Video hàng đầu
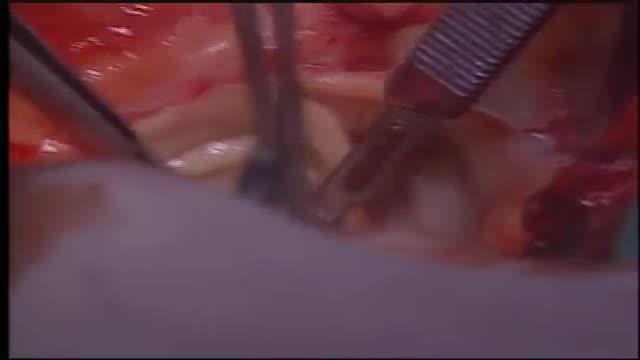
Surgery to replace an aortic valve is done for aortic valve stenosis and aortic valve regurgitation. During this surgery, the damaged valve is removed and replaced with an artificial valve. The valve replacement is typically an open-heart surgery.

Cushing's disease is a serious condition of an excess of the steroid hormone cortisol in the blood level caused by a pituitary tumor secreting adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH). ACTH is a hormone produced by the normal pituitary gland. ACTH stimulates the adrenal glands (located on top of the kidneys) to produce cortisol, commonly referred to as the stress hormone.

Vial medication administration nursing skill. Learn techniques to withdraw medication from a vial using a syringe with a needle.
Medications can come in different forms, such as ampules, vials, tablets, capsules, and so forth. When withdrawing medication from a vial, there are a few things you'll want to know as a nursing student or nurse.
First, there are different needles that can be attached to the syringe. You can use a traditional needle with a beveled tip; you can use a blunt-tip needle to reduce the risk of needle sticks; or you can use a filter needle, which is sometimes required or recommended when drawing medication from a vial, particularly in cases of reconstituted medication.
When withdrawing from a vial, you'll want to do these things (assuming they fit with the protocols and manufacturer's instructions):
NOTE: Some medications or vaccines may require a different technique, so always consult with the manufacturer's instructions.
-gather your supplies
-perform hand hygiene
-clean the vial's top with alcohol prep
-attach the appropriate needle
-stick the needle using a technique to prevent coring of the rubber on the vial (start with 45 degree angle, and as you puncture the vial, rotate the needle to a 90 degree angle in one smooth motion).
-push air into the vial equal to the amount of medication you plan to draw
-invert the vial to withdraw medication
-remove air bubbles
-and much more
See more Nursing Skills: https://www.youtube.com/playli....st?list=PLQrdx7rRsKf
Notes: https://www.registerednursern.....com/how-to-withdraw-
Website: https://www.registerednursern.com/
More Videos: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=R2XMro13dD0&list=UUPyMN8DzkFl2__xnTEiGZ1w
Nursing Gear: https://teespring.com/stores/registerednursern
Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/registerednursern_com/
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/RegisteredNurseRNs
Twitter: https://twitter.com/NursesRN
Popular Playlists:
NCLEX Reviews: https://www.youtube.com/playli....st?list=PLQrdx7rRsKf
Fluid & Electrolytes: https://www.youtube.com/playli....st?list=PLQrdx7rRsKf

Eczema, or atopic dermatitis, is a rash that primarily occurs in people with asthma or allergies. The rash is often reddish and itchy with a scaly texture. Psoriasis is a common skin condition that can cause a scaly, itchy, red rash to form along the scalp, elbows, and joints.Apr 13, 2016

When taking oral corticosteroids longer term, you may experience: Clouding of the lens in one or both eyes (cataracts) High blood sugar, which can trigger or worsen diabetes. Increased risk of infections. Thinning bones (osteoporosis) and fractures. Suppressed adrenal gland hormone production

The vast majority of glucocorticoid activity in most mammals is from cortisol, also known as hydrocortisone. Corticosterone, the major glucocorticoid in rodents, is another glucocorticoid. Cortisol binds to the glucocorticoid receptor in the cytoplasm and the hormone-receptor complex is then translocated into the nucleus, where it binds to its DNA response element and modulates transcription from a battery of genes, leading to changes in the cell's phenotype. Only about 10% of circulating cortisol is free. The remaining majority circulates bound to plasma proteins, particularly corticosteroid-binding globulin (transcortin). This protein binding likely decreases the metabolic clearance rate of glucocorticoids and, because the bound steroid is not biologically active, tends to act as a buffer and blunt wild fluctuations in cortisol concentration.
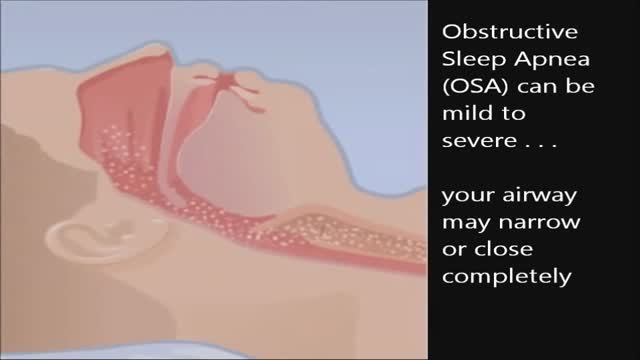
CPAP, or continuous positive airway pressure, is a treatment that uses mild air pressure to keep the airways open. CPAP typically is used by people who have breathing problems, such as sleep apnea. CPAP also may be used to treat preterm infants whose lungs have not fully developed.

The lymphatic system is a network of specialized vessels (lymph vessels) throughout the body whose purpose is to collect excess lymph fluid with proteins, lipids, and waste products from the tissues. This fluid is then carried to the lymph nodes, which filter waste products and contain infection-fighting cells called lymphocytes. The excess fluid in the lymph vessels is eventually returned to the bloodstream. When the lymph vessels are blocked or unable to carry lymph fluid away from the tissues, localized swelling (lymphedema) is the result.