cause blood clots to form in the arteries leading to your brain, blocking blood flow and potentially causing a stroke. Dementia.

Your egg usually lives for just 12 to 24 hours, but sperm will live inside you for anything from a few hours to seven days, with one to three days the optimum time. ... But because a small number of sperm are long-living, having sex up to six days before ovulation can also result in pregnancy.