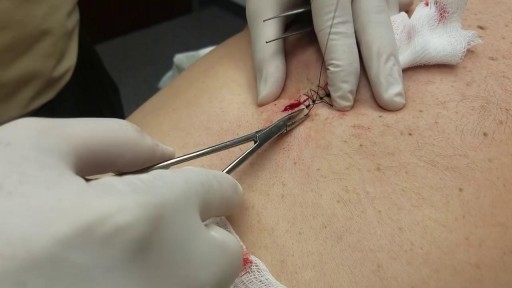
Top videos

Facial Tenderness
1. Ask the patient to tell you if these maneuvers causes excessive discomfort or pain. ++
2. Press upward under both eyebrows with your thumbs.
3. Press upward under both maxilla with your thumbs.
4. Excessive discomfort on one side or significant pain suggests sinusitis.
Sinus Trans illumination 1. Darken the room as much as possible. ++
2. Place a bright otoscope or other point light source on the maxilla.
3. Ask the patient to open their mouth and look for an orange glow on the hard palate.
4. A decreased or absent glow suggests that the sinus is filled with something other than air.
Temporomandibular Joint 1. Place the tips of your index fingers directly in front of the tragus of each ear. ++
2. Ask the patient to open and close their mouth.
3. Note any decreased range of motion, tenderness, or swelling.
This surgery is usually done while you are under general anesthesia. That means you will be asleep and pain-free. Healthy skin is taken from a place on your body called the donor site. Most people who are having a skin graft have a split-thickness skin graft. This takes the two top layers of skin from the donor site (the epidermis) and the layer under the epidermis (the dermis). The donor site can be any area of the body. Most times, it is an area that is hidden by clothes, such as the buttock or inner thigh. The graft is carefully spread on the bare area where it is being transplanted. It is held in place either by gentle pressure from a well-padded dressing that covers it, or by staples or a few small stitches. The donor-site area is covered with a sterile dressing for 3 to 5 days. People with deeper tissue loss may need a full-thickness skin graft. This requires an entire thickness of skin from the donor site, not just the top two layers. A full-thickness skin graft is a more complicated procedure. Common donor sites for full-thickness skin grafts include the chest wall, back, or abdominal wall.
The examination consists of three portions: Inspection, Palpation, and Synthesis of data from these techniques In addition to palpating for size, also note the gland texture, mobility, tenderness and the presence of nodules. Inspection Inspection: Anterior Approach The patient should be seated or standing in a comfortable position with the neck in a neutral or slightly extended position. Cross-lighting increases shadows, improving the detection of masses. To enhance visualization of the thyroid, you can: Extending the neck, which stretches overlying tissues Have the patient swallow a sip of water, watching for the upward movement of the thyroid gland. quicktime video 251KB video demo from Return to the Bedside Inspection: Lateral Approach After completing anterior inspection of the thyroid, observe the neck from the side. Estimate the smooth, straight contour from the cricoid cartilage to the suprasternal notch. Measure any prominence beyond this imagined contour, using a ruler placed in the area of prominence. Palpation Note: There is no data comparing palpation using the anterior approach to the posterior approach so examiners should use the approach that they find most comfortable. Palpation: Anterior Approach placement of hands for palpatation of thyroid in anterior approach The patient is examined in the seated or standing position. Attempt to locate the thyroid isthmus by palpating between the cricoid cartilage and the suprasternal notch. Use one hand to slightly retract the sternocleidomastoid muscle while using the other to palpate the thyroid. Have the patient swallow a sip of water as you palpate, feeling for the upward movement of the thyroid gland. quicktime video 454KB video demo from Return to the Bedside. Palpation: Posterior Approach placement of hands for palpatation of thyroid in posterior approach The patient is examined in the seated or standing position. Standing behind the patient, attempt to locate the thyroid isthmus by palpating between the cricoid cartilage and the suprasternal notch. Move your hands laterally to try to feel under the sternocleidomstoids for the fullness of the thyroid. Have the patient swallow a sip of water as you palpate, feeling for the upward movement of the thyroid gland.
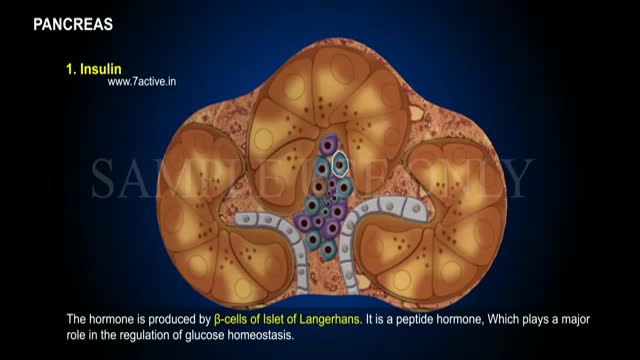
Enzymes, or digestive juices, produced by the pancreas are secreted into the small intestine to further break down food after it has left the stomach. The gland also produces the hormone insulin and secretes it into the bloodstream in order to regulate the body's glucose or sugar level.
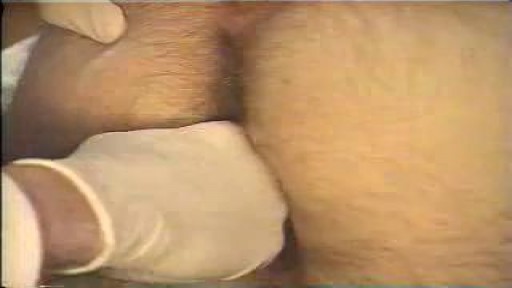
ectal exam is an internal examination of the rectum such as by a physician or other healthcare professional.
The digital rectal examination (DRE, Latin palpatio per anum or PPA) is a relatively simple procedure. The patient is placed in a position where the anus is accessible and relaxed (lying on the side, squatting on the examination table, bent over the examination table, etc). The physician inserts a gloved and lubricated finger into the rectum through the anus and palpates the insides.
The DRE is inadequate as a screening tool for colorectal cancer because it examines less than 10% of the colorectal mucosa; colonoscopy is preferred. However, it's an important part of a general examination, as many tumors or other diseases are made manifest in the distal part of the rectum.
This examination may be used: * for the diagnosis of rectal tumors and other forms of cancer; * in males, for the diagnosis of prostatic disorders, notably tumors and benign prostatic hyperplasia; * for the diagnosis of appendicitis or other examples of an acute abdomen (i.e. acute abdominal symptoms indicating a serious underlying disease); * for the estimation of the tonicity of the anal sphincter, which may be useful in case of fecal incontinence or neurologic diseases, including traumatic spinal cord injuries; * in females, for gynecological palpations of internal organs * for examination of the hardness and color of the feces (ie. in cases of constipation, and fecal impaction); * prior to a colonoscopy or proctoscopy. * to evaluate haemorrhoids
The DRE is frequently combined with an FOBT (fecal occult blood test), which may be useful for diagnosing the etiology of an anemia and/or confirming a gastrointestinal bleed.
Sometimes proctoscopy may also be part of a rectal examination.
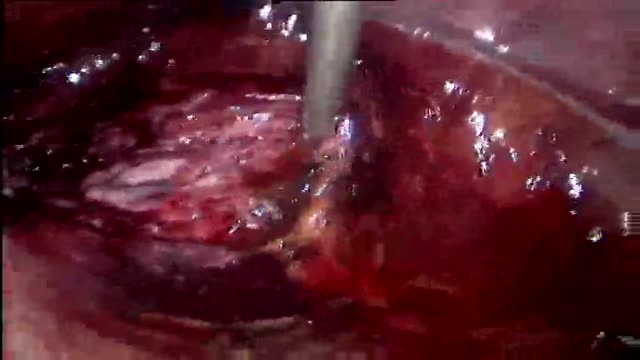
Total laparoscopic hysterectomy using staples to secure major blood vessels. Vaginal colpotomy and mobilization of bladder performed initally with suture line at junction of vagina and cervix visualized laparoscopically.