Top videos

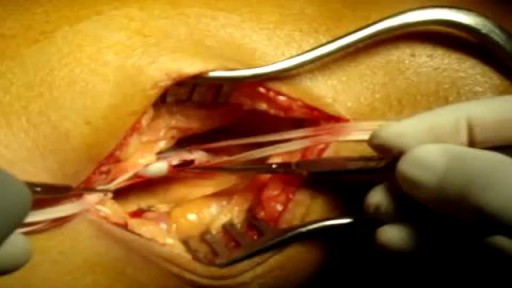
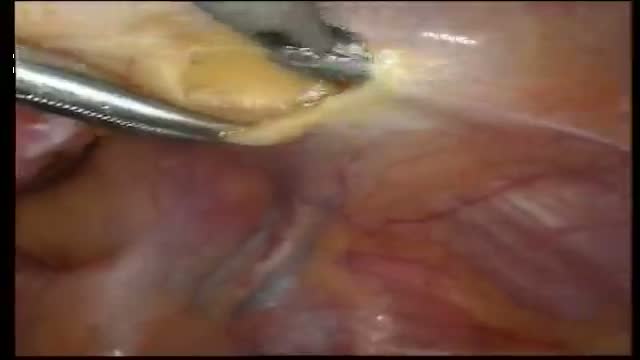
Liposuction is a surgical procedure that is done to remove fat deposits from underneath the skin. Common areas that are treated: the abdomen, buttocks, thighs, upper arms, chest and neck. (use medical graphic of body with labeled parts) The procedure is usually done as an outpatient under some combination of local anesthesia and/or sedation:. This means you are awake but relaxed and pain free. Depending on the number of areas to be treated and the specific technique selected, it may take from one to several hours. A small incision (cut) is made through the skin near the area of the fat deposit. Multiple incisions may be needed if a wide area or multiple areas are being done. A long hollow tube called a cannula will be inserted through this incision. Prior to inserting the cannula, the doctor may inject a solution of salt water that contains an anesthetic (numbing) medication and another medication to decrease bleeding. The cannula is then inserted and moved under the skin in a way to loosen the fat deposits so they may be suctioned out. Because a significant amount of body fluid is removed with the fat, an intravenous (through the veins) fluid line will be kept going during the procedure.
A recent technique called “ultrasound-assisted lipoplasty” uses a special cannula that liquefies the fat cells with ultrasonic energy. You should ask your doctor which technique he/she will use and how it will affect the type of anesthesia you will need and the length of the procedure.
Why is this procedure performed?
Liposuction is done to restore a more normal contour to the body. The procedure is sometimes described as body sculpting. It should be limited to fat deposits that are not responsive to diet and exercise. It is suggested that you should be within 20of your ideal body weight at the time of surgery. If you are planning to lose weight you should delay this procedure. This is not obesity surgery. The maximum amount of fat that can be removed is usually less than 10 pounds. The best results are achieved in people who still have firm and elastic skin. Although rare, there are risks and complications that can occur with liposuction. You should be aware that all the complications are increased if you are a smoker. You will need to quit smoking or at least avoid smoking for a month before and after surgery. If you have had prior surgeries near any of the areas to be treated, this may increase the risk of complications and you should discuss this with your doctor. Any history of heart disease, diabetes, bleeding problems or blood clots in your legs may make you more prone to post-operative problems and you should discuss these with your doctor. Finally, as with any cosmetic procedure it is important to have realistic expectations. The goals, limitations, and expectations of the procedure should be discussed openly and in detail with your doctor. Most insurance companies do not cover cosmetic surgery.
What should I expect during the post-operative period?
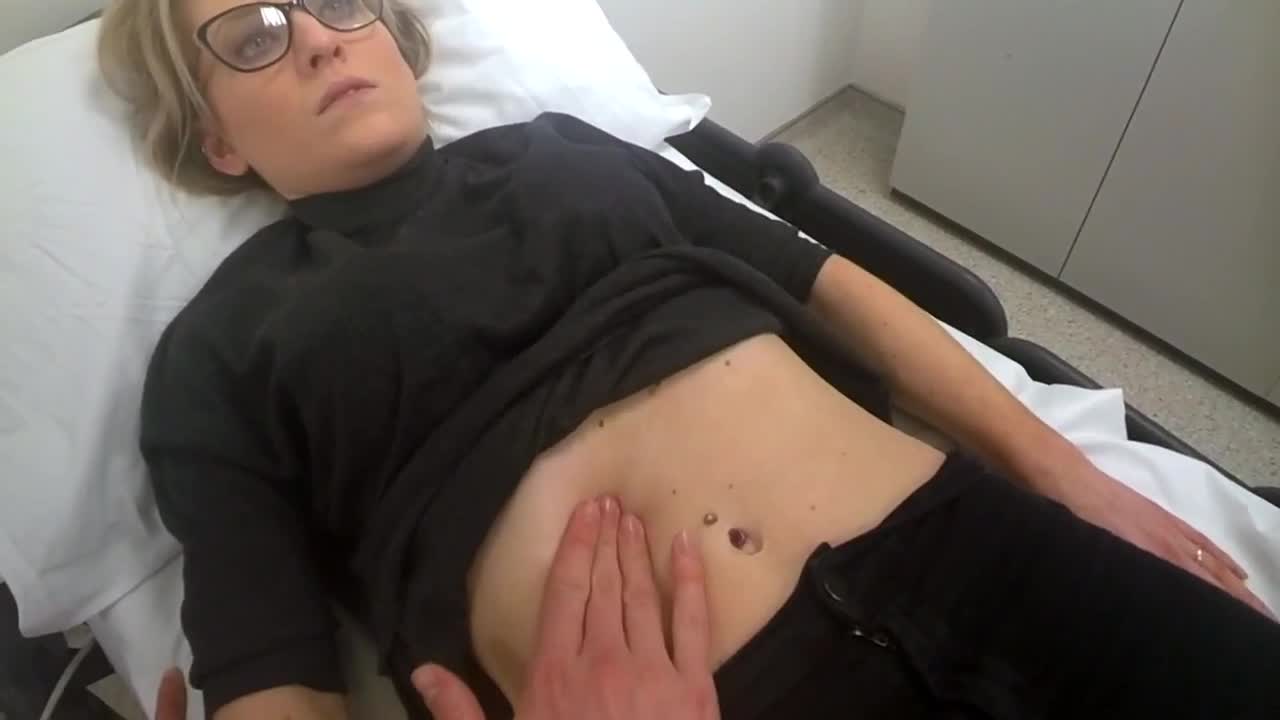
After surgery you should be able to go home but you will need someone to drive you. In the first few days after surgery it is common for the incisions to drain fluid and you will have to change dressings frequently. Fresh blood is not usual and if you have any bleeding you should call your doctor immediately. In some cases a small tube may have been placed through the skin to allow drainage. You will be limited to sponge baths until the drains and dressings are removed. After that you may take showers but no baths for 2 weeks. You may experience pain, burning, and numbness for a few days. Take pain medicine as prescribed by your doctor. You may notice a certain amount of bruising and swelling. The bruising will disappear gradually over 1 to 2 weeks. Some swelling may last for up to 6 months. If you have skin sutures they will be removed in 7 to 10 days. You should be able to be up and moving around the house the day after surgery but avoid any strenuous activity for about 1

This video documents the experience of one of our Mommy Makeover patients. She is 39 years old, 5’4” tall, and of average weight. Following the birth of her twins, she wanted to improve her abdominal wall contour and correct the lack of shape and firmness in her breasts.
Cancer, also called malignancy, is an abnormal growth of cells. There are more than 100 types of cancer, including breast cancer, skin cancer, lung cancer, colon cancer, prostate cancer, and lymphoma. Symptoms vary depending on the type. Cancer treatment may include chemotherapy, radiation, and/or surgery.
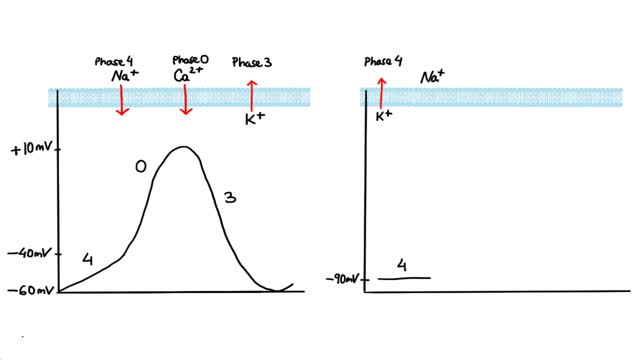
Antiarrhythmics are drugs that are used to treat abnormal heart rhythms resulting from irregular electrical activity of the heart. There are many different types of antiarrhythmic drugs. Examples include: Amiodarone (Cordarone) Flecainide (Tambocor) Procainamide (Procanbid) Sotalol (Betapace) In addition, there are other types of heart drugs that can be used to treat arrhythmias, including: Beta-blockers such as metoprolol or Toprol XL, which reduce the heart's workload and heart rate. Calcium channel blockers such as verapamil or Calan, which also reduces the heart rate.

Sleepiness, tiredness and fatigue are complaints which must be thoroughly analyzed to eliminate blur and ambiguity.
Physiological sleepiness (“sleep pressure”) increases while being awake and additionally underlies the circadian rhythm with a lower threshold to fall asleep during night time.
Excessive daytime sleepiness (EDS) is considered normal only after sleep deprivation. Clinically, EDS manifests by frequents daytime napping and/or reduced alertness with automatic behavior or - in its extreme form - in recurrent attacks of sudden, uncontrollable compulsion to sleep also in inappropriate situations (= “sleep attacks”).
EDS is “objectively” addressed by measuring the mean sleep latency to four to five nap opportunities throughout the day using the multiple sleep latency test (MSLT) or the maintenance of wakefulness test (MWT).
EDS denotes both, a ready entrance into sleep as well as difficulty in staying awake during daytime or accordingly in inappropriate situations. These two partially independent aspects of EDS are separately assessed by the “passive” MSLT and the “active” MWT respectively.
For that reason the MSLT and MWT only weakly correlate with each other when tested over a broad range of patients with EDS. It is important to keep in mind, that these tests are importantly influenced by a great variety of factors such as mood, anxiety, and motivation.
“Vigilance” comprises wakefulness, alertness and attention and therefore is more than just the reciprocal to sleepiness. Cognitive performance tasks such as Steer Clear Reaction Time Test (SCRTT) or driving simulators require the complete integrity of vigilance to achieve normal results. Hypersomnia is usually broadly defined as the combination of abnormally prolonged night-time sleep (regularly >10 h) with EDS during ≥1 months.
On the other hand, the term hypersomnia has also been used in a narrower scene for the isolated abnormality of a prolonged night-time sleep need (>10 h). “Tiredness”, also in colloquial language often used for sleepiness, in a broader sense also describes the feeling of lack of energy, motivation and initiative.
These patients seek rest rather than sleep. They often cannot fall asleep when given the opportunity in spite of feeling tired, and hence, in an MSLT, do not show an abnormally short sleep latency. Furthermore, tiredness (and fatigue) as opposed to sleepiness has a mental (“central”) and physiological (bodily or “peripheral”) component, which the patients can readily distinguish. Patients with insomnia, mild sleep apnea syndrome, or depression rather suffer from mental tiredness than sleepiness during the day.
The simple subjective self-assessment using the Epworth Sleepiness Scale (ESS) quite reliably differentiates between sleepiness and mental tiredness (without sleepiness), which makes it a widely used test. The term “fatigue” is also heterogeneously used.
In physiology the “fatigue” implied a “time on task performance decrement” to describe decreasing muscle force during a sustained physical effort. In clinical medicine one distinguishes physical (“peripheral”) from mental (“central”) fatigue and the term usually denotes a chronic and more abnormal situation than tiredness.
In a broad sense “fatigue” implies a deficiency in coping satisfactorily with mental and physical work load. The chronic fatigue syndrome entails both mental as well as a physical fatigue (so called “leaden paralysis” of limbs). Depressive states are often associated with insomnia and fatigue, but there are also cases with hypersomnia rather than insomnia ( non organic hypersomnia , “atypical depression” or “hypersomnolent depression”)
Sometimes these patients have a tendency to spend much of the day lying in the bed without actually sleeping (so called clinophilia). The basic and clinical aspects of fatigu

Insert the needle into the rubber stopper of the insulin bottle. Push the plunger down to inject air into the bottle (this allows the insulin to be drawn more easily). Leave the needle in the bottle. Turn the bottle and syringe upside-down.
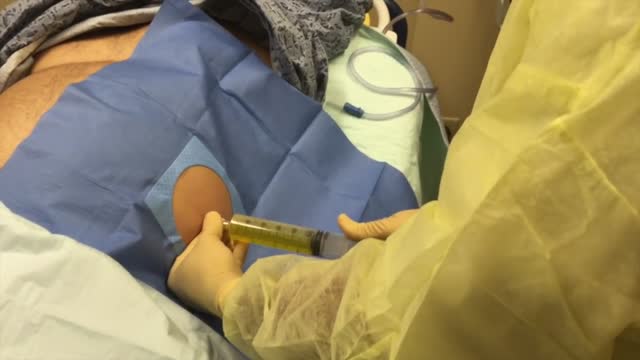
Paracentesis is a procedure to take out fluid that has collected in the belly (peritoneal fluid). This fluid buildup is called ascites . Ascites may be caused by infection, inflammation, an injury, or other conditions, such as cirrhosis or cancer. The fluid is taken out using a long, thin needle put through the belly.